Rubber offers excellent elasticity and durability, making it ideal for general-purpose applications, while crepe rubber is a natural, unprocessed form known for its unique texture and superior grip. Your choice between rubber and crepe rubber depends on whether you prioritize resilience or a textured, eco-friendly material.
Table of Comparison
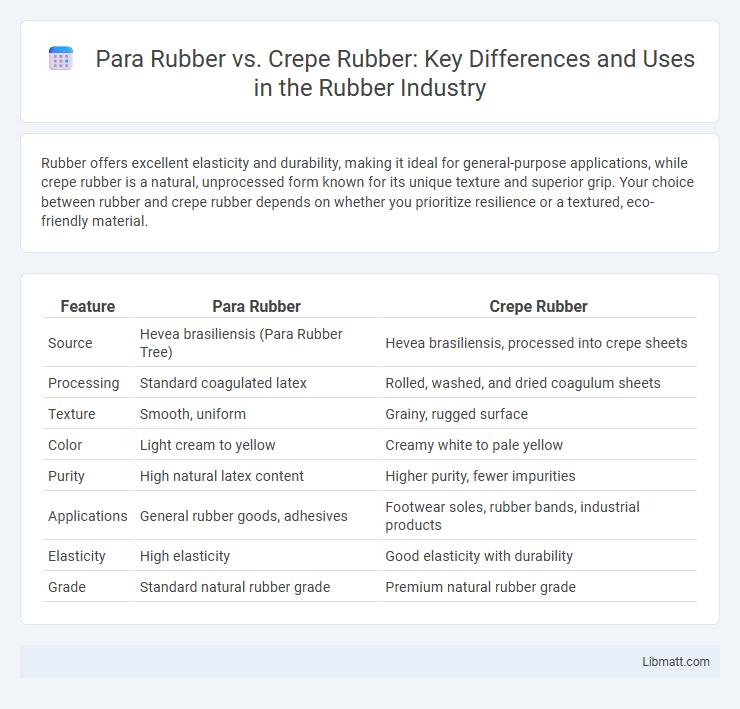
| Feature | Para Rubber | Crepe Rubber |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Hevea brasiliensis (Para Rubber Tree) | Hevea brasiliensis, processed into crepe sheets |
| Processing | Standard coagulated latex | Rolled, washed, and dried coagulum sheets |
| Texture | Smooth, uniform | Grainy, rugged surface |
| Color | Light cream to yellow | Creamy white to pale yellow |
| Purity | High natural latex content | Higher purity, fewer impurities |
| Applications | General rubber goods, adhesives | Footwear soles, rubber bands, industrial products |
| Elasticity | High elasticity | Good elasticity with durability |
| Grade | Standard natural rubber grade | Premium natural rubber grade |
Introduction to Para Rubber and Crepe Rubber
Para rubber, derived from the Hevea brasiliensis tree, is a natural latex known for its high elasticity, resilience, and widespread use in manufacturing tires, gloves, and various rubber products. Crepe rubber is processed from concentrated latex through coagulation and drying, resulting in a soft, flexible, and porous material primarily used in footwear and mattresses. Understanding the distinctions in texture, processing methods, and applications highlights the unique advantages of para rubber and crepe rubber in industrial and consumer goods.
Origin and Production Processes
Para rubber originates from the latex of the Hevea brasiliensis tree, primarily harvested through tapping in tropical plantations using controlled incisions. Crepe rubber is produced by coagulating natural latex with formic acid or acetic acid, followed by a mechanical process of masticating, washing, and drying into sheets with a characteristic crinkled texture. The key difference lies in para rubber being raw latex collection, while crepe rubber results from further coagulation and processing to create a consumable raw rubber sheet.
Physical Properties Comparison
Para rubber exhibits high elasticity, excellent tensile strength, and superior abrasion resistance, making it ideal for diverse applications requiring durability and flexibility. Crepe rubber, derived from coagulated latex sheets, displays a coarser texture with enhanced resilience but lower tensile strength compared to para rubber. The physical differences influence their usage, with para rubber favored for high-performance products and crepe rubber suited for applications needing cushioning and pliability.
Applications and End-Uses
Para rubber is widely used in manufacturing automotive tires, conveyor belts, and industrial gloves due to its excellent elasticity and tensile strength. Crepe rubber, characterized by its soft texture and high purity, is primarily utilized in medical gloves, balloons, and adhesives where flexibility and skin safety are critical. The end-uses of para rubber favor durability and heavy-duty applications, while crepe rubber is preferred for products requiring softness and fine texture.
Cost Differences and Market Value
Para rubber generally costs less than crepe rubber due to its less intensive processing requirements, making it more affordable for bulk industrial applications. Crepe rubber commands a higher market value because of its superior purity, elasticity, and softness, which are essential for high-quality products such as medical-grade goods and premium footwear. The price disparity reflects crepe rubber's labor-intensive manufacture and stringent quality standards, positioning it as a niche material with greater demand in specialized markets.
Durability and Performance
Para rubber offers superior durability and elasticity, making it highly effective for applications requiring long-lasting, flexible material. Crepe rubber, known for its porous texture and softness, provides excellent grip but tends to wear out faster under heavy stress. For performance-intensive uses, para rubber's higher tensile strength and abrasion resistance ensure greater longevity and reliability.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Para rubber, derived from Hevea brasiliensis trees, promotes sustainability through its renewable nature and carbon sequestration during growth. Crepe rubber, a processed form of natural rubber sheets, retains the environmental benefits of para rubber but may involve energy-intensive processing methods that affect its overall ecological footprint. Both materials offer biodegradable alternatives to synthetic rubbers, supporting eco-friendly industrial applications and reducing reliance on petroleum-based products.
Advantages of Para Rubber
Para Rubber offers superior elasticity and tensile strength compared to Crepe Rubber, making it ideal for products requiring high durability and flexibility. It provides enhanced resistance to weathering, oils, and abrasion, resulting in longer-lasting performance in automotive and industrial applications. The refined processing of Para Rubber ensures consistent quality and uniformity, beneficial for manufacturing precision rubber components.
Advantages of Crepe Rubber
Crepe rubber offers superior elasticity and durability compared to para rubber, making it ideal for products that require high resistance to wear and tear. Its natural texture provides excellent grip and cushioning, enhancing comfort in footwear and sports equipment. You benefit from crepe rubber's eco-friendly production process, which uses fewer chemicals and generates less waste than para rubber manufacturing.
Choosing the Right Rubber for Your Needs
Para rubber offers excellent elasticity and durability, making it ideal for applications requiring flexibility and resilience such as tires and gloves. Crepe rubber, derived from natural latex and processed into a dense, textured sheet, provides superior grip and cushioning, preferred for footwear soles and mats. Selecting between para rubber and crepe rubber depends on the specific performance requirements, including elasticity, texture, and intended use environment.
para Rubber vs crepe Rubber Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com