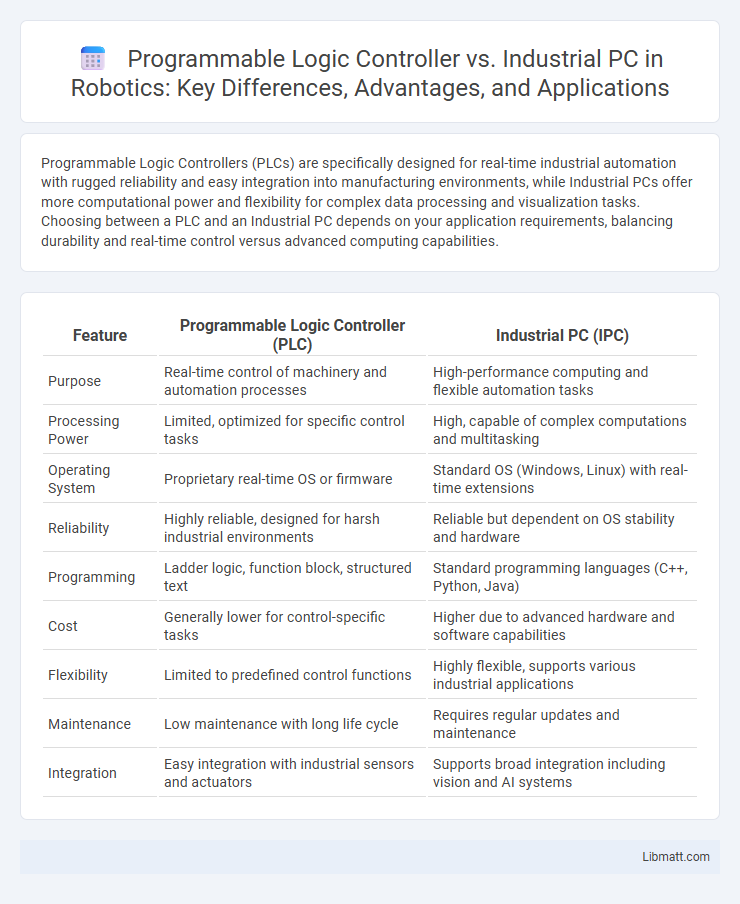
Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs) are specifically designed for real-time industrial automation with rugged reliability and easy integration into manufacturing environments, while Industrial PCs offer more computational power and flexibility for complex data processing and visualization tasks. Choosing between a PLC and an Industrial PC depends on your application requirements, balancing durability and real-time control versus advanced computing capabilities.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Programmable Logic Controller (PLC) | Industrial PC (IPC) |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Real-time control of machinery and automation processes | High-performance computing and flexible automation tasks |
| Processing Power | Limited, optimized for specific control tasks | High, capable of complex computations and multitasking |
| Operating System | Proprietary real-time OS or firmware | Standard OS (Windows, Linux) with real-time extensions |
| Reliability | Highly reliable, designed for harsh industrial environments | Reliable but dependent on OS stability and hardware |
| Programming | Ladder logic, function block, structured text | Standard programming languages (C++, Python, Java) |
| Cost | Generally lower for control-specific tasks | Higher due to advanced hardware and software capabilities |
| Flexibility | Limited to predefined control functions | Highly flexible, supports various industrial applications |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance with long life cycle | Requires regular updates and maintenance |
| Integration | Easy integration with industrial sensors and actuators | Supports broad integration including vision and AI systems |
Introduction to Programmable Logic Controllers and Industrial PCs
Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs) are specialized industrial computers designed for real-time control and automation of manufacturing processes, featuring rugged construction and reliable operation in harsh environments. Industrial PCs (IPCs) offer versatile computing platforms with higher processing power and flexibility, supporting complex data analysis and advanced automation tasks in industrial settings. Understanding the key differences in functionality and application between PLCs and IPCs helps you select the optimal control system for your industrial automation needs.
