Shaft alignment focuses on ensuring the drive shaft and motor shaft are precisely aligned to minimize vibration and wear, while propeller alignment specifically adjusts the propeller's position for optimal thrust and fuel efficiency. Your equipment's performance and longevity depend on correct alignment in both areas to avoid mechanical failures and maintain smooth operation.
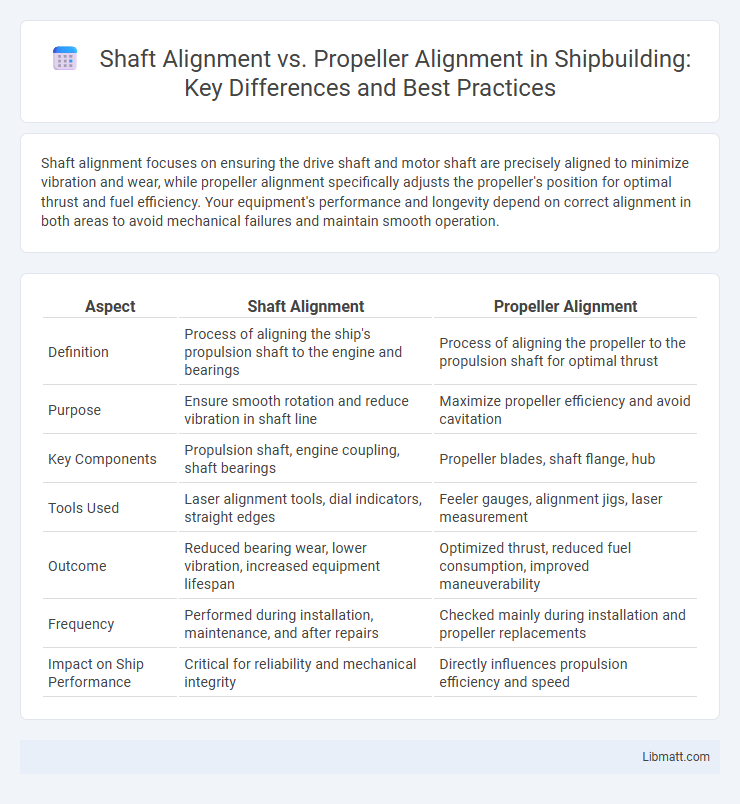
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Shaft Alignment | Propeller Alignment |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Process of aligning the ship's propulsion shaft to the engine and bearings | Process of aligning the propeller to the propulsion shaft for optimal thrust |
| Purpose | Ensure smooth rotation and reduce vibration in shaft line | Maximize propeller efficiency and avoid cavitation |
| Key Components | Propulsion shaft, engine coupling, shaft bearings | Propeller blades, shaft flange, hub |
| Tools Used | Laser alignment tools, dial indicators, straight edges | Feeler gauges, alignment jigs, laser measurement |
| Outcome | Reduced bearing wear, lower vibration, increased equipment lifespan | Optimized thrust, reduced fuel consumption, improved maneuverability |
| Frequency | Performed during installation, maintenance, and after repairs | Checked mainly during installation and propeller replacements |
| Impact on Ship Performance | Critical for reliability and mechanical integrity | Directly influences propulsion efficiency and speed |
Understanding Shaft Alignment: Definition and Importance
Shaft alignment ensures the precise positioning of a rotating shaft relative to another component, minimizing vibrations and mechanical wear. Proper shaft alignment enhances equipment efficiency, extends machinery lifespan, and reduces maintenance costs. It is crucial for avoiding operational failures and maintaining the smooth functioning of mechanical systems such as engines and pumps.
What is Propeller Alignment? Key Concepts Explained
Propeller alignment ensures the propeller shaft and engine output shaft are precisely positioned to minimize vibration and mechanical stress, critical for efficient propulsion systems. Key concepts include axial and angular alignment, tolerances, and the use of laser alignment tools to achieve optimal performance. Proper propeller alignment can enhance your vessel's fuel efficiency and reduce wear on bearings and seals.
Shaft vs. Propeller Alignment: Core Differences
Shaft alignment involves the precise positioning of the engine shaft relative to the driven equipment to minimize vibration and wear. Propeller alignment, however, focuses on adjusting the propeller's angle and position to optimize thrust and performance in marine vessels. Understanding these core differences ensures your machinery runs efficiently, reducing maintenance costs and enhancing operational reliability.
Impact of Shaft Misalignment on Vessel Performance
Shaft misalignment significantly reduces vessel performance by causing increased vibration, noise, and wear on bearings and seals, leading to higher maintenance costs and downtime. Improper shaft alignment can also result in power losses and decreased fuel efficiency, negatively affecting your vessel's operational reliability. Propeller alignment, while critical, primarily ensures optimal thrust and maneuverability, but shaft alignment remains fundamental to preventing mechanical failures and maintaining overall propulsion system health.
Effects of Improper Propeller Alignment
Improper propeller alignment causes vibrations that accelerate wear on shaft bearings and seals, leading to costly maintenance and potential engine failure. Misalignment disrupts thrust distribution, reducing propulsion efficiency and increasing fuel consumption. Over time, these issues result in compromised vessel performance and higher operational risks.
Methods and Tools for Shaft Alignment
Shaft alignment methods include laser alignment, dial indicator measurement, and reverse dial indicator techniques, utilizing tools such as laser alignment systems, dial gauges, and alignment brackets to ensure precise coupling alignment. Propeller alignment primarily involves methods like angular and lateral adjustments using alignment rigs, dial indicators, and slip gauges to position the propeller shaft correctly relative to the hull and engine axis. Your choice of tools and methods depends on the required accuracy and accessibility, with laser alignment systems offering enhanced precision for shaft alignment in marine propulsion systems.
Techniques for Ensuring Accurate Propeller Alignment
Techniques for ensuring accurate propeller alignment involve precision measurement tools such as laser alignment systems, dial indicators, and alignment jigs to minimize shaft misalignment and vibration. Regular use of these tools during installation and maintenance helps maintain optimal performance and prevent premature wear of bearings and couplings. You can achieve better fuel efficiency and reduce mechanical failures by prioritizing precise propeller alignment over just shaft alignment.
Common Alignment Challenges and How to Overcome Them
Shaft alignment and propeller alignment both face challenges such as misalignment due to vibration, thermal expansion, and installation errors that can lead to increased wear and reduced efficiency. Accurate measurement tools like laser alignment systems and regular maintenance schedules help detect and correct these issues before they cause significant damage. Proper alignment ensures optimal performance and extends the lifespan of your marine propulsion system.
Maintenance Best Practices: Shaft and Propeller Alignment
Regular maintenance of shaft and propeller alignment is critical for optimizing marine vessel performance and preventing costly damage. Precision tools such as laser alignment systems and dial indicators ensure accurate measurement of misalignment to reduce vibrations, wear on bearings, and fuel consumption. Implementing routine inspections and corrective adjustments prolongs equipment lifespan and enhances overall operational efficiency.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Alignment for Optimal Efficiency
Selecting the appropriate alignment method, whether shaft alignment or propeller alignment, directly impacts marine propulsion efficiency and reduces mechanical wear. Shaft alignment ensures precise positioning between the engine and propeller shaft for smooth power transmission, while propeller alignment focuses on optimizing the propeller's angle and position to maximize thrust and minimize vibration. Prioritizing the correct alignment based on vessel type and operating conditions enhances overall performance, fuel economy, and longevity of propulsion components.
Shaft alignment vs propeller alignment Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com