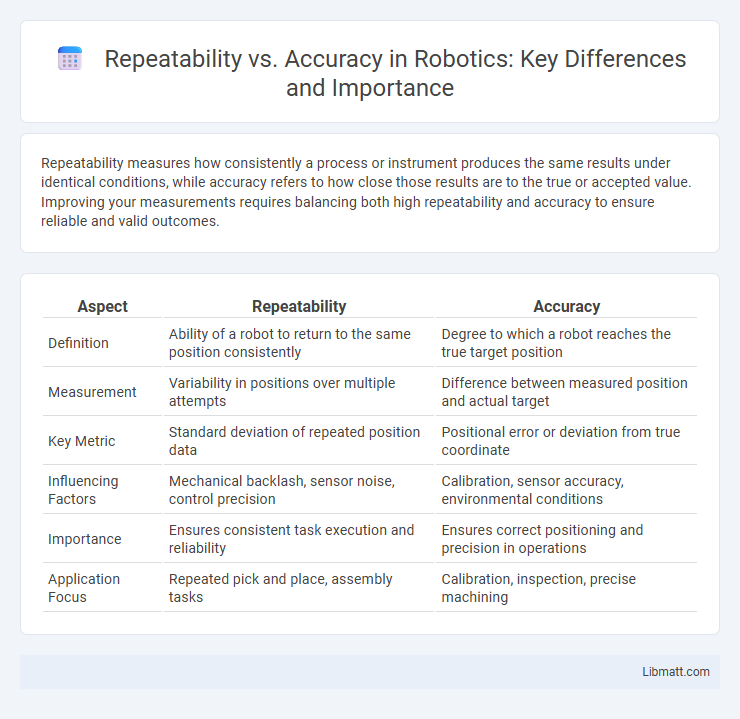
Repeatability measures how consistently a process or instrument produces the same results under identical conditions, while accuracy refers to how close those results are to the true or accepted value. Improving your measurements requires balancing both high repeatability and accuracy to ensure reliable and valid outcomes.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Repeatability | Accuracy |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Ability of a robot to return to the same position consistently | Degree to which a robot reaches the true target position |
| Measurement | Variability in positions over multiple attempts | Difference between measured position and actual target |
| Key Metric | Standard deviation of repeated position data | Positional error or deviation from true coordinate |
| Influencing Factors | Mechanical backlash, sensor noise, control precision | Calibration, sensor accuracy, environmental conditions |
| Importance | Ensures consistent task execution and reliability | Ensures correct positioning and precision in operations |
| Application Focus | Repeated pick and place, assembly tasks | Calibration, inspection, precise machining |
Understanding Repeatability and Accuracy
Repeatability refers to the consistency of measurement results under the same conditions, highlighting an instrument's ability to produce stable outcomes over multiple trials. Accuracy measures how close a measurement is to the true or accepted value, emphasizing correctness rather than consistency. Understanding the distinction between repeatability and accuracy is essential for evaluating measurement systems and improving data reliability in scientific and industrial processes.
Key Differences Between Repeatability and Accuracy
Repeatability refers to the consistency of measurement results when repeated under identical conditions, while accuracy indicates how close a measurement is to the true or accepted value. Key differences include that repeatability assesses precision within the same setup, whereas accuracy evaluates the correctness of results across varied conditions. Repeatability impacts the reliability of data, but high repeatability does not guarantee accuracy if systematic errors are present.
Importance of Repeatability in Measurements
Repeatability in measurements ensures that your results are consistent when repeated under the same conditions, minimizing random errors and increasing reliability. High repeatability is crucial as it allows for precise monitoring of changes over time and supports the validation of experimental procedures. Without strong repeatability, the accuracy of measurements becomes less meaningful, since inconsistent results hinder trust in the data's validity.
Why Accuracy Matters in Data Collection
Accuracy in data collection ensures that measurements truly reflect the real-world values, which is crucial for making reliable decisions and drawing valid conclusions. While repeatability guarantees consistency across measurements, only accurate data can provide trustworthy insights and support effective problem-solving. Accurate data minimizes errors that could lead to flawed analyses, costly mistakes, and reduced credibility in research and business operations.
Examples Illustrating Repeatability vs Accuracy
Repeatability refers to the consistency of measurements taken under identical conditions, such as a digital scale showing the same weight for an object multiple times; for example, a watch displaying the same time consistently every day demonstrates high repeatability. Accuracy indicates how close a measurement is to the true value, like a thermometer consistently reading 98.6degF when the actual temperature is 98.6degF, signifying high accuracy even if it varies slightly. You can encounter scenarios where an instrument is repeatable but not accurate, such as a bathroom scale that always shows 5 pounds heavier, or accurate but not repeatable, like a dial gauge that fluctuates around the true measurement.
Factors Affecting Measurement Repeatability
Measurement repeatability is influenced by factors such as instrument precision, environmental stability, and operator consistency. Variations in temperature, vibration, and tool calibration directly impact the reliability of repeated measurements. Consistent procedural methods and well-maintained equipment are critical for minimizing variability and enhancing repeatability in data collection.
Factors Influencing Measurement Accuracy
Measurement accuracy is influenced by factors such as instrument calibration, environmental conditions, and operator skill. Repeatability plays a key role in minimizing random errors, thereby enhancing the precision of repeated measurements under the same conditions. Systematic errors, often caused by equipment bias or external disturbances, must be controlled to achieve higher accuracy in measurement results.
How to Improve Repeatability and Accuracy
Improving repeatability involves maintaining consistent conditions such as stable environmental factors, calibrated instruments, and standardized procedures to minimize variability in measurements. Enhancing accuracy requires regular calibration against known standards, using high-quality sensors, and applying correction factors to reduce systematic errors. You can achieve optimal results by combining precise repeatability with proper calibration techniques to ensure both reliable and accurate measurement outcomes.
Applications in Science and Engineering
Repeatability refers to the consistency of measurement results under unchanged conditions, while accuracy indicates how close a measurement is to the true value. In scientific experiments and engineering processes, high repeatability ensures dependable data for validating models, whereas accuracy is crucial for meeting design specifications and quality standards. Your ability to balance both parameters directly impacts the reliability and precision of experimental outcomes and product performance.
Common Myths About Repeatability and Accuracy
Common myths about repeatability and accuracy often confuse these two critical measurement concepts, assuming that high repeatability guarantees accuracy. Repeatability refers to the consistency of results under unchanged conditions, while accuracy measures how close those results are to the true value. Understanding this distinction helps you avoid errors in interpreting data quality and ensures better decision-making in scientific and industrial applications.
Repeatability vs Accuracy Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com