Key Differences Between PLCs and Industrial PCs
Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs) are specialized devices designed for real-time control and automation in industrial environments, offering ruggedness, reliability, and ease of programming with ladder logic. Industrial PCs provide greater computational power, flexibility, and advanced networking capabilities, supporting complex data processing and integration with enterprise systems. Your choice depends on whether you prioritize dedicated automation control with high durability (PLC) or versatile computing and scalability (Industrial PC).
Hardware Architecture Comparison
Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs) feature ruggedized, modular hardware designed for real-time, deterministic control with dedicated input/output (I/O) modules and specialized processors tailored to industrial environments. Industrial PCs (IPCs) offer a more flexible, computer-based architecture with standard processors, expandable memory, and general-purpose I/O, supporting complex computations and advanced data handling. Your choice depends on whether you prioritize the robustness and reliability of PLC hardware over the scalability and versatility provided by IPC architecture.
Operating Systems and Software Flexibility
Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs) typically run on proprietary real-time operating systems optimized for fast, deterministic control tasks, ensuring reliable performance in industrial automation. Industrial PCs (IPCs) support standard operating systems like Windows or Linux, offering greater software flexibility and the ability to run complex applications, including custom software and multiple programming environments. Your choice depends on whether you require the robustness and predictability of PLCs or the versatile software capabilities provided by Industrial PCs.
Performance and Processing Capabilities
Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs) are engineered for real-time, deterministic control with rapid scan cycles optimized for automation and process control tasks. Industrial PCs offer superior processing power and multitasking capabilities, leveraging high-performance CPUs and advanced operating systems suitable for complex computations and data-intensive applications. While PLCs excel in reliability and straightforward control logic execution, Industrial PCs provide enhanced flexibility and scalability for integrating advanced analytics and machine learning in industrial environments.
Reliability and Environmental Suitability
Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs) are engineered for high reliability in harsh industrial environments, featuring robust hardware resistant to temperature extremes, vibrations, and electrical noise. Industrial PCs (IPCs) offer greater processing power and flexibility but typically require additional protective enclosures to ensure durability in challenging conditions. PLCs generally outperform IPCs in continuous operation stability and resistance to environmental stressors critical for automation tasks.
Scalability and Expansion Options
Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs) offer robust scalability with modular hardware designs that allow for easy expansion through additional I/O modules, making them ideal for diverse industrial automation tasks. Industrial PCs (IPCs) provide extensive expansion options, including customizable hardware configurations and compatibility with various peripheral devices, supporting complex processing and data-intensive applications. Your choice between PLC and IPC should consider the balance between the need for adaptable scalability and the complexity of integration within your specific industrial environment.
Integration with Industrial Networks
Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs) offer seamless integration with industrial networks through standardized communication protocols such as Modbus, Profibus, and Ethernet/IP, ensuring reliable real-time control and data exchange in manufacturing environments. Industrial PCs (IPCs) provide versatile network connectivity options, supporting a wider range of protocols and advanced data processing capabilities, which facilitates integration with complex IoT and Industry 4.0 systems. Choosing between PLCs and IPCs depends on the specific industrial network requirements, such as deterministic control versus flexible data handling and interoperability.
Cost Considerations and Total Cost of Ownership
Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs) typically have lower initial costs and simpler maintenance compared to Industrial PCs (IPCs), making them cost-effective for standard automation tasks. Industrial PCs often require higher upfront investment but offer greater flexibility, scalability, and long-term adaptability, which can lower total cost of ownership (TCO) in complex or evolving industrial environments. Evaluating your automation needs against these cost considerations ensures optimal budget allocation and operational efficiency over the system's lifecycle.
Choosing the Right Solution for Your Automation Needs
Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs) offer rugged, real-time control ideal for discrete manufacturing processes, while Industrial PCs (IPCs) provide higher computational power and flexibility for complex data-intensive applications. Selecting the right solution depends on factors like environmental conditions, required processing speed, integration complexity, and scalability preferences. Evaluating the specific automation tasks, industry standards compliance, and long-term maintenance costs ensures optimal performance and ROI.
Programmable Logic Controller vs Industrial PC Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com