TIG welding robots provide precise, high-quality welds ideal for thin materials and detailed projects, while MIG welding robots excel in speed and efficiency, making them suitable for thicker materials and high-volume production. Your choice depends on the balance between the desired weld quality and the required production speed.
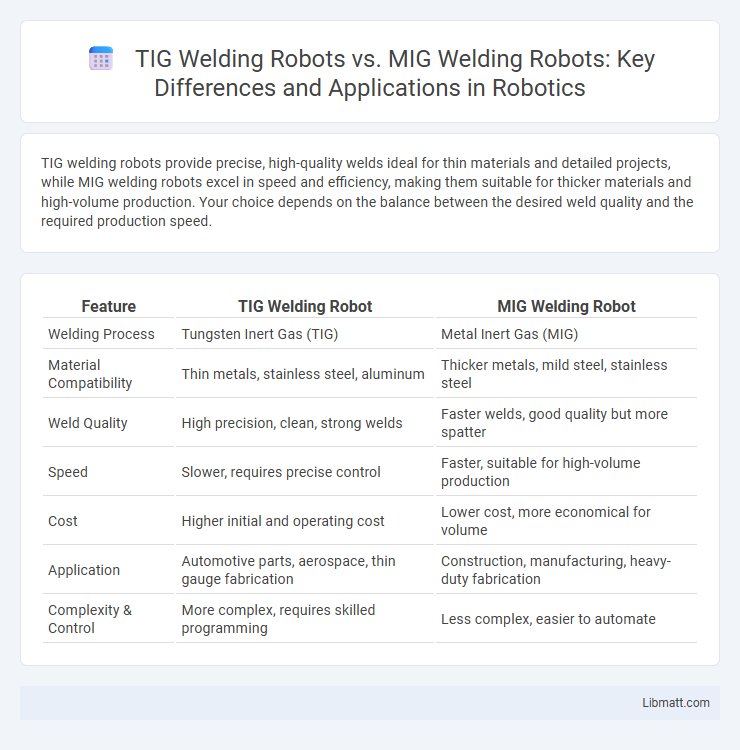
Table of Comparison
| Feature | TIG Welding Robot | MIG Welding Robot |
|---|---|---|
| Welding Process | Tungsten Inert Gas (TIG) | Metal Inert Gas (MIG) |
| Material Compatibility | Thin metals, stainless steel, aluminum | Thicker metals, mild steel, stainless steel |
| Weld Quality | High precision, clean, strong welds | Faster welds, good quality but more spatter |
| Speed | Slower, requires precise control | Faster, suitable for high-volume production |
| Cost | Higher initial and operating cost | Lower cost, more economical for volume |
| Application | Automotive parts, aerospace, thin gauge fabrication | Construction, manufacturing, heavy-duty fabrication |
| Complexity & Control | More complex, requires skilled programming | Less complex, easier to automate |
Introduction to Welding Robots: TIG vs MIG
TIG welding robots provide precise control for high-quality welds on thin metals and non-ferrous materials, making them ideal for applications requiring exceptional weld integrity. MIG welding robots offer faster deposition rates and greater adaptability for welding thicker materials in high-volume production environments. Your choice between TIG and MIG welding robots should consider material thickness, welding speed, and the desired finish quality.
Core Differences Between TIG and MIG Welding Robots
TIG welding robots utilize a non-consumable tungsten electrode to produce precise, high-quality welds ideal for thin materials and complex joints, whereas MIG welding robots use a consumable wire electrode fed through a gun, offering faster deposition rates and better suitability for thicker metals. TIG welding requires an inert gas such as argon to shield the weld area, providing cleaner results and less spatter compared to MIG welding, which often uses a mixed gas shield or pure CO2. The core differences lie in electrode consumption, welding speed, material compatibility, and weld quality, with TIG favored for precision and MIG for productivity in automated welding applications.
Advantages of TIG Welding Robots
TIG welding robots offer superior precision and control, making them ideal for applications that require high-quality, clean welds on thin or delicate materials such as stainless steel and aluminum. These robots produce minimal spatter, reducing post-weld cleanup and improving overall production efficiency. If your project demands fine, detailed welds with strong, corrosion-resistant joints, a TIG welding robot ensures consistent results with enhanced accuracy.
Advantages of MIG Welding Robots
MIG welding robots offer faster welding speeds and higher deposition rates, making them ideal for large-scale production environments. Their ability to handle thin and thick materials with minimal spatter improves overall weld quality and reduces post-processing time. MIG welding robots also provide greater flexibility in welding positions, enhancing efficiency in complex assembly tasks.
Applications and Industries for TIG Welding Robots
TIG welding robots are widely used in industries requiring high-precision and clean welds, such as aerospace, automotive, and medical device manufacturing. Applications include welding thin materials, stainless steel, aluminum, and exotic metals where superior weld quality and minimal spatter are critical. Your production benefits from TIG welding robots in sectors that demand meticulous control and consistent weld integrity, especially for small, intricate parts.
Applications and Industries for MIG Welding Robots
MIG welding robots are widely used in the automotive industry for assembling car bodies and manufacturing exhaust systems due to their high speed and efficiency in welding thin materials. These robots are also prevalent in the construction and heavy equipment sectors, where they handle structural steel welding for frames and machinery with consistent quality. Their adaptability to various metal types, including carbon steel and aluminum, makes MIG welding robots essential in manufacturing appliances and metal furniture.
Quality and Precision: TIG vs MIG Robotic Welding
TIG welding robots deliver superior quality and precision due to their ability to produce cleaner, more controlled welds with minimal spatter, ideal for thin or complex materials requiring fine detail. MIG welding robots, while faster and more efficient for high-volume production, typically generate more spatter and less precise weld beads, making them suitable for thicker materials and less critical applications. The choice between TIG and MIG robotic welding hinges on balancing high-precision requirements against production speed and material type.
Operational Speed and Efficiency Comparison
TIG welding robots offer precise control suitable for thin materials but typically operate at slower speeds compared to MIG welding robots, which excel in high-speed applications and thicker materials. MIG welding robots deliver higher deposition rates and faster cycle times, enhancing overall production efficiency in mass manufacturing. The choice depends on balancing precision requirements and throughput demands, with MIG robots favored for speed and TIG robots for detailed weld quality.
Cost Considerations: TIG vs MIG Welding Robots
TIG welding robots typically have higher upfront costs compared to MIG welding robots due to their precise control systems and specialized equipment requirements. MIG welding robots offer cost-effective solutions with faster welding speeds and lower consumable expenses, making them ideal for high-volume production. Your choice between these systems should balance budget constraints with the specific welding quality and application needs.
Choosing the Right Welding Robot for Your Needs
TIG welding robots excel in precision and control, making them ideal for applications requiring high-quality, clean welds on thin materials or non-ferrous metals like aluminum and stainless steel. MIG welding robots offer faster deposition rates and greater versatility, suitable for thicker materials and high-volume production in industries such as automotive manufacturing and construction. Selecting the right welding robot depends on factors like metal type, production speed, weld quality requirements, and budget constraints.
TIG welding robot vs MIG welding robot Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com