Offline programming allows you to create and test robot programs in a virtual environment without interrupting production, saving time and reducing errors. Online programming involves teaching robots directly on the production floor, providing real-time adjustments but often causing downtime and requiring expert operators.
Table of Comparison
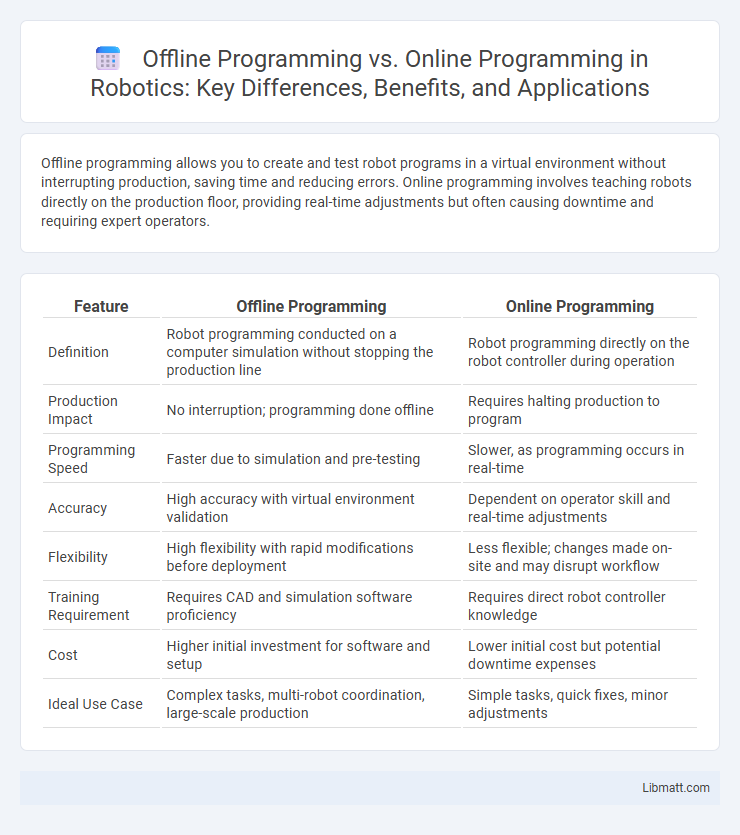
| Feature | Offline Programming | Online Programming |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Robot programming conducted on a computer simulation without stopping the production line | Robot programming directly on the robot controller during operation |
| Production Impact | No interruption; programming done offline | Requires halting production to program |
| Programming Speed | Faster due to simulation and pre-testing | Slower, as programming occurs in real-time |
| Accuracy | High accuracy with virtual environment validation | Dependent on operator skill and real-time adjustments |
| Flexibility | High flexibility with rapid modifications before deployment | Less flexible; changes made on-site and may disrupt workflow |
| Training Requirement | Requires CAD and simulation software proficiency | Requires direct robot controller knowledge |
| Cost | Higher initial investment for software and setup | Lower initial cost but potential downtime expenses |
| Ideal Use Case | Complex tasks, multi-robot coordination, large-scale production | Simple tasks, quick fixes, minor adjustments |
Introduction to Offline and Online Programming
Offline programming involves creating and simulating robotic instructions using specialized software without interrupting actual production, enhancing efficiency and reducing downtime. Online programming requires direct teaching or manual input of commands to the robot in the physical environment, often used for fine-tuning or immediate adjustments. Understanding the advantages of both methods helps you optimize robotic system performance and minimize operational disruptions.
Key Differences Between Offline and Online Programming
Offline programming enables robot paths and operations to be created in a virtual environment without halting production, increasing efficiency and reducing downtime. Online programming, in contrast, involves direct modifications and adjustments on the robot during actual operation, allowing real-time error correction but potentially interrupting workflow. Main differences lie in flexibility, implementation time, and impact on production continuity, with offline programming promoting safer, faster deployment and online programming offering immediate responsiveness.
Advantages of Offline Programming
Offline programming offers the advantage of allowing you to create, simulate, and optimize robotic or CNC toolpaths without halting production, significantly reducing downtime and increasing overall efficiency. This approach enables precise error detection and correction before actual execution, enhancing accuracy and minimizing costly mistakes in manufacturing processes. By decoupling programming from machine operation, offline programming supports parallel workflow development, leading to faster project completion and improved resource utilization.
Benefits of Online Programming
Online programming enables real-time control and immediate feedback, significantly enhancing precision and reducing errors during robotic operations. This approach allows for dynamic adjustments directly on the production floor, minimizing downtime and increasing overall efficiency. You can optimize your manufacturing processes by leveraging the flexibility and responsiveness of online programming to meet tight deadlines and complex task requirements.
Use Cases and Applications
Offline programming excels in scenarios where simulation, complex robot path planning, and precise toolpath generation are critical, such as automotive manufacturing and aerospace assembly. Online programming is preferred for real-time adjustments, quick troubleshooting, and on-the-fly modifications during production processes like packaging or small-batch customizations. Your choice between offline and online programming depends on the need for pre-production optimization versus in-the-moment adaptability.
Speed and Efficiency Comparison
Offline programming allows for faster and more efficient robot task planning by enabling simulation and verification without halting production, reducing downtime. Online programming requires the robot to be stopped during code adjustments, leading to slower cycle times and less operational efficiency. Leveraging offline programming tools significantly improves throughput by optimizing tasks in a virtual environment before real-world implementation.
Required Tools and Technologies
Offline programming relies heavily on advanced simulation software, CAD/CAM systems, and virtual environment tools to create and test programs without interrupting actual machine operations. Online programming requires real-time interfaces, programmable logic controllers (PLCs), and direct machine control systems to input, adjust, and monitor code on the physical equipment. Essential technologies for offline programming include robotics simulation platforms like RoboDK and Siemens NX, whereas online programming depends on hardware connectivity protocols such as OPC UA and Ethernet/IP.
Challenges and Limitations
Offline programming faces challenges such as limited real-time feedback and the risk of inaccuracies due to discrepancies between virtual models and actual robot conditions. Online programming allows for immediate adjustments but can be disruptive to production workflows and requires skilled operators to manage real-time errors. You must weigh these limitations carefully to optimize efficiency and minimize downtime in your automation processes.
Industry Trends and Future Outlook
Offline Programming in industrial automation is gaining traction due to its ability to reduce downtime and enhance precision by simulating robot paths and processes before deployment. Online Programming remains essential for real-time adjustments and adaptive control in dynamic production environments, especially in sectors like automotive and electronics manufacturing. Industry trends indicate a hybrid approach combining offline simulation with online fine-tuning will dominate, driven by advancements in AI, machine learning, and digital twin technologies, ensuring greater flexibility and efficiency in future manufacturing systems.
Choosing the Right Approach
Choosing the right programming approach depends on project requirements, with Offline Programming offering simulation and error detection in a virtual environment, reducing downtime and minimizing risks. Online Programming enables real-time adjustments and direct control of robotic systems, ideal for tasks requiring immediate feedback and fine-tuning. Factors such as complexity, time constraints, and resource availability significantly influence the decision between offline and online programming methods.
Offline Programming vs Online Programming Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com