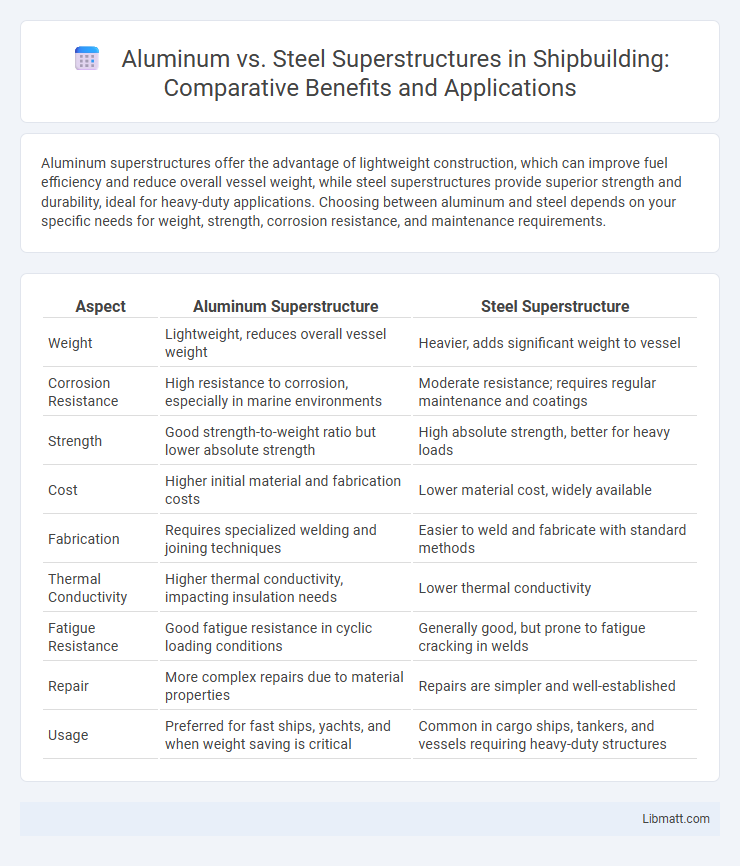
Aluminum superstructures offer the advantage of lightweight construction, which can improve fuel efficiency and reduce overall vessel weight, while steel superstructures provide superior strength and durability, ideal for heavy-duty applications. Choosing between aluminum and steel depends on your specific needs for weight, strength, corrosion resistance, and maintenance requirements.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Aluminum Superstructure | Steel Superstructure |
|---|---|---|
| Weight | Lightweight, reduces overall vessel weight | Heavier, adds significant weight to vessel |
| Corrosion Resistance | High resistance to corrosion, especially in marine environments | Moderate resistance; requires regular maintenance and coatings |
| Strength | Good strength-to-weight ratio but lower absolute strength | High absolute strength, better for heavy loads |
| Cost | Higher initial material and fabrication costs | Lower material cost, widely available |
| Fabrication | Requires specialized welding and joining techniques | Easier to weld and fabricate with standard methods |
| Thermal Conductivity | Higher thermal conductivity, impacting insulation needs | Lower thermal conductivity |
| Fatigue Resistance | Good fatigue resistance in cyclic loading conditions | Generally good, but prone to fatigue cracking in welds |
| Repair | More complex repairs due to material properties | Repairs are simpler and well-established |
| Usage | Preferred for fast ships, yachts, and when weight saving is critical | Common in cargo ships, tankers, and vessels requiring heavy-duty structures |
Introduction to Ship Superstructures
Aluminum superstructures offer significant weight reduction compared to traditional steel, enhancing vessel speed and fuel efficiency in ship design. Steel superstructures provide superior strength and durability, ideal for heavy-duty maritime applications requiring enhanced impact resistance. Your choice between aluminum and steel impacts overall vessel performance, maintenance costs, and operational lifespan.
