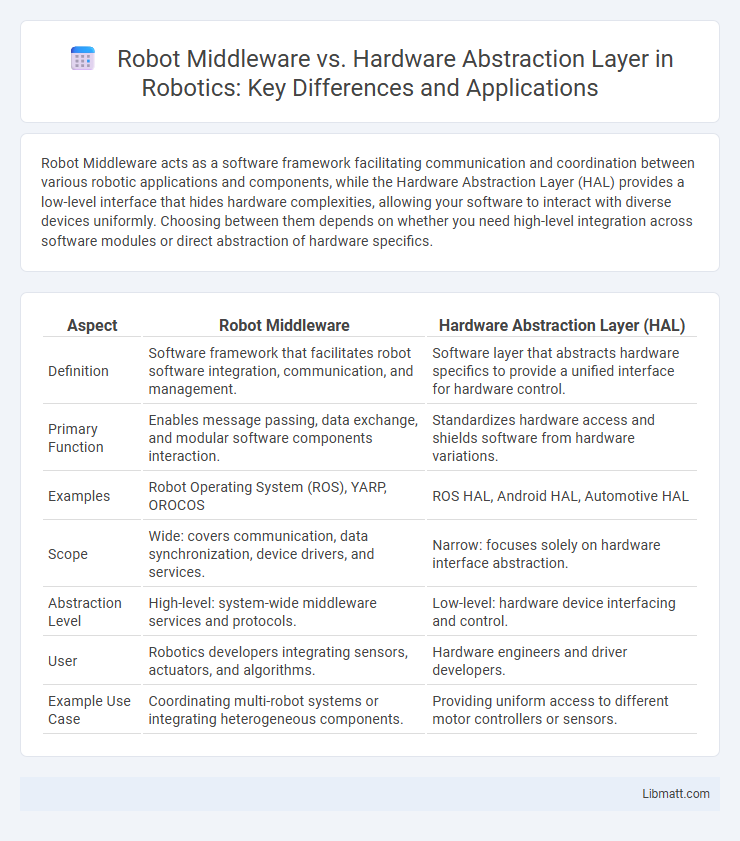
Robot Middleware acts as a software framework facilitating communication and coordination between various robotic applications and components, while the Hardware Abstraction Layer (HAL) provides a low-level interface that hides hardware complexities, allowing your software to interact with diverse devices uniformly. Choosing between them depends on whether you need high-level integration across software modules or direct abstraction of hardware specifics.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Robot Middleware | Hardware Abstraction Layer (HAL) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Software framework that facilitates robot software integration, communication, and management. | Software layer that abstracts hardware specifics to provide a unified interface for hardware control. |
| Primary Function | Enables message passing, data exchange, and modular software components interaction. | Standardizes hardware access and shields software from hardware variations. |
| Examples | Robot Operating System (ROS), YARP, OROCOS | ROS HAL, Android HAL, Automotive HAL |
| Scope | Wide: covers communication, data synchronization, device drivers, and services. | Narrow: focuses solely on hardware interface abstraction. |
| Abstraction Level | High-level: system-wide middleware services and protocols. | Low-level: hardware device interfacing and control. |
| User | Robotics developers integrating sensors, actuators, and algorithms. | Hardware engineers and driver developers. |
| Example Use Case | Coordinating multi-robot systems or integrating heterogeneous components. | Providing uniform access to different motor controllers or sensors. |
Introduction to Robot Middleware and Hardware Abstraction Layers
Robot Middleware provides a communication framework that enables seamless interaction between various robotic components and software modules, facilitating efficient data exchange and coordination. Hardware Abstraction Layers (HAL) act as an intermediary between the physical hardware and higher-level software, standardizing hardware interfaces to simplify software development and ensure portability. Understanding these foundational elements helps optimize your robotics system design by improving modularity and scalability.
Defining Robot Middleware: Core Functions and Purpose
Robot middleware serves as a software framework that simplifies the integration of diverse robotic components by providing standardized communication, data management, and processing capabilities. It abstracts complex hardware details to enable seamless interaction between sensors, actuators, and applications, enhancing modularity and scalability in robotic systems. You can leverage robot middleware to streamline development and ensure interoperability across various hardware platforms without dealing with low-level hardware specifics.
