Tug assisted berthing relies on external tugboats to maneuver the vessel safely into the berth, providing strong, controlled pushing or pulling forces, especially useful in challenging weather or tight spaces. Thruster assisted berthing uses the ship's own bow and stern thrusters to enhance maneuverability, allowing for more precise and independent docking without needing external support.
Table of Comparison
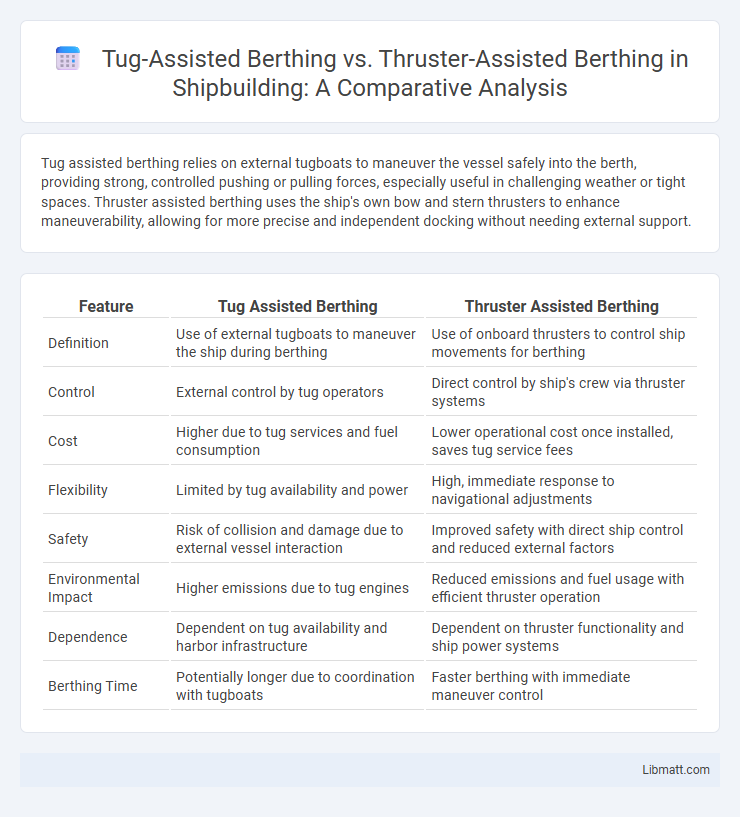
| Feature | Tug Assisted Berthing | Thruster Assisted Berthing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Use of external tugboats to maneuver the ship during berthing | Use of onboard thrusters to control ship movements for berthing |
| Control | External control by tug operators | Direct control by ship's crew via thruster systems |
| Cost | Higher due to tug services and fuel consumption | Lower operational cost once installed, saves tug service fees |
| Flexibility | Limited by tug availability and power | High, immediate response to navigational adjustments |
| Safety | Risk of collision and damage due to external vessel interaction | Improved safety with direct ship control and reduced external factors |
| Environmental Impact | Higher emissions due to tug engines | Reduced emissions and fuel usage with efficient thruster operation |
| Dependence | Dependent on tug availability and harbor infrastructure | Dependent on thruster functionality and ship power systems |
| Berthing Time | Potentially longer due to coordination with tugboats | Faster berthing with immediate maneuver control |
Introduction to Berthing Methods
Tug assisted berthing relies on powerful tugboats to maneuver large vessels safely into dock, offering precise control in challenging conditions like strong currents or limited space. Thruster assisted berthing uses onboard bow and stern thrusters to adjust the vessel's position independently, enhancing maneuverability without external assistance. Your choice between these methods depends on vessel size, port infrastructure, and environmental factors to ensure safe and efficient docking.
Overview of Tug Assisted Berthing
Tug assisted berthing involves the use of powerful tugboats that provide external forces to maneuver vessels safely into docks, especially in confined or congested ports. These tugs offer precise control over a ship's movement, counteracting environmental factors such as wind and currents while enhancing navigation accuracy. Compared to thruster assisted berthing, tugboats provide greater flexibility and force, making them essential for large vessels with limited onboard maneuverability.
Overview of Thruster Assisted Berthing
Thruster assisted berthing utilizes specialized bow and stern thrusters installed on a vessel to maneuver it precisely alongside a berth, enhancing control without external support. This system reduces dependency on tugboats, leading to cost savings and faster berthing operations in confined or busy ports. Your ship gains greater autonomy and safety during docking, especially in challenging wind or current conditions.
Key Differences Between Tug and Thruster Assistance
Tug assisted berthing relies on powerful external vessels maneuvering your ship by pushing or pulling, offering versatility in various weather and port conditions. Thruster assisted berthing uses the ship's own built-in transversal thrusters to move laterally, providing precise control but limited by the vessel's power and environmental constraints. Understanding these key differences helps you choose the optimal assistance method for safe, efficient docking operations.
Advantages of Tug Assisted Berthing
Tug assisted berthing provides enhanced control and maneuverability for large vessels in tight or congested ports, reducing the risk of collisions and grounding. These tugs offer powerful external propulsion and precise positioning, especially beneficial in adverse weather conditions or strong currents where thrusters alone may be insufficient. Your ship benefits from increased safety margins and operational flexibility, as tugboats can adapt to varying vessel sizes and port layouts more effectively than fixed thruster systems.
Advantages of Thruster Assisted Berthing
Thruster assisted berthing offers enhanced maneuverability and precision by utilizing ship-mounted propellers to control vessel movement independently, reducing reliance on external tugboats. This method lowers operational costs and shortens berthing times, improving overall port efficiency and turnaround. Environmental benefits also include decreased emissions and noise pollution compared to traditional tug-assisted approaches.
Operational Considerations for Both Methods
Tug assisted berthing relies on powerful external vessels to maneuver ships safely into the berth, requiring coordination with tug operators and consideration of harbor traffic and weather conditions. Thruster assisted berthing uses a vessel's built-in bow and stern thrusters, providing more direct control but demanding sufficient thruster power and stable vessel systems. Your choice between these methods depends on vessel size, port infrastructure, and operational constraints such as time efficiency and safety protocols.
Cost Implications: Tug vs. Thruster Use
Tug-assisted berthing typically incurs higher operational costs due to fuel consumption, crew wages, and maintenance of tug vessels compared to thruster-assisted berthing, which primarily relies on the ship's onboard propulsion system. However, thruster systems require significant upfront investment and ongoing maintenance expenses, which can offset the savings in certain port environments. Your choice between tug and thruster use should consider the balance of immediate operational costs against long-term capital expenditures and vessel maneuverability.
Environmental and Safety Factors
Tug assisted berthing reduces emissions by using powerful, specialized vessels that minimize fuel consumption during docking maneuvers, enhancing environmental sustainability compared to thruster assisted berthing. Safety is improved with tug assistance as experienced pilots control the vessel's momentum precisely, reducing collision risks and structural damage. Your operation benefits from lower environmental impact and increased docking reliability when prioritizing tug assisted berthing over thruster dependent methods.
Choosing the Right Berthing Solution
Tug assisted berthing provides enhanced maneuverability and control for large vessels in tight or challenging port environments, leveraging powerful external tugboats to guide ships safely to berth. Thruster assisted berthing utilizes ships' built-in bow and stern thrusters for precise, self-powered positioning, ideal for smaller vessels or ports with adequate space and calm conditions. Selecting the optimal berthing method depends on vessel size, port infrastructure, environmental factors, and operational efficiency requirements.
Tug assisted berthing vs thruster assisted berthing Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com