Piping insulation specifically focuses on wrapping pipes to prevent heat loss or gain, reduce condensation, and improve energy efficiency in plumbing and HVAC systems. Thermal insulation, a broader category, applies to various surfaces and materials to maintain temperature control, enhance energy savings, and provide comfort in buildings and industrial applications.
Table of Comparison
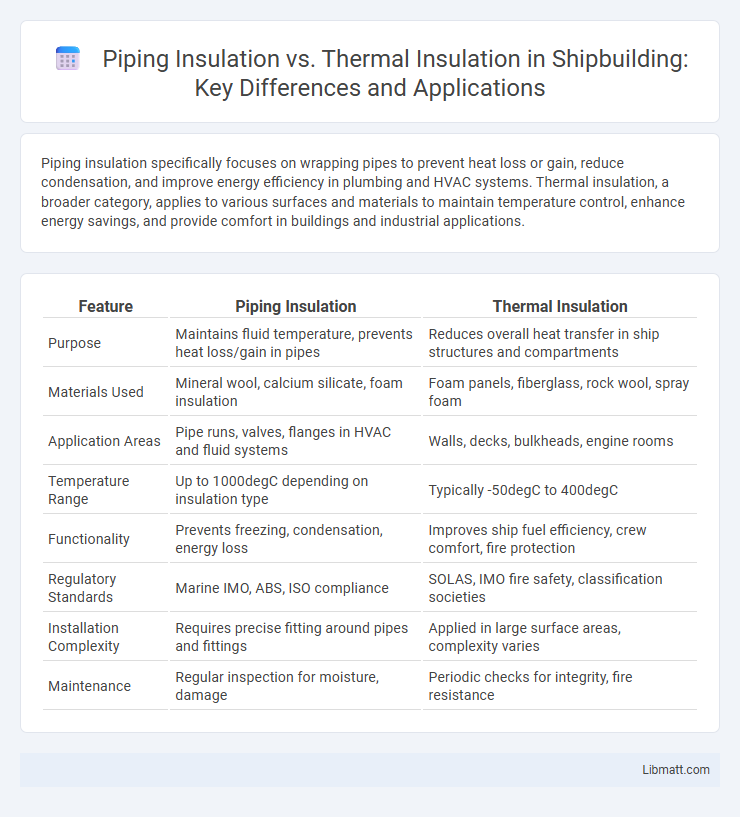
| Feature | Piping Insulation | Thermal Insulation |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Maintains fluid temperature, prevents heat loss/gain in pipes | Reduces overall heat transfer in ship structures and compartments |
| Materials Used | Mineral wool, calcium silicate, foam insulation | Foam panels, fiberglass, rock wool, spray foam |
| Application Areas | Pipe runs, valves, flanges in HVAC and fluid systems | Walls, decks, bulkheads, engine rooms |
| Temperature Range | Up to 1000degC depending on insulation type | Typically -50degC to 400degC |
| Functionality | Prevents freezing, condensation, energy loss | Improves ship fuel efficiency, crew comfort, fire protection |
| Regulatory Standards | Marine IMO, ABS, ISO compliance | SOLAS, IMO fire safety, classification societies |
| Installation Complexity | Requires precise fitting around pipes and fittings | Applied in large surface areas, complexity varies |
| Maintenance | Regular inspection for moisture, damage | Periodic checks for integrity, fire resistance |
Introduction to Piping Insulation vs Thermal Insulation
Piping insulation primarily focuses on reducing heat loss or gain in pipes to improve energy efficiency and prevent condensation, while thermal insulation broadly encompasses materials and methods used to control heat transfer in various building components. Piping insulation materials are selected based on pipe temperature, environment, and durability, often including foam, fiberglass, or mineral wool. Thermal insulation, on the other hand, applies to walls, roofs, and floors, utilizing materials like rigid foam boards, spray foam, or reflective barriers to optimize overall energy performance.
