Homogeneous swarms consist of identical agents working collaboratively, offering simplicity in coordination and maintenance, while heterogeneous swarms combine diverse agents with specialized capabilities, enhancing versatility and task efficiency. You can optimize operations by selecting a swarm type that aligns with your mission requirements and environmental complexities.
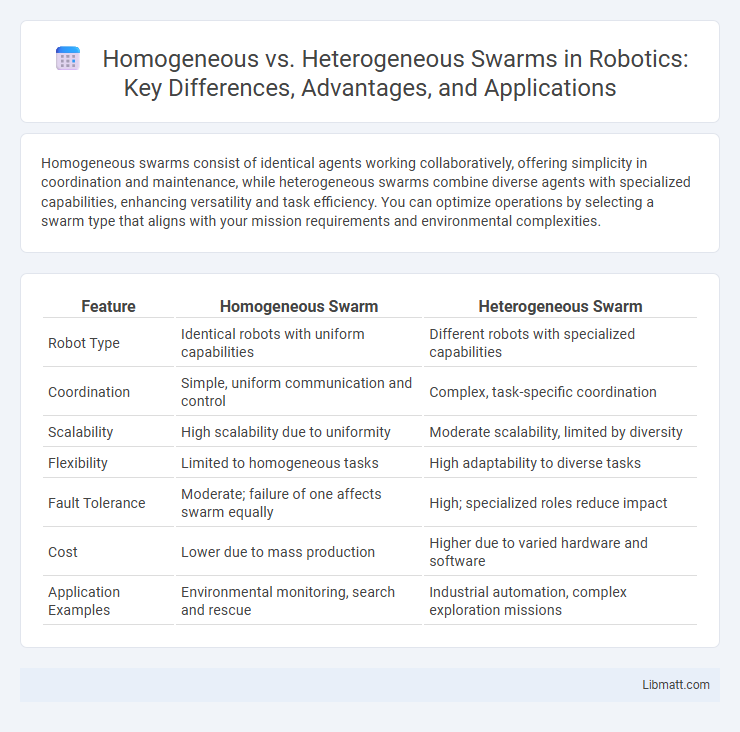
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Homogeneous Swarm | Heterogeneous Swarm |
|---|---|---|
| Robot Type | Identical robots with uniform capabilities | Different robots with specialized capabilities |
| Coordination | Simple, uniform communication and control | Complex, task-specific coordination |
| Scalability | High scalability due to uniformity | Moderate scalability, limited by diversity |
| Flexibility | Limited to homogeneous tasks | High adaptability to diverse tasks |
| Fault Tolerance | Moderate; failure of one affects swarm equally | High; specialized roles reduce impact |
| Cost | Lower due to mass production | Higher due to varied hardware and software |
| Application Examples | Environmental monitoring, search and rescue | Industrial automation, complex exploration missions |
Introduction to Swarm Robotics
Swarm robotics studies the coordination of multiple robots working collaboratively to complete complex tasks. Homogeneous swarms consist of identical robots with uniform capabilities, enabling scalable and fault-tolerant systems, while heterogeneous swarms incorporate robots with varied functions and specializations for enhanced task diversity. Understanding the differences between homogeneous and heterogeneous swarms can help you optimize robotic deployments for specific applications such as search and rescue, agriculture, or environmental monitoring.
Defining Homogeneous Swarms
Homogeneous swarms consist of multiple identical agents or robots that share the same hardware, software, and behavioral capabilities, enabling uniform task execution and simplified coordination. These swarms are often utilized in applications requiring scalability and redundancy, such as environmental monitoring and agricultural automation. The uniformity of agents enhances system robustness and predictability but may limit adaptability to diverse or complex tasks compared to heterogeneous swarms.
Key Features of Heterogeneous Swarms
Heterogeneous swarms consist of multiple types of agents with diverse capabilities, sensors, and roles, enabling complex and adaptive task execution in dynamic environments. These swarms leverage specialized functions such as reconnaissance, payload delivery, and communication relay, enhancing overall system resilience and flexibility. The coordinated interaction among different agent types allows for improved efficiency and scalability compared to homogeneous swarms.
Communication Strategies in Swarm Systems
Communication strategies in homogeneous swarms rely on uniform protocols and data exchange formats, enabling seamless interaction and coordination among identical agents. Heterogeneous swarms necessitate adaptive communication frameworks that support diverse hardware and software capabilities, allowing agents with different roles and functions to effectively share information. Efficiency in data transmission and robustness in message interpretation are critical for maintaining swarm cohesion and achieving collective objectives in both systems.
Task Allocation and Flexibility
Homogeneous swarms feature identical agents that excel in uniform task allocation but may lack adaptability to diverse challenges. Heterogeneous swarms incorporate varied agents with specialized capabilities, enhancing flexibility and enabling dynamic task distribution based on individual strengths. Your choice between these approaches depends on whether consistent performance or versatile response to complex environments is prioritized.
Scalability and System Complexity
Homogeneous swarms offer enhanced scalability due to uniform hardware and software components, simplifying deployment and maintenance while ensuring consistent performance across all units. In contrast, heterogeneous swarms increase system complexity by integrating varied agents with distinct capabilities, requiring advanced coordination algorithms and communication protocols to manage diverse interactions efficiently. Your choice between these architectures impacts scalability, with homogeneous swarms facilitating easier expansion and heterogeneous swarms demanding sophisticated system design to handle complexity.
Adaptability to Dynamic Environments
Homogeneous swarms consist of identical agents, offering streamlined coordination but limited adaptability to dynamic environments due to uniform capabilities. In contrast, heterogeneous swarms comprise diverse agents with specialized functions, enabling your system to respond more effectively to changing conditions and complex tasks. This diversity enhances resilience and flexibility, making heterogeneous swarms better suited for unpredictable or evolving environments.
Cost and Resource Optimization
Homogeneous swarms, composed of identical agents, often reduce costs through streamlined production and simpler maintenance processes, enhancing your resource optimization. In contrast, heterogeneous swarms integrate diverse agents with specialized capabilities, potentially increasing upfront expenses but maximizing operational efficiency by leveraging varied strengths for complex tasks. Balancing your budget against mission requirements is crucial to determine whether uniformity or diversity in swarm composition yields the optimal cost-resource trade-off.
Real-World Applications and Case Studies
Homogeneous swarms, composed of identical robots, excel in tasks like environmental monitoring and agricultural crop inspection, where uniform capabilities ensure scalability and simplicity. Heterogeneous swarms integrate varied robot types, optimizing complex missions such as search and rescue or military reconnaissance by leveraging diverse sensor and mobility functions. Your operational goals dictate the swarm choice, with case studies showing homogeneous swarms excel in controlled, repetitive environments while heterogeneous teams outperform in dynamic, unpredictable scenarios.
Future Trends in Swarm Robotics
Future trends in swarm robotics emphasize the integration of heterogeneous swarms, where diverse robots with specialized capabilities cooperate to enhance adaptability and efficiency in complex environments. Advances in AI and communication protocols will enable seamless coordination among heterogeneous agents, improving task allocation and resilience. The development of scalable algorithms tailored for mixed robot types promises to revolutionize applications in disaster response, agriculture, and industrial automation.
Homogeneous Swarm vs Heterogeneous Swarm Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com