Cargo holds are compartments on ships designed to store and transport goods securely, while ballast tanks are specialized spaces used to control the vessel's stability by managing water weight. Understanding the distinct roles of cargo holds and ballast tanks ensures optimal ship performance and safety.
Table of Comparison
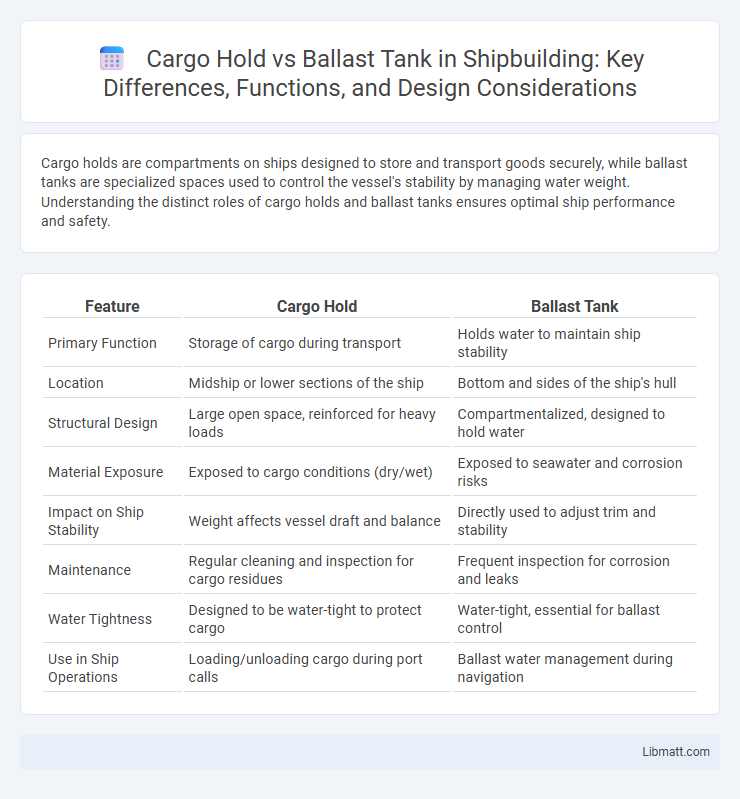
| Feature | Cargo Hold | Ballast Tank |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Function | Storage of cargo during transport | Holds water to maintain ship stability |
| Location | Midship or lower sections of the ship | Bottom and sides of the ship's hull |
| Structural Design | Large open space, reinforced for heavy loads | Compartmentalized, designed to hold water |
| Material Exposure | Exposed to cargo conditions (dry/wet) | Exposed to seawater and corrosion risks |
| Impact on Ship Stability | Weight affects vessel draft and balance | Directly used to adjust trim and stability |
| Maintenance | Regular cleaning and inspection for cargo residues | Frequent inspection for corrosion and leaks |
| Water Tightness | Designed to be water-tight to protect cargo | Water-tight, essential for ballast control |
| Use in Ship Operations | Loading/unloading cargo during port calls | Ballast water management during navigation |
Introduction to Cargo Holds and Ballast Tanks
Cargo holds are large, enclosed spaces within a ship designed to store and transport various types of cargo securely. Ballast tanks, on the other hand, are compartments that fill with water or air to stabilize and balance the vessel during voyages. Understanding the distinct roles of cargo holds and ballast tanks is essential for managing your ship's safety and operational efficiency.
Core Functions: Cargo Storage vs. Stability Control
Cargo holds are designed primarily for safely storing and transporting goods, providing a controlled environment to protect cargo from damage and environmental factors. Ballast tanks are integral to a ship's stability system, managing weight distribution by filling with water to balance the vessel during various operational conditions. Effective coordination between cargo holds and ballast tanks ensures optimal ship stability and safety throughout the voyage.
Structural Design Differences
Cargo holds are designed with reinforced steel frameworks and flat, open spaces to accommodate heavy loads and ensure maximum storage capacity, featuring robust bulkheads and floors to withstand concentrated stresses from cargo weight. Ballast tanks incorporate curved, watertight compartments integrated into the ship's hull structure, optimized for fluid containment and pressure distribution, with corrosion-resistant linings and specialized coatings to prevent damage from seawater. The structural design of cargo holds prioritizes rigidity and load-bearing capacity, whereas ballast tanks emphasize fluid tightness, structural integrity under hydrostatic pressure, and resistance to corrosion.
Materials and Construction Methods
Cargo holds are constructed using high-strength steel with reinforced bulkheads to withstand heavy loads and ensure structural integrity during transport. Ballast tanks utilize corrosion-resistant materials like coated steel or specialized alloys to prevent rust and degradation from seawater exposure. Your choice between these compartments depends on their materials and construction methods tailored for specific maritime functions.
Operational Procedures and Maintenance
Cargo holds require regular cleaning and inspection to prevent contamination and structural damage, with operational procedures emphasizing cargo loading sequences and secure stowage to maintain vessel stability. Ballast tanks demand routine inspection for corrosion, sediment buildup, and coating integrity, utilizing procedures that ensure proper ballasting and de-ballasting cycles to optimize trim and draft. Maintenance of ballast tanks often involves cathodic protection and timely repainting, while cargo hold upkeep prioritizes ventilation and moisture control to safeguard cargo quality and safety.
Safety Considerations and Regulations
Cargo holds and ballast tanks have distinct safety considerations governed by international regulations such as SOLAS and MARPOL. Cargo holds require strict ventilation and fire prevention measures to protect against hazardous cargo risks, while ballast tanks must be monitored to prevent structural corrosion and contamination, ensuring environmental safety. Compliance with IMO guidelines mandates regular inspections, proper maintenance, and accurate record-keeping to mitigate potential hazards in both compartments.
Impact on Vessel Performance
Cargo holds and ballast tanks have distinct impacts on vessel performance, with cargo holds primarily affecting load capacity and stability by storing commercial goods, while ballast tanks are crucial for maintaining proper trim, draft, and balance during sailing. Efficient management of ballast tanks enhances fuel efficiency and reduces hull stress, directly influencing vessel speed and maneuverability. Your ship's operational efficiency depends on the optimized interaction between these compartments to maintain safety and maximize performance at sea.
Common Issues and Solutions
Cargo holds often face issues like corrosion, water ingress, and structural damage, which can lead to cargo contamination and compromise vessel integrity. Ballast tanks frequently encounter problems such as corrosion, bacterial growth, and coating failure, affecting stability and polluting ballast water discharge. You can mitigate these challenges by implementing regular inspections, applying advanced protective coatings, and maintaining effective cleaning and monitoring systems.
Environmental Considerations
Cargo holds store goods and materials, potentially leading to contamination risks if hazardous cargo leaks, impacting marine ecosystems. Ballast tanks manage ship stability by holding water, which can introduce invasive species and pollutants into new environments when discharged. Effective environmental management requires strict monitoring of cargo integrity and ballast water treatment systems to minimize ecological damage.
Innovations and Future Trends
Innovations in cargo holds are increasingly focused on modular designs and advanced climate control systems to enhance cargo safety and efficiency during transit. Ballast tanks are evolving with smart sensors and automated monitoring technologies to optimize ship stability and reduce environmental impact. Future trends highlight integrated digital platforms that enable real-time data analytics for both cargo holds and ballast tanks, improving operational decision-making and sustainability in maritime logistics.
Cargo hold vs ballast tank Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com