Latex dipping produces thin, flexible latex products by repeatedly immersing a mold in liquid latex, ideal for gloves and balloons with precise thickness control. Latex molding involves injecting or pouring liquid latex into a mold to create thicker, more complex shapes with enhanced durability and detail, making it suitable for medical devices and prosthetics.
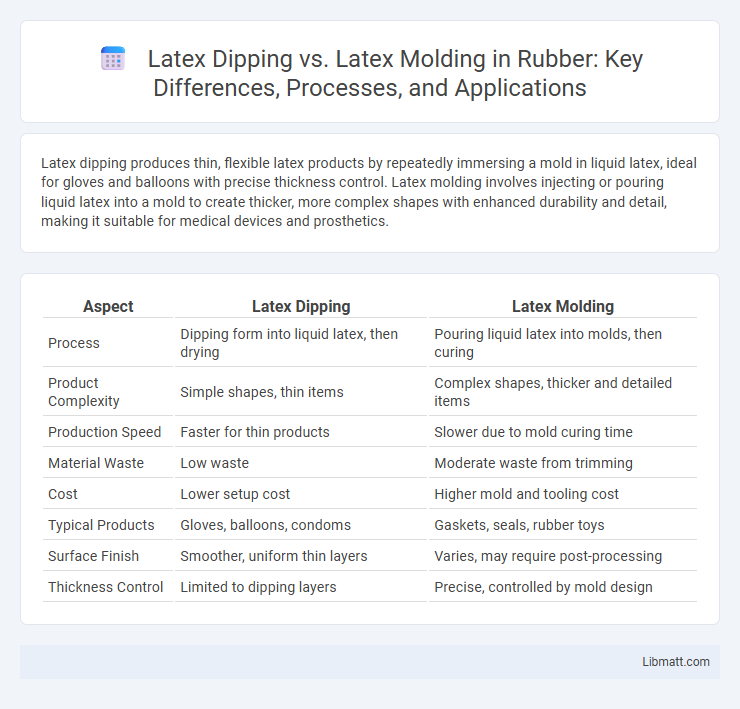
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Latex Dipping | Latex Molding |
|---|---|---|
| Process | Dipping form into liquid latex, then drying | Pouring liquid latex into molds, then curing |
| Product Complexity | Simple shapes, thin items | Complex shapes, thicker and detailed items |
| Production Speed | Faster for thin products | Slower due to mold curing time |
| Material Waste | Low waste | Moderate waste from trimming |
| Cost | Lower setup cost | Higher mold and tooling cost |
| Typical Products | Gloves, balloons, condoms | Gaskets, seals, rubber toys |
| Surface Finish | Smoother, uniform thin layers | Varies, may require post-processing |
| Thickness Control | Limited to dipping layers | Precise, controlled by mold design |
Introduction to Latex Processing Techniques
Latex dipping and latex molding are two primary techniques used in latex processing, each suited for different applications and product types. Latex dipping involves immersing a form or mold into liquid latex to create thin, flexible coatings ideal for gloves and balloons, while latex molding uses pre-shaped molds to form thicker, more durable latex items such as medical devices and industrial components. Understanding these methods helps you choose the right process based on the desired product durability, thickness, and precision.
What is Latex Dipping?
Latex dipping is a manufacturing process where a form, usually a mold or a hand-shaped tool, is repeatedly dipped into liquid latex to build up layers and create a flexible, seamless product such as gloves, balloons, or catheters. This technique allows for precise control over thickness and texture while producing lightweight, elastic items essential in medical and industrial applications. Understanding the differences between latex dipping and latex molding helps you choose the most suitable method for durability, detail, and cost-efficiency in your specific project.
What is Latex Molding?
Latex molding is a manufacturing process where liquid latex is poured or brushed into a mold to create detailed, flexible rubber parts with precise shapes and textures. This method allows for high-quality, complex designs by capturing fine surface details and ensures consistency across multiple units. It is commonly used in industries like special effects, prosthetics, and costume design for producing durable, lightweight latex products.
Key Differences Between Latex Dipping and Molding
Latex dipping involves submerging a form into liquid latex to create thin, flexible layers, while latex molding uses a mold filled with liquid latex to produce thicker, more detailed shapes. Key differences include the texture and thickness of the final product; dipping yields lightweight, stretchable items, whereas molding results in rigid, durable components. Your choice depends on whether you need flexibility and lightness or precision and sturdiness in latex products.
Materials and Equipment Required
Latex dipping utilizes liquid natural rubber applied over a form, requiring a dipping tank, drying oven, and release agents to create thin, flexible coatings ideal for gloves and balloons. Latex molding involves pouring liquid latex into molds, demanding precise molds, curing chambers, and temperature controls to shape durable, complex items like masks and industrial components. Both processes rely on high-quality latex, but molding requires more specialized equipment to maintain detailed shapes and consistent wall thicknesses.
Step-by-Step Process: Latex Dipping
Latex dipping involves immersing a mold into liquid latex, allowing a thin, uniform layer to form as the latex clings to the mold's surface before it is slowly removed and cured. This step-by-step process includes mold preparation with a release agent, repeated dipping to achieve the desired thickness, and drying between each dip to build multiple layers. Your final product benefits from the controlled layering and consistent texture that latex dipping ensures, making it ideal for flexible, seamless items.
Step-by-Step Process: Latex Molding
Latex molding begins by creating a detailed master model, often from clay or silicone, which serves as the template for the mold. A release agent is applied to the model before dipping it into liquid latex multiple times, allowing each layer to dry partially to build up thickness. After reaching the desired thickness, the latex mold is carefully peeled off, inspected for defects, and then cured or vulcanized to enhance durability and flexibility for final use.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Each Method
Latex dipping offers advantages such as flexibility, lightweight characteristics, and cost-effectiveness for producing thin, seamless gloves and balloons, but it has limitations in uniform thickness control and slower production rates. Latex molding provides superior precision and consistency in shape and thickness, making it ideal for complex, durable products like medical gloves, yet it involves higher tooling costs and longer setup times. Choosing between dipping and molding depends on product requirements, balancing factors like production volume, quality consistency, and cost efficiency.
Applications in Industry and Product Manufacturing
Latex dipping is widely utilized in industries producing gloves, balloons, and medical devices due to its ability to create thin, flexible coatings with precise thickness control. Latex molding, on the other hand, is favored for manufacturing durable items such as seals, gaskets, and complex-shaped automotive components because of its capability to form intricate, three-dimensional structures. Both techniques are integral to diverse industrial applications, with dipping excelling in disposable or lightweight products and molding suited for robust, long-lasting parts.
Choosing the Right Technique for Your Project
Latex dipping offers flexible, thin, and seamless products ideal for small-scale manufacturing or prototypes requiring high detail and elasticity. Latex molding suits large production runs needing consistent thickness, intricate shapes, and enhanced durability with controlled curing conditions. Assess project scale, design complexity, and material performance requirements to determine the optimal latex processing method.
Latex Dipping vs Latex Molding Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com