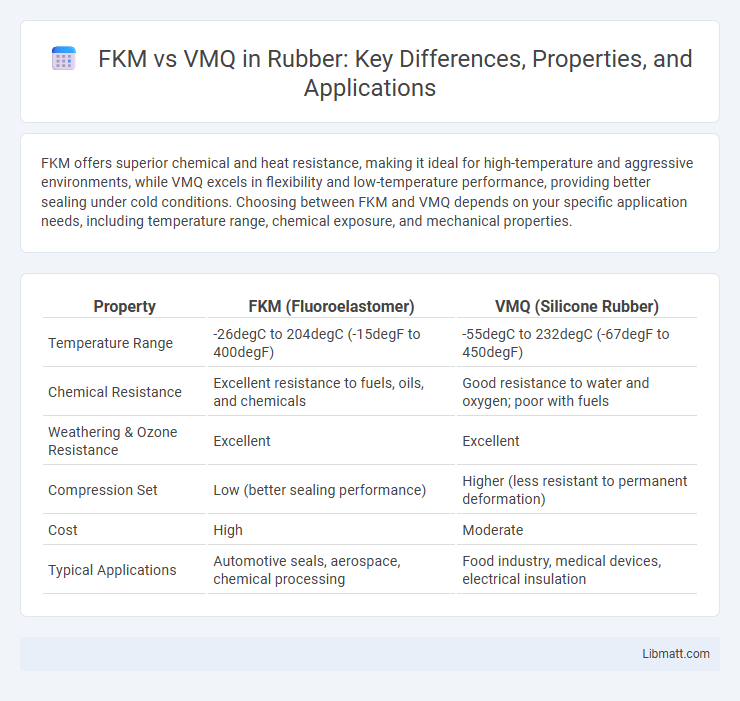
FKM offers superior chemical and heat resistance, making it ideal for high-temperature and aggressive environments, while VMQ excels in flexibility and low-temperature performance, providing better sealing under cold conditions. Choosing between FKM and VMQ depends on your specific application needs, including temperature range, chemical exposure, and mechanical properties.
Table of Comparison
| Property | FKM (Fluoroelastomer) | VMQ (Silicone Rubber) |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature Range | -26degC to 204degC (-15degF to 400degF) | -55degC to 232degC (-67degF to 450degF) |
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent resistance to fuels, oils, and chemicals | Good resistance to water and oxygen; poor with fuels |
| Weathering & Ozone Resistance | Excellent | Excellent |
| Compression Set | Low (better sealing performance) | Higher (less resistant to permanent deformation) |
| Cost | High | Moderate |
| Typical Applications | Automotive seals, aerospace, chemical processing | Food industry, medical devices, electrical insulation |
Introduction to FKM and VMQ
FKM (fluoroelastomer) and VMQ (silicone) are two widely used elastomers in industrial applications. FKM is renowned for its exceptional chemical resistance, high-temperature stability up to 200-250degC, and durability in harsh environments, making it ideal for automotive and aerospace seals. VMQ offers excellent flexibility, broad temperature range from -60degC to 230degC, and superior electrical insulation, which suits it for medical devices, food processing, and electronics where biocompatibility and thermal resistance are critical.
Chemical Composition Comparison
FKM (fluoroelastomer) contains vinylidene fluoride, hexafluoropropylene, and tetrafluoroethylene, providing exceptional resistance to oils, chemicals, and high temperatures. VMQ (silicone rubber) is composed primarily of polydimethylsiloxane, offering superior flexibility and thermal stability but lower chemical resistance compared to FKM. The fluorine atoms in FKM's backbone enhance its chemical inertness, whereas VMQ's silicon-oxygen backbone grants excellent oxidation resistance but limited protection against fuels and solvents.
Key Physical Properties
FKM exhibits superior chemical resistance, high-temperature stability up to 200-250degC, and excellent oil and fuel resistance, making it ideal for automotive and aerospace applications. VMQ offers excellent low-temperature flexibility, maintaining elasticity down to -60degC, with good weathering and ozone resistance but lower resistance to hydrocarbons and chemicals. Both elastomers differ significantly in tensile strength, compression set, and operating temperature ranges, influencing their suitability based on environmental and chemical exposure requirements.
Temperature Resistance Analysis
FKM exhibits superior temperature resistance, maintaining chemical stability and mechanical properties in high-temperature environments up to 200-250degC, compared to VMQ, which typically withstands temperatures up to 150-200degC before degradation occurs. FKM's fluorocarbon composition provides enhanced resistance to thermal oxidation and aggressive chemicals, making it ideal for demanding automotive and industrial applications. Your choice between FKM and VMQ depends on the specific temperature range and chemical exposure of your application, with FKM offering greater durability under extreme heat.
Chemical Resistance: FKM vs VMQ
FKM (fluoroelastomer) offers superior chemical resistance compared to VMQ (silicone rubber), excelling in exposure to fuels, oils, and aggressive chemicals. VMQ performs adequately with water, alcohols, and mild acids but degrades rapidly when exposed to aromatic hydrocarbons or ketones. Your choice should prioritize FKM for environments requiring robust chemical durability and VMQ for applications with less aggressive chemical exposure.
Mechanical Performance Differences
FKM elastomers exhibit superior mechanical performance compared to VMQ, offering higher tensile strength, better abrasion resistance, and enhanced compression set characteristics. VMQ, or silicone rubber, provides excellent flexibility and low temperature performance but generally falls short in wear resistance and mechanical durability under heavy loads. Your choice should consider FKM for demanding applications requiring robust mechanical strength and longevity, while VMQ suits environments prioritizing flexibility and temperature stability.
Typical Applications of FKM
FKM, commonly known as fluoroelastomer, is extensively used in automotive fuel systems, aerospace sealing, and chemical processing due to its excellent resistance to high temperatures, fuels, oils, and aggressive chemicals. Typical applications include O-rings, gaskets, and seals in environments exposed to harsh fluids and extreme heat. Its superior chemical stability and durability make FKM ideal for use in fuel injectors, hydraulic systems, and industrial machinery where VMQ (silicone rubber) may degrade more rapidly.
Common Uses of VMQ
VMQ (silicone rubber) is commonly used in automotive seals, medical devices, cookware, and electrical insulation due to its excellent flexibility, heat resistance, and biocompatibility. It performs well in applications requiring exposure to extreme temperatures and UV radiation, making it ideal for outdoor and food-grade environments. VMQ is preferred when elasticity and thermal stability over a wide temperature range (-60degC to 230degC) are critical.
Cost and Availability
FKM (fluoroelastomer) typically commands higher prices due to its superior chemical and temperature resistance, making it less cost-effective for large-scale applications compared to VMQ (silicone rubber). VMQ is widely available and more affordable, favored for general-purpose use where extreme chemical resistance is not required. Businesses often choose VMQ for its cost efficiency and availability, reserving FKM for specialized environments demanding durability and resistance.
Choosing Between FKM and VMQ
Choosing between FKM (fluoroelastomer) and VMQ (silicone rubber) depends on application-specific factors such as temperature range, chemical resistance, and mechanical properties. FKM excels in high-temperature environments up to 250degC and offers superior resistance to fuels, oils, and solvents, making it ideal for automotive and aerospace seals. VMQ performs well at extreme low temperatures down to -60degC, provides excellent flexibility and weatherability, and is preferred for food-grade, medical, and electrical insulation applications.
FKM vs VMQ Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com