What Is a Hardware Abstraction Layer (HAL)?
A Hardware Abstraction Layer (HAL) is a software layer that enables operating systems or applications to interact with hardware devices through a consistent interface, regardless of the underlying hardware differences. HAL simplifies hardware management by providing standardized access to various devices, allowing your software to run on multiple hardware platforms without modification. In contrast to robot middleware, which facilitates communication between different software components, HAL focuses specifically on bridging software and physical hardware components.
Key Differences Between Middleware and HAL
Robot Middleware operates as a software layer managing communication, data processing, and integration between diverse robotic components, whereas Hardware Abstraction Layer (HAL) provides a standardized interface directly to the hardware, hiding the complexities of physical devices. Middleware enables interoperability and higher-level functions like sensor fusion and task coordination, while HAL focuses on device driver abstraction and low-level hardware control. Your choice depends on whether the priority is seamless system integration or optimized hardware manipulation.
Architectural Overview: Middleware vs. HAL
Robot Middleware provides a high-level architectural framework enabling seamless communication, data exchange, and integration among diverse robotic components and systems, abstracting complex software interactions. In contrast, the Hardware Abstraction Layer (HAL) operates at a lower level, directly interfacing with hardware devices to standardize access and control across various hardware platforms. Your robotic applications benefit from Middleware's flexible, modular design, while HAL ensures consistent hardware management and real-time responsiveness.
Integration and Interoperability Considerations
Robot Middleware facilitates seamless integration by providing standardized communication protocols and data exchange formats, enabling diverse robotic components and subsystems to work together efficiently. Hardware Abstraction Layer (HAL) simplifies interoperability by offering a uniform interface to hardware devices, masking hardware-specific details and allowing software to interact with different hardware platforms without modification. Your choice between Robot Middleware and HAL depends on whether your focus is on high-level software integration or low-level hardware abstraction for ensuring compatibility across varied robotic systems.
Real-World Applications of Middleware and HAL in Robotics
Robot middleware facilitates seamless integration and communication between various robotic software components, enabling complex tasks such as autonomous navigation and sensor data processing in real-world applications. Hardware Abstraction Layer (HAL) provides a standardized interface to underlying hardware, allowing software to operate across diverse robotic platforms without modification, crucial for modular robots and industrial automation. In factory automation and service robotics, middleware manages high-level behaviors while HAL ensures consistent hardware interaction, optimizing performance and scalability.
Benefits and Trade-Offs of Each Approach
Robot middleware offers seamless integration of diverse software components, enhancing scalability and flexibility for complex robotic systems, while the hardware abstraction layer (HAL) provides direct control over hardware resources, ensuring real-time performance and reliability. Middleware benefits include easier software development and platform independence, but may introduce latency and resource overhead; HAL excels in minimizing latency and maximizing hardware efficiency but requires more specialized programming and reduces portability. Your choice depends on whether you prioritize system adaptability and ease of use or low-level hardware control and performance optimization.
Choosing the Right Layer for Your Robotics Project
Selecting the right layer for your robotics project hinges on understanding the distinct roles of Robot Middleware and Hardware Abstraction Layer (HAL). Robot Middleware facilitates communication and coordination between various software components, enabling interoperability and scalability across diverse systems. The Hardware Abstraction Layer provides a uniform interface to hardware devices, simplifying development by hiding hardware-specific complexities and ensuring portability across different platforms.
Future Trends in Robot Middleware and Hardware Abstraction Layers
Future trends in robot middleware emphasize enhanced interoperability through standardized communication protocols and AI-driven context awareness for seamless integration across diverse robotic systems. Hardware abstraction layers are evolving to support modular, plug-and-play architectures, enabling faster hardware upgrades and easier maintenance in complex robotic platforms. Your robotics projects can benefit from these advancements by achieving greater flexibility, scalability, and real-time responsiveness in both middleware and hardware management.
Robot Middleware vs Hardware Abstraction Layer Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com