In robotic welding, wire feeders deliver a consistent wire supply with simplicity and cost-effectiveness, while push-pull feeders excel in feeding softer or aluminum wires through complex torch setups, reducing wire deformation and improving weld quality. Choosing the right system impacts Your welding efficiency and ensures precise control tailored to the specific material and application demands.
Table of Comparison
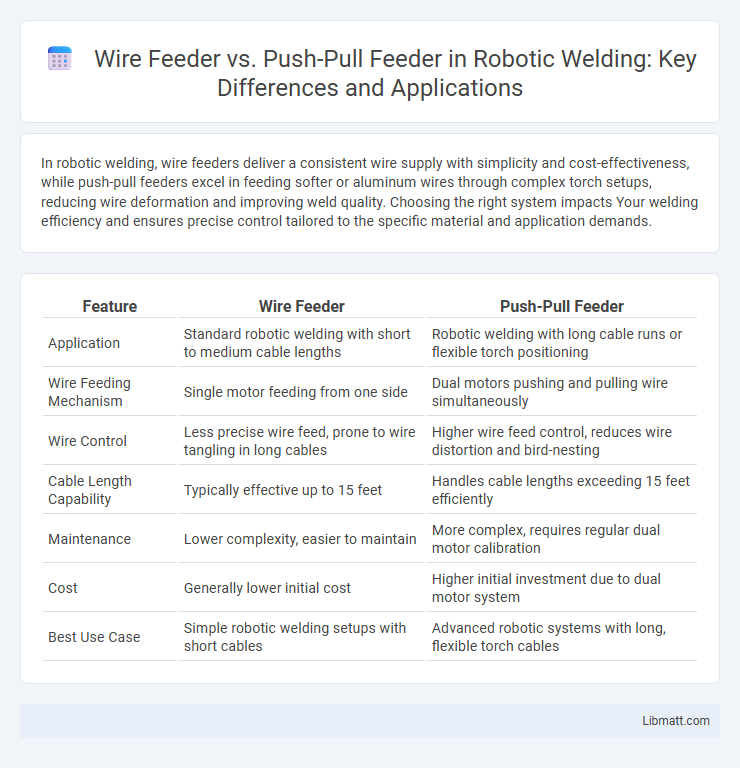
| Feature | Wire Feeder | Push-Pull Feeder |
|---|---|---|
| Application | Standard robotic welding with short to medium cable lengths | Robotic welding with long cable runs or flexible torch positioning |
| Wire Feeding Mechanism | Single motor feeding from one side | Dual motors pushing and pulling wire simultaneously |
| Wire Control | Less precise wire feed, prone to wire tangling in long cables | Higher wire feed control, reduces wire distortion and bird-nesting |
| Cable Length Capability | Typically effective up to 15 feet | Handles cable lengths exceeding 15 feet efficiently |
| Maintenance | Lower complexity, easier to maintain | More complex, requires regular dual motor calibration |
| Cost | Generally lower initial cost | Higher initial investment due to dual motor system |
| Best Use Case | Simple robotic welding setups with short cables | Advanced robotic systems with long, flexible torch cables |
Introduction to Robotic Welding Feeders
Robotic welding feeders, including Wire Feeders and Push-Pull Feeders, are essential components that control wire delivery during automated welding processes. Wire Feeders use a single motor to push the wire through the cable, suitable for short cable lengths and softer wires. Push-Pull Feeders employ two synchronized drives--one pushing and one pulling the wire--offering precise wire control for longer cable lengths and softer or more flexible wires, minimizing feed-related issues in robotic welding.
What is a Wire Feeder?
A wire feeder is a crucial component in robotic welding systems that consistently supplies welding wire to the welding torch, ensuring a steady and precise arc. This device controls the wire's speed, tension, and feed rate, which directly influences weld quality and efficiency. Your choice between wire feeder types impacts wire delivery reliability and ease of handling, especially when welding with aluminum or soft wires.
What is a Push-Pull Feeder?
A push-pull feeder in robotic welding is a wire feeding mechanism that combines both pushing and pulling actions to deliver wire smoothly through long or complex cable conduits, reducing wire deformation and breakage. Unlike traditional wire feeders that rely solely on pushing, the push-pull system features two synchronized drive motors: a push motor near the welder and a pull motor at the robotic arm, ensuring consistent wire tension and feeding accuracy. This design enhances welding efficiency and precision, especially important when working with softer or larger diameter wires in automated applications.
Key Differences Between Wire Feeders and Push-Pull Feeders
Wire feeders primarily use a single motor to push welding wire through the cable, optimal for short cable lengths and softer wires. Push-pull feeders combine a push mechanism at the power source and a pull mechanism at the welding gun, providing enhanced feeding control and reduced wire deformation, especially beneficial for long cable runs and softer or softer-to-feed wires like aluminum. Key differences include wire feeding mechanism complexity, suitability for cable length, and effectiveness in handling flexible or soft wires during robotic welding processes.
Advantages of Wire Feeders in Robotic Welding
Wire feeders in robotic welding provide consistent and precise wire delivery, enhancing weld quality and reducing spatter compared to manual feeding methods. Their robust design accommodates high welding speeds and wire feed rates, improving overall productivity in automated welding processes. Compatibility with various wire types and ease of integration with robotic welders make wire feeders indispensable for efficient and reliable robotic welding operations.
Benefits of Push-Pull Feeders for Automation
Push-pull feeders enhance robotic welding automation by providing precise wire control for softer or delicate welding wires, reducing issues like bird-nesting and wire tangling. Their dual motor drive offers consistent wire feeding over complex robotic torch movements, improving weld quality and minimizing downtime. Improved wire feeding reliability in push-pull systems directly contributes to higher productivity and reduced maintenance costs in automated welding environments.
Applications: When to Use Wire Feeders vs Push-Pull Feeders
Wire feeders are ideal for robotic welding applications involving short, stiff wires and standard materials, providing consistent wire delivery in high-speed, precise operations. Push-pull feeders excel in welding flexible, soft, or lightweight wires, especially in complex geometries or long cable runs, ensuring smooth feeding without wire deformation. Your choice between the two depends on wire type, length, and specific robotic system demands to maintain optimal weld quality and efficiency.
Common Challenges and Solutions
Wire feeders commonly face feeding inconsistencies and wire tangling issues in robotic welding, which can cause weld defects and downtime. Push-pull feeders address these challenges by combining a push mechanism at the wire spool with a pull motor near the torch, ensuring smoother wire delivery and reduced feeder motor stress. To optimize your robotic welding performance, investing in a properly maintained push-pull feeder can significantly reduce feeding problems and enhance weld consistency.
Cost Considerations and Maintenance
Wire feeders in robotic welding typically offer lower initial costs and simpler maintenance due to their straightforward design and fewer moving parts, making them ideal for budget-sensitive operations. Push-pull feeders, while more expensive upfront due to their complex drive systems designed for flexible or softer wires, reduce wire feeding issues and minimize downtime by providing more consistent wire delivery and less wire stubbing. Maintenance costs for push-pull systems can be higher, but the improved wire control often leads to better productivity and less frequent wire-related failures, balancing overall operating expenses.
Choosing the Right Feeder for Your Robotic Welding Needs
Selecting the right feeder for robotic welding depends on wire type, wire diameter, and application requirements. Wire feeders offer simplicity and cost-effectiveness for solid wires up to 0.045 inches, ideal for general-purpose welding. Push-pull feeders excel with softer, flux-cored, or larger diameter wires by reducing feeding resistance and ensuring consistent wire delivery for precision welds.
Wire Feeder vs Push-Pull Feeder (in Robotic Welding) Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com