Marine HVAC systems are specifically designed to withstand harsh saltwater environments and limited space aboard ships, ensuring optimal air quality and temperature control in confined, motion-prone settings. Industrial HVAC systems focus on managing large-scale heating, ventilation, and cooling needs in factories or warehouses, prioritizing durability, energy efficiency, and precise climate control for varied industrial processes.
Table of Comparison
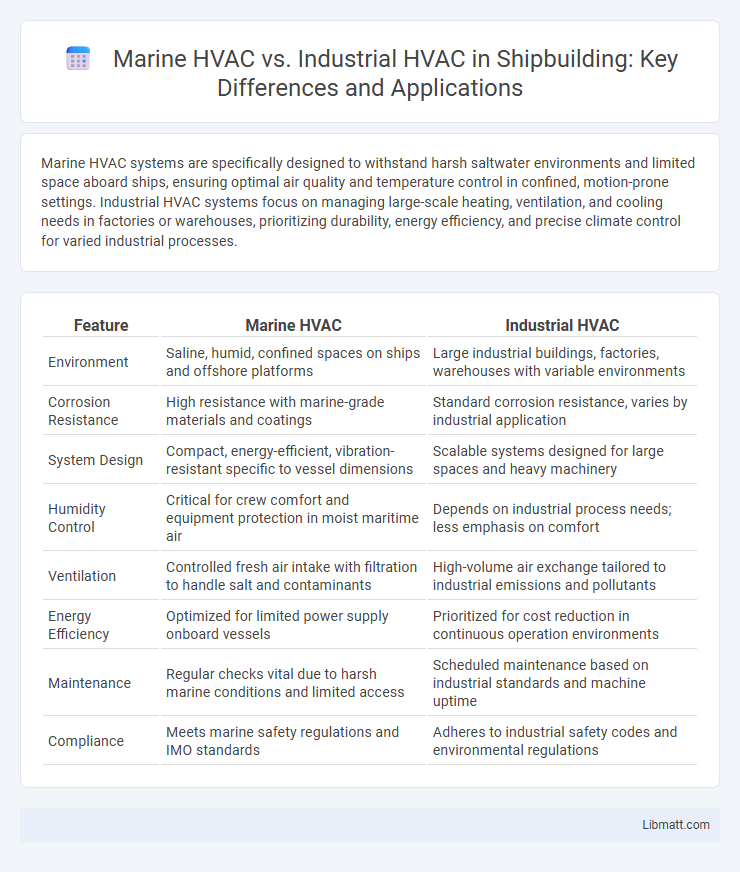
| Feature | Marine HVAC | Industrial HVAC |
|---|---|---|
| Environment | Saline, humid, confined spaces on ships and offshore platforms | Large industrial buildings, factories, warehouses with variable environments |
| Corrosion Resistance | High resistance with marine-grade materials and coatings | Standard corrosion resistance, varies by industrial application |
| System Design | Compact, energy-efficient, vibration-resistant specific to vessel dimensions | Scalable systems designed for large spaces and heavy machinery |
| Humidity Control | Critical for crew comfort and equipment protection in moist maritime air | Depends on industrial process needs; less emphasis on comfort |
| Ventilation | Controlled fresh air intake with filtration to handle salt and contaminants | High-volume air exchange tailored to industrial emissions and pollutants |
| Energy Efficiency | Optimized for limited power supply onboard vessels | Prioritized for cost reduction in continuous operation environments |
| Maintenance | Regular checks vital due to harsh marine conditions and limited access | Scheduled maintenance based on industrial standards and machine uptime |
| Compliance | Meets marine safety regulations and IMO standards | Adheres to industrial safety codes and environmental regulations |
Introduction to Marine HVAC and Industrial HVAC
Marine HVAC systems are specifically engineered to withstand harsh maritime environments, offering corrosion resistance, compact design, and energy efficiency for ships, yachts, and offshore platforms. Industrial HVAC systems prioritize robust performance, scalability, and precise climate control for large manufacturing facilities, warehouses, and processing plants. Both systems incorporate advanced filtration, temperature regulation, and ventilation technologies tailored to their unique operational demands.
Key Differences Between Marine and Industrial HVAC
Marine HVAC systems are specifically designed to withstand harsh saltwater environments, high humidity, and vibration, whereas industrial HVAC focuses on large-scale climate control within factories and warehouses. Marine HVAC units prioritize corrosion resistance and compact design for tight spaces on vessels, while industrial HVAC emphasizes airflow volume and temperature regulation in expansive areas. Your choice depends on whether you need specialized maritime durability or robust industrial capacity.