Key Material Properties: Aluminum vs Steel
Aluminum superstructures offer a lightweight advantage with a density approximately one-third that of steel, resulting in easier handling and reduced overall weight of the structure. Steel superstructures provide superior tensile strength and higher modulus of elasticity, making them ideal for applications requiring greater load-bearing capacity and rigidity. Your choice between aluminum and steel should consider corrosion resistance, as aluminum naturally forms a protective oxide layer, while steel often requires coatings or treatments to prevent rusting in harsh environments.
Weight Comparison and Its Impacts
Aluminum superstructures weigh significantly less than steel superstructures, often reducing the overall weight by up to 50%, which enhances fuel efficiency and increases payload capacity in transportation and construction applications. The lower density of aluminum leads to easier handling and faster assembly, cutting labor costs and project timelines. Your choice of aluminum can improve structural performance without compromising strength, making it ideal for weight-sensitive projects.
Corrosion Resistance and Durability
Aluminum superstructures offer superior corrosion resistance compared to steel, as aluminum forms a protective oxide layer that prevents further oxidation, making it ideal for marine and coastal applications. Steel superstructures require specialized coatings and regular maintenance to avoid rust and corrosion, which can compromise structural integrity over time. Aluminum's inherent durability in harsh environments enhances longevity, reducing long-term repair costs and ensuring sustained performance in corrosive conditions.
Structural Strength and Safety Considerations
Aluminum superstructures offer a high strength-to-weight ratio, reducing overall building load while maintaining structural integrity, but steel superstructures provide superior tensile strength and durability under heavy loads and extreme conditions. Safety considerations favor steel in scenarios requiring high impact resistance and fire resistance, as steel maintains performance at higher temperatures compared to aluminum. Your choice between aluminum and steel superstructures should account for specific project demands, including load requirements, environmental exposure, and safety codes.
Construction and Fabrication Differences
Aluminum superstructures offer significant weight reduction compared to steel, facilitating easier handling and faster installation during construction. Fabrication of aluminum requires specialized welding techniques such as TIG welding to manage its thermal conductivity and prevent warping, whereas steel fabrication benefits from more traditional methods like MIG welding and bolting. The corrosion resistance of aluminum reduces the need for extensive protective coatings, while steel structures often require galvanization or painting to enhance durability.
Maintenance Requirements and Lifecycle Costs
Aluminum superstructures require less frequent maintenance due to their inherent corrosion resistance, significantly reducing costs associated with surface treatment and repairs over time. Steel superstructures demand regular inspections, painting, and protection against rust, which can escalate lifecycle expenses despite steel's initial lower material cost. The total lifecycle cost of aluminum tends to be lower in corrosive environments, balancing higher upfront investment with savings from reduced upkeep and extended service life.
Fire Resistance and Thermal Properties
Aluminum superstructures offer lower fire resistance compared to steel due to aluminum's lower melting point, which can compromise structural integrity under high temperatures. Steel superstructures excel in fire resistance, maintaining strength longer during a fire, often enhanced by fireproof coatings or insulation treatments. Your choice between aluminum and steel should consider the specific fire safety requirements and thermal performance of your building project.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Aluminum superstructures offer superior corrosion resistance and are highly recyclable, reducing environmental impact through lower maintenance and longer lifespan compared to steel. Steel superstructures, while durable and strong, require substantial energy for production and generate higher carbon emissions, though advances in recycling and manufacturing efficiency improve their sustainability. Both materials contribute to sustainable construction depending on lifecycle assessment, with aluminum favored for lightweight, corrosion-resistant applications and steel dominating heavy-load structural roles.
Application Scenarios: Choosing the Right Material
Aluminum superstructures are ideal for applications requiring lightweight construction, such as marine vessels, aerospace, and transport vehicles, where reducing overall weight enhances fuel efficiency and performance. Steel superstructures excel in heavy-duty construction projects like high-rise buildings, bridges, and industrial facilities, providing superior strength, durability, and resistance to impact. Selecting between aluminum and steel depends on factors like load-bearing requirements, environmental conditions, and cost-efficiency tailored to the specific application scenario.
Aluminum superstructure vs steel superstructure Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com