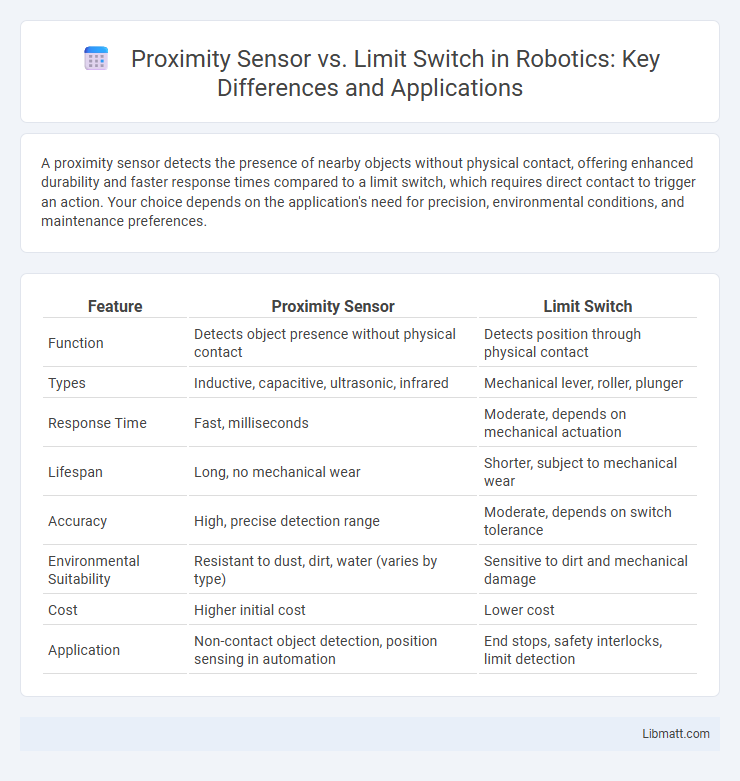
A proximity sensor detects the presence of nearby objects without physical contact, offering enhanced durability and faster response times compared to a limit switch, which requires direct contact to trigger an action. Your choice depends on the application's need for precision, environmental conditions, and maintenance preferences.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Proximity Sensor | Limit Switch |
|---|---|---|
| Function | Detects object presence without physical contact | Detects position through physical contact |
| Types | Inductive, capacitive, ultrasonic, infrared | Mechanical lever, roller, plunger |
| Response Time | Fast, milliseconds | Moderate, depends on mechanical actuation |
| Lifespan | Long, no mechanical wear | Shorter, subject to mechanical wear |
| Accuracy | High, precise detection range | Moderate, depends on switch tolerance |
| Environmental Suitability | Resistant to dust, dirt, water (varies by type) | Sensitive to dirt and mechanical damage |
| Cost | Higher initial cost | Lower cost |
| Application | Non-contact object detection, position sensing in automation | End stops, safety interlocks, limit detection |
Introduction to Proximity Sensors and Limit Switches
Proximity sensors use electromagnetic fields or light to detect the presence or absence of objects without physical contact, offering high-speed and maintenance-free operation in automated systems. Limit switches rely on mechanical actuation triggered by physical contact, providing precise position feedback and reliable control in industrial applications. Understanding your specific requirements for contactless detection or mechanical actuation will help determine whether a proximity sensor or limit switch best suits your automation needs.
Working Principles: Proximity Sensor vs Limit Switch
Proximity sensors detect the presence of objects without physical contact by emitting electromagnetic fields or waves and sensing changes in these fields, making them ideal for detecting metallic or non-metallic targets. Limit switches operate through mechanical actuation, requiring physical contact with an object to trigger an electrical circuit, typically using a lever or plunger mechanism. The non-contact operation of proximity sensors allows for faster response times and reduced wear, whereas limit switches provide reliable feedback in harsh environments with direct mechanical interaction.
Key Differences Between Proximity Sensors and Limit Switches
Proximity sensors detect the presence or absence of objects without physical contact using electromagnetic fields, light, or ultrasonic waves, while limit switches require direct mechanical contact to operate. Proximity sensors offer faster response times and longer lifespan due to non-contact operation, making them ideal for high-speed automation and harsh environments, whereas limit switches provide reliable physical feedback for position control in simpler, low-speed applications. Sensitivity range and installation flexibility also differ, with proximity sensors accommodating varying distances and limit switches typically positioned at fixed points.
Types of Proximity Sensors
Proximity sensors include inductive, capacitive, ultrasonic, photoelectric, and magnetic types, each designed to detect objects without direct contact by sensing changes in electromagnetic fields, sound waves, or light. Inductive sensors detect metal objects via electromagnetic fields, while capacitive sensors respond to any material with a dielectric constant different from air. Ultrasonic sensors use sound waves to detect distances, photoelectric sensors rely on light beams, and magnetic sensors detect magnetic fields, making proximity sensors versatile compared to mechanical limit switches.
Types of Limit Switches
Limit switches come in various types, including mechanical, snap-action, and roller lever, each designed for specific industrial applications requiring precise position detection. Mechanical limit switches feature a physical actuator triggered by direct contact, while snap-action switches provide fast response with minimal wear. Roller lever limit switches use a rolling arm to detect motion, offering increased durability in applications with repeated mechanical movement, enabling you to select the appropriate switch based on your machinery's operational needs.
Common Applications of Proximity Sensors
Proximity sensors are widely used in industrial automation for object detection, positioning, and counting tasks, where non-contact sensing improves reliability and reduces wear. These sensors are common in robotics, conveyor systems, and manufacturing equipment to detect metal or non-metal objects without physical contact. You can rely on proximity sensors for applications requiring fast response times and maintenance-free operation compared to traditional limit switches.
Typical Uses of Limit Switches in Industry
Limit switches are commonly used in industrial automation to detect the presence or position of objects, ensuring safety and operational control in machinery. They serve critical roles in conveyor systems, packaging equipment, and robotic arms by providing precise mechanical feedback to prevent overtravel or detect end-of-travel positions. Their durability in harsh environments and ability to handle high current loads make them ideal for heavy-duty applications requiring reliable position sensing.
Advantages and Disadvantages: Proximity Sensors
Proximity sensors offer non-contact detection, resulting in less wear and longer lifespan compared to limit switches, which rely on physical contact. They provide faster response times and higher reliability in harsh environments, but their performance can be affected by environmental factors like dust, moisture, and electromagnetic interference. While proximity sensors typically require more complex calibration and higher initial costs, their minimal maintenance needs and enhanced durability make them ideal for automated industrial applications.
Advantages and Disadvantages: Limit Switches
Limit switches offer reliable mechanical operation with clear on/off signals, making them highly suitable for applications requiring precise position detection in harsh environments. However, their physical contact nature leads to wear and tear, resulting in reduced lifespan and frequent maintenance compared to non-contact proximity sensors. Despite durability challenges, limit switches remain cost-effective and straightforward to install for industrial automation tasks.
Choosing the Right Sensor for Your Application
Choosing the right sensor for your application depends on factors like detection distance, environmental conditions, and required durability. Proximity sensors offer non-contact detection with adjustable sensing ranges, ideal for applications needing precise positioning without wear and tear. Limit switches provide reliable mechanical actuation in harsh environments where physical contact and tactile feedback are essential for safety and control.
Proximity Sensor vs Limit Switch Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com