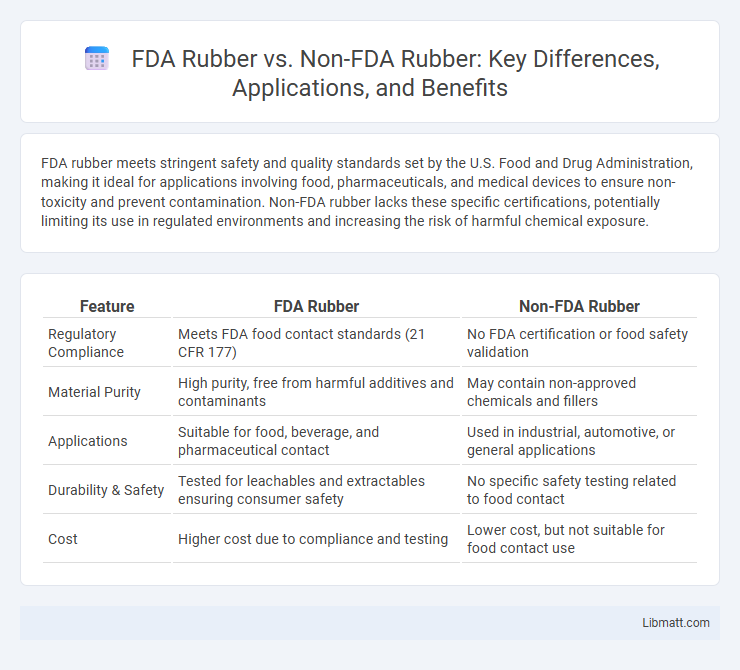
FDA rubber meets stringent safety and quality standards set by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration, making it ideal for applications involving food, pharmaceuticals, and medical devices to ensure non-toxicity and prevent contamination. Non-FDA rubber lacks these specific certifications, potentially limiting its use in regulated environments and increasing the risk of harmful chemical exposure.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | FDA Rubber | Non-FDA Rubber |
|---|---|---|
| Regulatory Compliance | Meets FDA food contact standards (21 CFR 177) | No FDA certification or food safety validation |
| Material Purity | High purity, free from harmful additives and contaminants | May contain non-approved chemicals and fillers |
| Applications | Suitable for food, beverage, and pharmaceutical contact | Used in industrial, automotive, or general applications |
| Durability & Safety | Tested for leachables and extractables ensuring consumer safety | No specific safety testing related to food contact |
| Cost | Higher cost due to compliance and testing | Lower cost, but not suitable for food contact use |
Introduction to FDA Rubber vs Non-FDA Rubber
FDA rubber complies with strict regulations set by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration to ensure safety for food and medical applications, emphasizing non-toxicity and resistance to chemical leaching. Non-FDA rubber may lack these certifications and could contain additives or contaminants unsuitable for direct contact with consumables. Understanding these differences is crucial for industries requiring materials that meet health and safety standards.
What is FDA Rubber?
FDA Rubber refers to rubber materials that meet the strict safety and quality standards established by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration, ensuring they are safe for use in food, beverage, and pharmaceutical applications. These rubbers are free from harmful chemicals and contaminants that could leach into products during contact. Your choice of FDA-approved rubber guarantees compliance with regulatory requirements and protection of consumer health.
What is Non-FDA Rubber?
Non-FDA rubber refers to rubber materials that have not been certified or approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration for use in food, medical, or pharmaceutical applications. These rubbers may contain additives or contaminants that do not meet FDA safety standards, making them unsuitable for direct contact with consumables or sensitive environments. When selecting materials for your product, understanding the distinction between FDA and non-FDA rubber ensures compliance and safety in critical applications.
Key Differences Between FDA and Non-FDA Rubber
FDA rubber complies with stringent U.S. Food and Drug Administration regulations ensuring it is safe for direct food and medical contact, while non-FDA rubber lacks these certifications and may contain harmful chemicals unsuitable for such applications. The key differences include FDA rubber's enhanced purity, resistance to contaminants, and ability to maintain integrity under sterilization processes. Your choice of FDA rubber guarantees compliance with health standards essential for consumer safety, unlike non-FDA rubber which is typically used in industrial or non-food-related contexts.
Applications of FDA Rubber
FDA rubber is specifically formulated to meet the strict safety and hygiene standards set by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration, making it ideal for applications in the food, beverage, and pharmaceutical industries where contamination must be avoided. This type of rubber is commonly used for seals, gaskets, tubing, and hoses that come into direct contact with consumable products, ensuring compliance with health regulations and maintaining product integrity. Your equipment benefits from FDA rubber by reducing the risk of chemical leaching and supporting sanitary processing environments.
Common Uses for Non-FDA Rubber
Non-FDA rubber is commonly used in industrial applications where direct contact with food or pharmaceuticals is not required, such as automotive seals, gaskets, and machinery components. It is favored for its flexibility, durability, and cost-effectiveness in manufacturing products like hoses, conveyor belts, and vibration dampening parts. Unlike FDA-approved rubber, non-FDA variants do not meet stringent safety standards needed for medical or food-grade environments, limiting their use to non-consumable or external applications.
Regulatory Standards and Compliance
FDA rubber complies with strict FDA regulatory standards ensuring it is safe for food and medical applications, meeting criteria for biocompatibility, chemical resistance, and non-toxicity. Non-FDA rubber may not adhere to these stringent regulations, potentially posing risks in sensitive uses due to unknown additives or contaminants. Your choice of FDA-approved rubber guarantees compliance with federal guidelines, reducing liability and ensuring product safety.
Material Properties Comparison
FDA rubber complies with stringent Food and Drug Administration regulations ensuring biocompatibility, chemical resistance, and non-toxicity, making it ideal for food-grade and medical applications. Non-FDA rubber lacks these certified material properties, often showing variable chemical resistance and potential for leachable harmful substances. The key differences lie in FDA rubber's ability to withstand high temperatures, resist oils, acids, and alkalis, and maintain physical stability, whereas non-FDA rubber may degrade or contaminate products under similar conditions.
Choosing the Right Rubber for Your Application
Selecting the right rubber for your application requires understanding the differences between FDA-approved rubber and non-FDA rubber materials. FDA rubber complies with strict regulations for safety and hygiene, making it ideal for food, pharmaceutical, and medical applications where contamination risks must be minimized. Non-FDA rubber may offer cost or performance benefits but lacks certification for direct contact with consumables, limiting its use in regulated industries.
Conclusion: FDA vs Non-FDA Rubber
FDA rubber meets stringent safety and biocompatibility standards, making it suitable for food, pharmaceutical, and medical applications where regulatory compliance is critical. Non-FDA rubber may offer cost benefits and diverse material properties but lacks certification for direct contact with sensitive substances. Choosing FDA rubber ensures adherence to health regulations and minimizes risk in contamination-sensitive environments.
FDA Rubber vs Non-FDA Rubber Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com