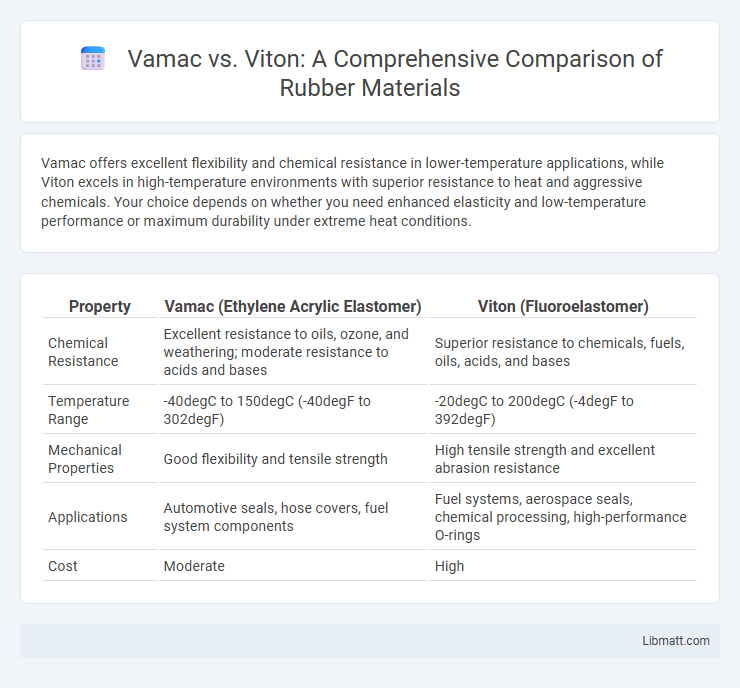
Vamac offers excellent flexibility and chemical resistance in lower-temperature applications, while Viton excels in high-temperature environments with superior resistance to heat and aggressive chemicals. Your choice depends on whether you need enhanced elasticity and low-temperature performance or maximum durability under extreme heat conditions.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Vamac (Ethylene Acrylic Elastomer) | Viton (Fluoroelastomer) |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent resistance to oils, ozone, and weathering; moderate resistance to acids and bases | Superior resistance to chemicals, fuels, oils, acids, and bases |
| Temperature Range | -40degC to 150degC (-40degF to 302degF) | -20degC to 200degC (-4degF to 392degF) |
| Mechanical Properties | Good flexibility and tensile strength | High tensile strength and excellent abrasion resistance |
| Applications | Automotive seals, hose covers, fuel system components | Fuel systems, aerospace seals, chemical processing, high-performance O-rings |
| Cost | Moderate | High |
Introduction to Vamac and Viton
Vamac and Viton are high-performance elastomers widely used in industries requiring exceptional chemical and thermal resistance. Vamac, an ethylene acrylic rubber (AEM), excels in ozone, weather, and heat resistance, making it ideal for automotive and industrial applications. Viton, a fluoroelastomer (FKM), offers superior chemical resistance and is often chosen for sealing solutions in harsh chemical environments, ensuring long-lasting durability for your equipment.
Chemical Composition and Structure
Vamac is an ethylene acrylic elastomer composed primarily of ethylene and acrylic acid or its derivatives, featuring a polar acrylic component that enhances oil and chemical resistance. Viton, a brand of fluoroelastomer, consists mainly of vinylidene fluoride and hexafluoropropylene monomers, providing a highly fluorinated polymer backbone that delivers superior heat and chemical durability. The key structural distinction lies in Vamac's acrylic polarity versus Viton's fluorocarbon chains, influencing their respective compatibility and performance in harsh chemical environments.
Key Properties Comparison
Vamac elastomers offer superior flexibility and excellent resistance to ozone, weathering, and polar solvents, making them ideal for automotive and electrical applications. Viton fluoroelastomers exhibit exceptional chemical resistance, high-temperature stability up to 200degC, and outstanding resistance to fuels, oils, and aggressive chemicals. While Viton outperforms Vamac in thermal and chemical resistance, Vamac provides better elasticity and resistance to polar solvents, defining distinct use-case advantages for each material.
Performance in Extreme Temperatures
Vamac elastomers maintain flexibility and compression set resistance in temperatures ranging from -40degC to 150degC, making them ideal for dynamic sealing in automotive and industrial applications. Viton fluoroelastomers exhibit superior performance at high temperatures up to 250degC and exceptional chemical resistance, suitable for harsh environments like aerospace and chemical processing. Vamac performs better in low-temperature flexibility while Viton excels in extreme heat and chemical exposure.
Resistance to Chemicals and Fluids
Vamac delivers superior resistance to a broad range of chemicals, including aliphatic hydrocarbons, ketones, and esters, making it ideal for applications exposed to aggressive solvents. Viton excels in resisting aromatic and chlorinated hydrocarbons, as well as high-temperature fluids like hydraulic oils and fuels, ensuring durability in harsh industrial environments. Your choice between Vamac and Viton should consider the specific chemical exposure and fluid compatibility requirements to optimize performance and longevity.
Durability and Longevity
Vamac and Viton are fluoropolymer elastomers known for exceptional durability and longevity in harsh environments. Vamac offers superior flexibility and resistance to mechanical fatigue, making it ideal for applications with dynamic stresses. Viton excels in chemical resistance and high-temperature stability, providing long-lasting performance in aggressive chemical and thermal conditions.
Typical Industrial Applications
Vamac and Viton are fluoroelastomers widely used for sealing and gasket applications in the automotive, chemical processing, and aerospace industries. Vamac excels in environments requiring excellent flexibility and resistance to ozone, weathering, and fuels, often found in fuel system components and air conditioning seals. Viton's superior chemical resistance and high-temperature stability make it ideal for oil seals, O-rings, and gaskets in harsh chemical environments and high-performance engines, ensuring your equipment operates reliably under demanding conditions.
Cost and Availability
Vamac elastomers generally cost less than Viton due to simpler manufacturing processes and more abundant raw materials, making them a budget-friendly choice for various applications. Availability of Vamac is relatively widespread but more limited compared to Viton, which benefits from extensive global distribution and multiple supplier networks. Your decision between Vamac and Viton should consider both cost sensitivity and regional access to ensure timely procurement.
Environmental and Safety Considerations
Vamac offers superior environmental resilience with lower emissions of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) compared to Viton, making it a safer option for applications requiring strict air quality compliance. Viton, while excellent in chemical resistance and high-temperature performance, can release hazardous fumes when exposed to extreme heat or burning, necessitating careful handling and disposal. Your choice between Vamac and Viton should consider the specific environmental regulations and safety standards relevant to your industry to ensure compliance and workplace safety.
Choosing Between Vamac and Viton
Choosing between Vamac and Viton depends on your application's chemical resistance and temperature requirements; Vamac excels in flex resistance and performance in hot, humid environments, while Viton offers superior resistance to extreme temperatures and aggressive chemicals. Vamac is ideal for environments with exposure to acids, alcohols, and ketones, whereas Viton is preferred for fuel systems, automotive, and aerospace applications due to its exceptional resistance to hydrocarbons and high heat. Evaluate the specific exposure conditions and mechanical demands to determine which elastomer best suits your needs for durability and longevity.
Vamac vs Viton Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com