Environmental Challenges in Marine vs. Industrial Settings
Marine HVAC systems face unique environmental challenges such as high humidity, salt corrosion, and constant exposure to seawater, which demand robust corrosion-resistant materials and specialized filtration. Industrial HVAC systems must handle harsh airborne contaminants, extreme temperatures, and large-scale air quality control to protect sensitive machinery and worker health. Your choice between marine and industrial HVAC should consider these environmental factors to ensure optimal performance and system longevity.
System Design and Engineering Considerations
Marine HVAC systems require compact, corrosion-resistant components and must withstand harsh saltwater environments, prioritizing space optimization and energy efficiency. Industrial HVAC systems focus on scalability, high-capacity air handling, and integration with heavy machinery, emphasizing durability and precise climate control in large, open spaces. Both systems demand specialized engineering to address unique operational challenges, including vibration isolation on marine vessels and robust filtration standards for industrial contaminants.
Energy Efficiency Comparison
Marine HVAC systems are specifically designed to maximize energy efficiency in challenging maritime environments by incorporating advanced heat exchangers and corrosion-resistant materials, which reduce energy consumption compared to standard industrial HVAC units. Industrial HVAC systems often prioritize robust capacity for large-scale facilities but may experience higher energy losses due to less specialized materials and less optimized heat recovery methods. Your choice between marine and industrial HVAC should consider the unique operational conditions and energy-saving technologies tailored to each application to achieve optimal efficiency.
Materials and Corrosion Resistance
Marine HVAC systems use specialized materials like marine-grade stainless steel and corrosion-resistant alloys to withstand harsh saltwater environments and high humidity levels. Industrial HVAC units often incorporate robust, heavy-duty metals and coatings designed for resistance against chemicals, dust, and extreme temperatures typical in manufacturing settings. Your choice between marine and industrial HVAC should consider the specific corrosion challenges and material durability requirements of each environment.
Maintenance and Longevity Requirements
Marine HVAC systems demand specialized maintenance routines to withstand harsh saltwater environments and constant moisture exposure, ensuring corrosion resistance and optimal performance. Industrial HVAC systems prioritize robust durability and continuous operation with maintenance protocols centered on handling heavy-duty usage, contaminant filtration, and thermal efficiency. Regular inspections, timely filter replacements, and tailored servicing schedules extend the longevity of both systems, although marine HVAC requires more frequent anti-corrosion treatments compared to industrial counterparts.
Safety and Regulatory Standards
Marine HVAC systems must comply with stringent maritime safety standards such as SOLAS (Safety of Life at Sea) and ABS (American Bureau of Shipping) regulations to ensure fire protection, ventilation efficiency, and corrosion resistance in harsh saltwater environments. Industrial HVAC systems follow standards defined by organizations like ASHRAE (American Society of Heating, Refrigerating and Air-Conditioning Engineers) and OSHA (Occupational Safety and Health Administration), prioritizing workplace safety, air quality, and energy efficiency within factories or warehouses. The regulatory frameworks differ significantly, with marine HVAC focused on survival and emergency scenarios, while industrial HVAC emphasizes occupational health and environmental compliance.
Cost Factors and Budgeting
Marine HVAC systems typically incur higher costs than industrial HVAC due to specialized corrosion-resistant materials, compact design requirements, and stringent safety standards for maritime environments. Budgeting for marine HVAC must account for installation complexity in confined ship spaces and ongoing maintenance to withstand saltwater exposure. Industrial HVAC costs vary widely based on factory size, ventilation needs, and energy consumption, often allowing for economies of scale but requiring substantial upfront investment in durable, high-capacity equipment.
Choosing the Right HVAC System for Your Application
Selecting the right HVAC system depends on the environment and operational requirements; marine HVAC systems are specifically designed to withstand harsh saltwater corrosion, high humidity, and compact spaces on ships or offshore platforms. Industrial HVAC systems prioritize large-scale air quality control, temperature regulation, and energy efficiency for manufacturing plants, warehouses, or factories. Evaluating factors such as exposure to corrosive elements, space constraints, airflow needs, and regulatory compliance ensures optimal performance and durability in the chosen HVAC solution.
Marine HVAC vs industrial HVAC Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com