A vision system captures and processes images to analyze object details, providing high accuracy and versatility in complex environments, while a proximity sensor detects the presence or absence of objects within a specific range using electromagnetic fields or ultrasonic waves. Your choice depends on the required precision and application complexity, with vision systems ideal for detailed inspection and proximity sensors preferred for simple presence detection.
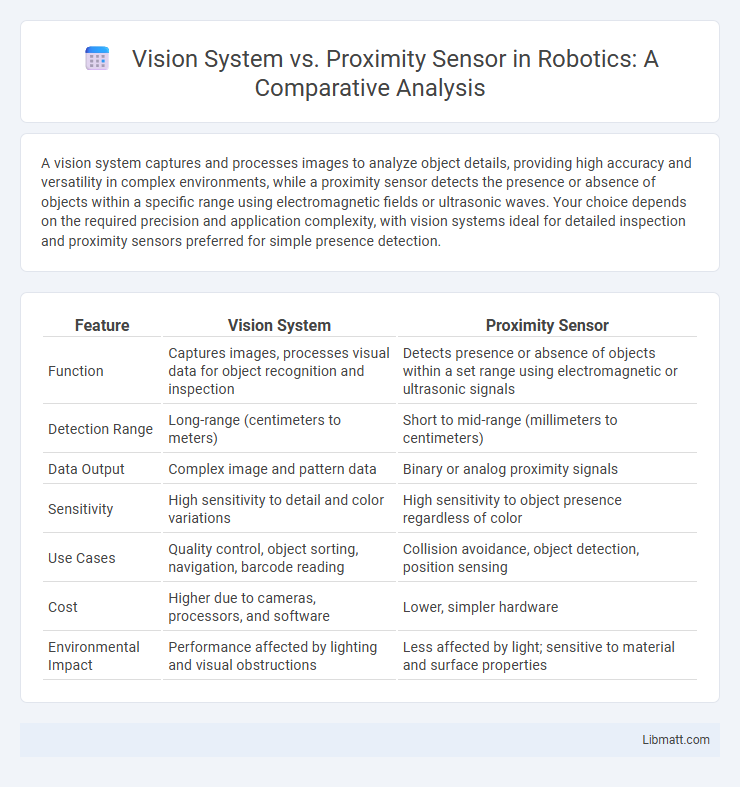
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Vision System | Proximity Sensor |
|---|---|---|
| Function | Captures images, processes visual data for object recognition and inspection | Detects presence or absence of objects within a set range using electromagnetic or ultrasonic signals |
| Detection Range | Long-range (centimeters to meters) | Short to mid-range (millimeters to centimeters) |
| Data Output | Complex image and pattern data | Binary or analog proximity signals |
| Sensitivity | High sensitivity to detail and color variations | High sensitivity to object presence regardless of color |
| Use Cases | Quality control, object sorting, navigation, barcode reading | Collision avoidance, object detection, position sensing |
| Cost | Higher due to cameras, processors, and software | Lower, simpler hardware |
| Environmental Impact | Performance affected by lighting and visual obstructions | Less affected by light; sensitive to material and surface properties |
Introduction to Vision Systems and Proximity Sensors
Vision systems utilize cameras and image processing algorithms to detect, analyze, and interpret visual information for applications like quality control and object recognition. Proximity sensors detect the presence or absence of objects based on physical properties such as capacitance, inductance, or ultrasonic waves, offering simple and reliable object detection. Your choice between these technologies depends on the complexity of the task and required precision in automation processes.
How Vision Systems Work
Vision systems operate by capturing images using cameras and processing these images with advanced algorithms to analyze features such as shape, color, and pattern. They employ machine learning and deep learning techniques to identify objects, detect defects, and perform complex inspections with high accuracy. Unlike proximity sensors that detect the presence or absence of objects through electromagnetic fields or ultrasonic waves, vision systems provide detailed spatial information enabling precise measurement and quality control.
How Proximity Sensors Operate
Proximity sensors operate by detecting the presence or absence of objects within a specific range without physical contact, using technologies such as capacitive, inductive, ultrasonic, or infrared sensing. These sensors emit signals or fields that react when an object interrupts or changes the return signal, enabling precise detection in automation and safety applications. Their real-time response and robustness make them ideal for detecting object proximity in diverse industrial environments.
Key Differences Between Vision Systems and Proximity Sensors
Vision systems capture detailed images using cameras and advanced algorithms, enabling object recognition, measurement, and inspection in complex environments. Proximity sensors detect the presence or absence of objects through electromagnetic fields or ultrasonic waves, offering simpler binary detection without image processing. Your choice between these technologies depends on the required level of detail and application complexity.
Advantages of Vision Systems
Vision systems offer superior accuracy and detailed object recognition compared to proximity sensors, enabling precise quality control and complex inspections. They can detect shape, color, and surface defects, which proximity sensors cannot, making them ideal for advanced automation applications. Your manufacturing process benefits from increased flexibility and reduced errors through the comprehensive analysis provided by vision systems.
Advantages of Proximity Sensors
Proximity sensors offer several advantages including reliable detection of objects without physical contact, which minimizes wear and tear and extends sensor lifespan. They provide consistent performance in harsh environments involving dust, dirt, or moisture, where vision systems may struggle due to lens contamination or lighting variability. Proximity sensors also typically consume less power and are easier to integrate with industrial automation systems, ensuring faster response times and lower maintenance costs.
Typical Applications of Vision Systems
Vision systems are commonly used in quality control, robotic guidance, and automated inspection processes where precise object identification and measurement are required. In manufacturing, they enable defect detection, part verification, and assembly validation with high accuracy. Your production line can benefit from vision systems to enhance efficiency and reduce errors compared to proximity sensors, which primarily detect object presence without detailed analysis.
Common Uses of Proximity Sensors
Proximity sensors are commonly used in industrial automation for object detection, positioning, and safety interlocks, enabling machines to operate efficiently without physical contact. They are also essential in consumer electronics for screen activation and in automotive systems for parking assistance and obstacle detection. Your choice between a vision system and a proximity sensor depends on the required accuracy, environment, and complexity of the application.
Choosing the Right Sensor for Your Application
Choosing the right sensor depends on application requirements such as detection range, object complexity, and environmental conditions. Vision systems excel in detailed object recognition and provide high-resolution data for complex inspections, while proximity sensors offer reliable, simple presence detection with faster response times in harsh or confined environments. Evaluating factors like accuracy, cost, installation complexity, and real-time processing needs ensures optimal sensor selection for industrial automation or quality control tasks.
Future Trends in Vision and Proximity Sensing Technologies
Vision systems are rapidly advancing with AI-driven image processing and 3D depth sensing, enhancing accuracy and enabling complex inspections in automated environments. Proximity sensors are evolving through integration with IoT and wireless connectivity, offering real-time data for predictive maintenance and adaptive control systems. Your automation solutions will benefit significantly from the convergence of these technologies, improving efficiency and enabling smarter decision-making.
Vision System vs Proximity Sensor Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com