Oil-resistant materials prevent degradation when exposed to oils, while oil-resistant rubber specifically refers to elastomers designed to maintain flexibility and durability in oily environments. Choosing the right oil-resistant rubber ensures your applications withstand oil exposure without cracking or swelling, enhancing longevity and performance.
Table of Comparison
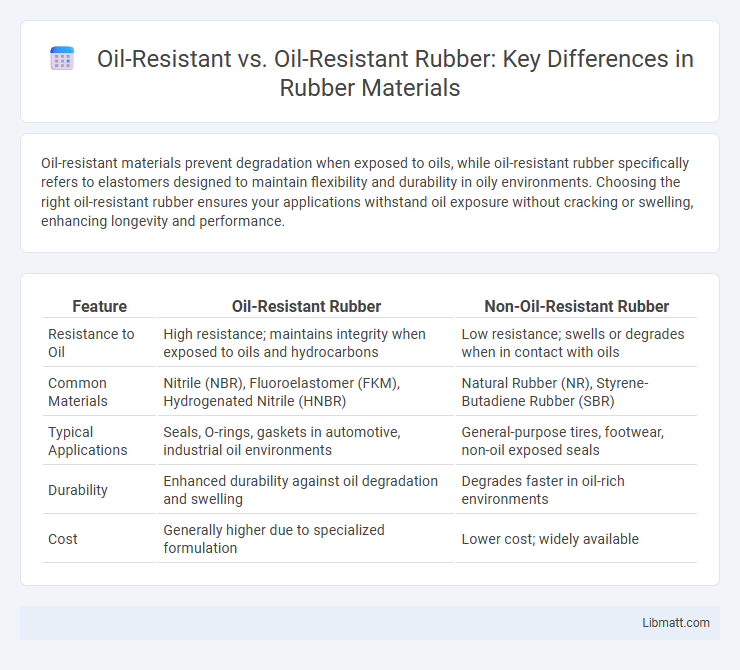
| Feature | Oil-Resistant Rubber | Non-Oil-Resistant Rubber |
|---|---|---|
| Resistance to Oil | High resistance; maintains integrity when exposed to oils and hydrocarbons | Low resistance; swells or degrades when in contact with oils |
| Common Materials | Nitrile (NBR), Fluoroelastomer (FKM), Hydrogenated Nitrile (HNBR) | Natural Rubber (NR), Styrene-Butadiene Rubber (SBR) |
| Typical Applications | Seals, O-rings, gaskets in automotive, industrial oil environments | General-purpose tires, footwear, non-oil exposed seals |
| Durability | Enhanced durability against oil degradation and swelling | Degrades faster in oil-rich environments |
| Cost | Generally higher due to specialized formulation | Lower cost; widely available |
Understanding Oil Resistance in Rubber Materials
Oil-resistant rubber materials are engineered to maintain flexibility and durability when exposed to oils, petroleum-based fluids, and hydrocarbons. Key polymers like nitrile (NBR), hydrogenated nitrile (HNBR), and fluorocarbon (FKM) offer varying levels of resistance depending on the specific application environment. Understanding oil resistance in rubber ensures you select the right compound for optimal performance and longevity in oil-rich conditions.
Key Differences: Oil-Resistant vs. Non-Oil-Resistant Rubber
Oil-resistant rubber is specifically formulated with additives like nitrile or fluorocarbon polymers to withstand degradation caused by oils, fuels, and hydrocarbons, whereas non-oil-resistant rubber lacks these properties and deteriorates quickly upon exposure. The molecular structure of oil-resistant rubber resists swelling and maintains elasticity, making it ideal for automotive seals, gaskets, and industrial hoses. In contrast, non-oil-resistant rubber is better suited for applications where oil exposure is minimal, prioritizing cost-effectiveness and general durability over chemical resistance.
Types of Oil-Resistant Rubber Compounds
Oil-resistant rubber compounds include nitrile rubber (NBR), hydrogenated nitrile rubber (HNBR), fluorocarbon rubber (FKM), and silicone rubber, each engineered for specific oil exposure conditions and temperatures. NBR offers excellent resistance to petroleum-based oils, while HNBR provides enhanced durability and heat resistance for longer service life in harsh environments. You can select the appropriate type based on the oil type, operating temperature, and mechanical demands of your application.
Common Applications for Oil-Resistant Rubber
Oil-resistant rubber is widely used in automotive seals, gaskets, and hoses due to its ability to withstand harsh exposure to petroleum-based oils and fuels. Industrial machinery also relies on this material to maintain integrity in environments with frequent oil contact, ensuring durability and reducing maintenance costs. You can find oil-resistant rubber in conveyor belts, oil seals, and vibration dampening components, making it essential for prolonging equipment lifespan in oil-intensive applications.
Performance Factors: Durability and Lifespan
Oil-resistant rubber outperforms standard rubber in durability by maintaining its integrity against petroleum-based oils, preventing swelling, cracking, and degradation. The chemical composition of oil-resistant rubber, often incorporating nitrile or fluorocarbon compounds, significantly extends its lifespan in harsh environments compared to non-resistant alternatives. Performance factors such as abrasion resistance, temperature tolerance, and elasticity further contribute to the prolonged service life of oil-resistant rubber products in industrial applications.
Industry Standards for Oil-Resistant Rubber
Industry standards for oil-resistant rubber include ASTM D2000, which classifies rubber materials based on their resistance to various chemicals, including oils and petroleum products. ISO 1817 specifies testing methods for determining the resistance of rubber to oils and fluids commonly encountered in automotive and industrial applications. Compliance with these standards ensures that oil-resistant rubber meets durability, performance, and safety requirements essential for use in seals, gaskets, hoses, and other components exposed to aggressive oil environments.
Testing Methods for Oil Resistance
Testing methods for oil resistance in rubber materials primarily involve ASTM D471, where specimens are immersed in specific oils at controlled temperatures to measure changes in volume, weight, hardness, and tensile strength. Other standardized tests include ISO 1817, which evaluates rubber's swelling and degradation in oil, providing comparative data on rubber compound resilience. These tests ensure materials meet industry requirements for durability in oil-rich environments, crucial for automotive and industrial sealing applications.
Benefits of Using Oil-Resistant Rubber
Oil-resistant rubber enhances the durability and performance of seals, gaskets, and hoses exposed to petroleum-based oils, preventing swelling, cracking, and degradation. This specialized material maintains flexibility and strength in harsh environments, significantly extending the lifespan of industrial and automotive components. Using oil-resistant rubber reduces maintenance costs and improves operational reliability in machinery subject to oil exposure.
Limitations and Considerations
Oil-resistant rubber offers protection against various hydrocarbons, but its effectiveness is limited by the type and concentration of oils, temperature, and exposure duration. Some oil-resistant rubbers may degrade or swell when exposed to specific oils, reducing durability and performance in harsh environments. Your choice should consider the chemical compatibility charts and application conditions to ensure long-term reliability and avoid premature material failure.
Choosing the Right Oil-Resistant Rubber for Your Needs
Selecting the right oil-resistant rubber depends on factors such as chemical compatibility, temperature range, and durability requirements specific to your application. Nitrile rubber (NBR) offers excellent resistance to petroleum-based oils and fuels, while fluorocarbon rubber (FKM) provides superior performance in high-temperature and aggressive chemical environments. Evaluating the operational conditions ensures you choose oil-resistant rubber that maximizes longevity and efficiency in your equipment.
Oil-resistant vs Oil-resistant rubber Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com