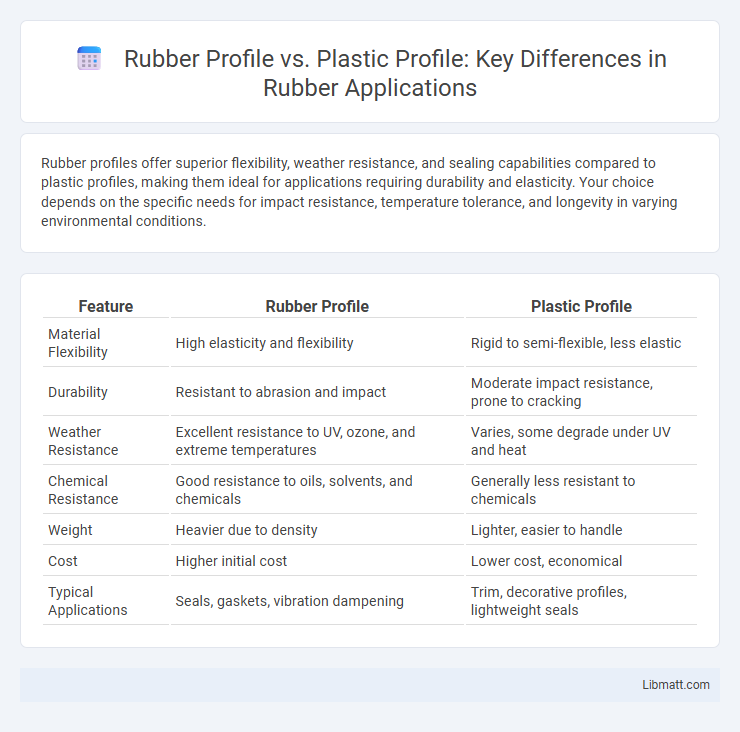
Rubber profiles offer superior flexibility, weather resistance, and sealing capabilities compared to plastic profiles, making them ideal for applications requiring durability and elasticity. Your choice depends on the specific needs for impact resistance, temperature tolerance, and longevity in varying environmental conditions.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Rubber Profile | Plastic Profile |
|---|---|---|
| Material Flexibility | High elasticity and flexibility | Rigid to semi-flexible, less elastic |
| Durability | Resistant to abrasion and impact | Moderate impact resistance, prone to cracking |
| Weather Resistance | Excellent resistance to UV, ozone, and extreme temperatures | Varies, some degrade under UV and heat |
| Chemical Resistance | Good resistance to oils, solvents, and chemicals | Generally less resistant to chemicals |
| Weight | Heavier due to density | Lighter, easier to handle |
| Cost | Higher initial cost | Lower cost, economical |
| Typical Applications | Seals, gaskets, vibration dampening | Trim, decorative profiles, lightweight seals |
Introduction to Rubber and Plastic Profiles
Rubber profiles are flexible, durable seals made from natural or synthetic elastomers, designed for applications requiring elasticity and resistance to weather, chemicals, and abrasion. Plastic profiles, typically manufactured from PVC, polyethylene, or polypropylene, offer rigidity and structural support while maintaining lightweight properties ideal for construction and automotive uses. Both materials serve as essential components in sealing, insulation, and protection across various industries, with each selected based on specific performance requirements and environmental conditions.
Material Composition: Rubber vs Plastic
Rubber profiles consist primarily of natural or synthetic elastomers, providing superior flexibility, elasticity, and resistance to abrasion and weathering. Plastic profiles, typically made from PVC, polyethylene, or polypropylene, offer rigidity, durability, and resistance to chemicals but lack the elasticity found in rubber. Understanding the material composition helps you choose the right profile based on elasticity, durability, and environmental resistance required for your specific application.
Key Applications in Various Industries
Rubber profiles excel in sealing, vibration damping, and weather resistance, making them ideal for automotive door seals, HVAC gaskets, and industrial machinery components. Plastic profiles are preferred for structural trims, insulation, and decorative elements in construction, electronics casing, and furniture manufacturing. Both materials serve crucial roles tailored to industry-specific demands, with rubber providing flexibility and durability, while plastic offers rigidity and design versatility.
Durability and Longevity Comparison
Rubber profiles typically offer superior durability and longevity due to their excellent flexibility, resistance to abrasion, and ability to withstand extreme temperatures without cracking or degrading. Plastic profiles, while often more cost-effective, can become brittle over time when exposed to UV light or harsh environmental conditions, leading to reduced lifespan. Choosing a rubber profile for your applications ensures enhanced performance and extended service life in demanding environments.
Flexibility and Performance
Rubber profiles offer superior flexibility and excellent resilience under dynamic stress, making them ideal for applications requiring frequent compression and expansion, such as seals and gaskets. Plastic profiles provide rigidity and dimensional stability, performing well in structural applications but often lacking the elastic recovery of rubber. The performance of rubber profiles excels in vibration dampening and weather resistance, while plastic profiles are better suited for environments demanding chemical resistance and load-bearing capabilities.
Resistance to Chemicals and Environmental Factors
Rubber profiles exhibit superior resistance to a wide range of chemicals, including oils, solvents, and acids, making them ideal for harsh industrial environments. Plastic profiles, while generally resistant to UV radiation and moisture, tend to degrade faster under exposure to certain chemicals and extreme temperatures. Selecting the optimal profile depends on the specific environmental conditions and chemical exposure expected in the application.
Cost-Effectiveness and Economic Considerations
Rubber profiles generally offer greater flexibility and durability, making them cost-effective for applications requiring high elasticity and weather resistance, though initial material costs can be higher than plastic profiles. Plastic profiles often provide lower upfront costs and easier mass production, but may incur higher long-term expenses due to reduced wear resistance and potential for brittleness in harsh environments. Evaluating lifecycle costs, including maintenance, replacement frequency, and environmental conditions, is essential for determining the most economical choice between rubber and plastic profiles.
Customization and Design Flexibility
Rubber profiles offer superior customization and design flexibility due to their inherent elasticity and ability to conform to complex shapes, making them ideal for sealing, cushioning, and vibration damping applications. Plastic profiles, while versatile, are generally more rigid and provide limited stretchability, which restricts their use in dynamic or high-compression environments. Advanced manufacturing processes like extrusion and molding enhance the customization options for both materials, but rubber's diverse compound formulations allow for tailored hardness, color, and chemical resistance, giving it a distinct advantage in adaptive design requirements.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Rubber profiles typically offer better sustainability due to their recyclability and longer lifespan compared to many plastic profiles, which often rely on non-renewable fossil fuels and can contribute to microplastic pollution. Natural rubber is biodegradable, reducing environmental impact, whereas plastic profiles, especially those made from PVC or other synthetic polymers, tend to persist in ecosystems. Choosing rubber profiles can significantly reduce carbon footprint and waste accumulation in manufacturing and end-of-life disposal processes.
Choosing the Right Profile for Your Needs
Rubber profiles offer superior flexibility, durability, and resistance to extreme temperatures, making them ideal for sealing and vibration absorption in automotive and industrial applications. Plastic profiles provide lightweight, cost-effective solutions with excellent corrosion resistance and are suited for aesthetic trims and protective edging. Understanding the specific environmental conditions and mechanical requirements is crucial when choosing between rubber and plastic profiles to ensure optimal performance and longevity.
Rubber Profile vs Plastic Profile Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com