Defining Piping Insulation
Piping insulation specifically refers to materials applied around pipes to reduce heat loss or gain, prevent condensation, and protect against freezing temperatures. It enhances energy efficiency by maintaining the desired temperature of fluids transported through the pipes, improving system performance. Unlike general thermal insulation used in buildings or machinery, piping insulation is tailored for cylindrical surfaces and often addresses factors like moisture resistance and ease of installation.
Understanding Thermal Insulation
Thermal insulation reduces heat transfer in piping systems, maintaining temperature control and energy efficiency by using materials like fiberglass, mineral wool, and foam. Piping insulation specifically protects pipes from temperature fluctuations, condensation, and freezing, optimizing system performance and safety. Selecting appropriate insulation enhances thermal resistance (R-value), minimizes energy loss, and prolongs equipment lifespan in industrial and residential applications.
Key Differences Between Piping and Thermal Insulation
Piping insulation primarily focuses on preventing heat loss or gain in pipes to maintain fluid temperatures, reduce energy costs, and avoid condensation, while thermal insulation broadly targets minimizing heat transfer in buildings or industrial equipment. Materials used for piping insulation, such as fiberglass, foam, or mineral wool, are selected for their resistance to moisture, temperature range, and mechanical durability, whereas thermal insulation can include a wider variety of materials like reflective barriers and insulated panels. Understanding these key differences helps you choose the right insulation method to improve system efficiency and protect assets effectively.
Materials Used in Piping Insulation
Piping insulation primarily uses materials such as fiberglass, mineral wool, foam rubber, and polyurethane foam, designed to reduce heat loss and prevent condensation on pipes. These materials offer varying levels of thermal conductivity, durability, and resistance to moisture, making them suitable for different temperature ranges and environments. Your choice of piping insulation material impacts energy efficiency and system longevity, highlighting the importance of selecting the right option for your specific application.
Materials Used in General Thermal Insulation
Thermal insulation materials commonly include fiberglass, mineral wool, foam boards, and spray foam, designed to reduce heat transfer in various applications. Piping insulation specifically uses materials such as foam rubber, fiberglass sleeves, and polyethylene to prevent heat loss or gain along pipes, ensuring energy efficiency and system protection. Your choice of insulation material impacts thermal performance, durability, and suitability for temperature ranges in your project.
Applications of Piping Insulation
Piping insulation primarily serves to reduce heat loss or gain in fluid transport systems, ensuring energy efficiency and preventing condensation or freezing in industrial and residential applications. It is essential in sectors such as HVAC, oil and gas, chemical processing, and power generation, where maintaining temperature control within pipelines enhances system performance and safety. Your choice of piping insulation can significantly impact operational costs and compliance with energy regulations.
Applications of Thermal Insulation
Thermal insulation is widely applied in buildings, industrial equipment, and HVAC systems to reduce heat transfer and improve energy efficiency. It helps maintain desired temperatures, protect surfaces from extreme temperatures, and prevent condensation, making it essential for both residential and commercial thermal management. Your choice of thermal insulation materials and applications directly impacts energy savings and comfort.
Benefits and Challenges of Piping Insulation
Piping insulation improves energy efficiency by reducing heat loss and preventing condensation, which helps maintain fluid temperatures and lowers operational costs. It also protects personnel from hot surface burns and minimizes environmental impact through reduced energy consumption. Challenges include ensuring proper material selection for diverse pipe sizes and temperatures, managing installation complexities, and addressing insulation degradation over time due to moisture or mechanical damage.
Choosing the Right Insulation Solution for Your Needs
Piping insulation specifically targets heat retention or prevention of heat loss in pipes, reducing energy costs and protecting against freezing, while thermal insulation broadly covers materials that manage heat flow in various applications, including walls, roofs, and HVAC systems. Choosing the right insulation solution requires assessing factors like temperature range, moisture resistance, and installation environment to ensure optimal energy efficiency and durability. Your choice should align with specific operational needs and regulatory standards to maximize performance and cost-effectiveness.
Piping insulation vs thermal insulation Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com