A Teach Pendant offers direct robot control with intuitive programming and real-time adjustments, ideal for on-site robotic tasks, while an HMI (Human-Machine Interface) provides a broader operational overview, enabling you to monitor and manage various industrial processes through graphical displays. Choosing between a Teach Pendant and an HMI depends on whether your priority is hands-on robot programming or comprehensive system interaction.
Table of Comparison
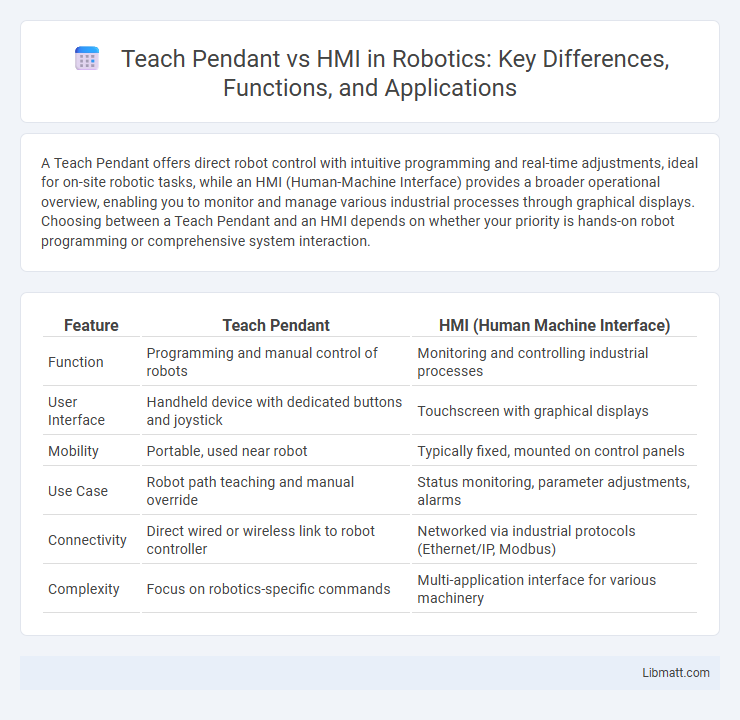
| Feature | Teach Pendant | HMI (Human Machine Interface) |
|---|---|---|
| Function | Programming and manual control of robots | Monitoring and controlling industrial processes |
| User Interface | Handheld device with dedicated buttons and joystick | Touchscreen with graphical displays |
| Mobility | Portable, used near robot | Typically fixed, mounted on control panels |
| Use Case | Robot path teaching and manual override | Status monitoring, parameter adjustments, alarms |
| Connectivity | Direct wired or wireless link to robot controller | Networked via industrial protocols (Ethernet/IP, Modbus) |
| Complexity | Focus on robotics-specific commands | Multi-application interface for various machinery |
Introduction to Teach Pendants and HMIs
Teach pendants are handheld devices specifically designed for programming and controlling industrial robots, offering direct interaction and precise motion control. HMIs (Human-Machine Interfaces) serve as user-friendly graphical interfaces that provide operators with real-time data visualization and system control for various automated processes. Your choice between a teach pendant and an HMI depends on the level of interaction and control needed for your automation tasks.
Key Functions of Teach Pendants
Teach pendants provide precise manual control of robotic arms, enabling operators to program and adjust robot movements directly at the machine. They offer real-time feedback and allow for intuitive task setup, calibration, and troubleshooting without the need for complex software interfaces. Your ability to quickly teach and modify robot paths on-site significantly enhances operational efficiency compared to traditional HMI systems.
Core Features of HMIs
Human-Machine Interfaces (HMIs) offer advanced visualization, real-time monitoring, and enhanced control capabilities, unlike basic teach pendants primarily designed for manual robot programming. HMIs support complex data integration, customizable dashboards, and remote access, facilitating efficient process management and diagnostics. Core features of HMIs include intuitive touchscreen displays, multi-protocol communication, and extensive connectivity options to optimize industrial automation workflows.
User Interface Comparison: Teach Pendant vs HMI
Teach pendants feature tactile buttons and a small screen designed for direct robotic control, providing precise manual input during programming and operation. HMIs offer larger, touch-enabled displays with intuitive graphics that simplify monitoring and managing complex automation processes in real time. Your choice depends on whether you prioritize hands-on robot manipulation or comprehensive process visualization and control.
Industrial Applications: When to Use Each
Teach pendants are primarily used for direct robot programming and manual control during commissioning or maintenance in industrial automation, offering precise input for robotics tasks. HMIs (Human-Machine Interfaces) provide broader control and monitoring capabilities across entire production lines, ideal for operators managing complex system processes and real-time data visualization. Select teach pendants for hands-on robot configuration, and HMIs for comprehensive system operation and monitoring in manufacturing environments.
Programming Capabilities and Flexibility
Teach pendants offer direct, hands-on programming tailored for robotic control with intuitive step-by-step guidance, making them highly flexible for on-the-spot adjustments. HMIs provide advanced programming capabilities through graphical interfaces and customizable touchscreens, enabling complex process control and integration with various industrial systems. Your choice depends on whether you prioritize direct manipulator command or broad system automation and monitoring flexibility.
Safety and Ergonomics Considerations
Teach pendants offer enhanced safety features such as emergency stop buttons and two-handed operation to prevent accidental robot movements, ensuring operator protection during programming and manual control. HMIs (Human-Machine Interfaces) are designed with ergonomic touchscreens and intuitive interfaces that reduce operator fatigue and improve interaction efficiency, supporting safer and more comfortable long-term use. Integrating both devices in automation systems maximizes safety protocols while optimizing ergonomic benefits for diverse operational scenarios.
Integration with Robotic and Automation Systems
Teach pendants offer seamless integration with robotic systems by providing direct control and programming capabilities, enabling precise manipulation of robots in real-time. HMIs (Human-Machine Interfaces) facilitate broader automation system management through intuitive graphical displays and monitoring tools, allowing you to oversee multiple processes simultaneously. Choosing between a teach pendant and an HMI depends on whether your priority is hands-on robot programming or comprehensive system visualization and control.
Cost and Maintenance Analysis
Teach pendants generally incur lower upfront costs compared to HMIs, making them a budget-friendly choice for basic robotic control. Maintenance expenses for teach pendants tend to be minimal due to their simpler design and fewer components, whereas HMIs often require more frequent software updates and hardware servicing, increasing long-term costs. Investing in an HMI can lead to higher operational expenses, but it offers enhanced functionality and user interface customization that may justify the price in complex industrial environments.
Choosing the Right Solution: Factors to Consider
Choosing the right solution between a Teach Pendant and an HMI depends on your specific application needs, including user interface complexity, operational environment, and required control precision. Teach Pendants excel in programming and direct robot control with portability, while HMIs offer comprehensive process visualization and user-friendly touchscreen interfaces for broader industrial automation tasks. Evaluate factors like ease of use, integration capability, and safety features to ensure optimal performance and user experience.
Teach Pendant vs HMI Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com