Blow room and carding are crucial steps in the textile manufacturing process where the blow room cleans and opens raw fibers, removing impurities while forming a fiber web. Carding further processes this web by disentangling, aligning, and blending fibers to produce a continuous sliver suitable for spinning, ensuring uniformity and strength in Your final yarn.
Table of Comparison
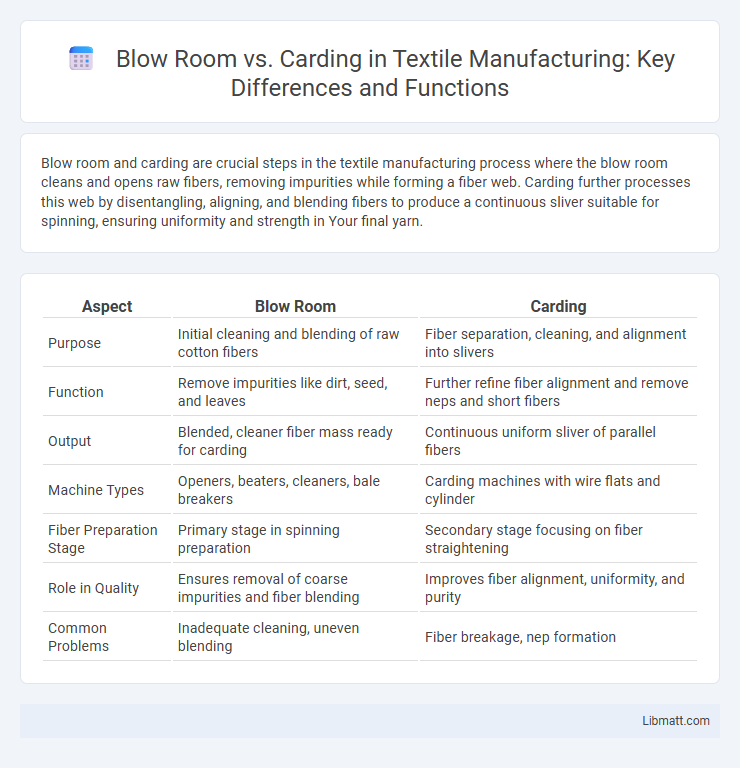
| Aspect | Blow Room | Carding |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Initial cleaning and blending of raw cotton fibers | Fiber separation, cleaning, and alignment into slivers |
| Function | Remove impurities like dirt, seed, and leaves | Further refine fiber alignment and remove neps and short fibers |
| Output | Blended, cleaner fiber mass ready for carding | Continuous uniform sliver of parallel fibers |
| Machine Types | Openers, beaters, cleaners, bale breakers | Carding machines with wire flats and cylinder |
| Fiber Preparation Stage | Primary stage in spinning preparation | Secondary stage focusing on fiber straightening |
| Role in Quality | Ensures removal of coarse impurities and fiber blending | Improves fiber alignment, uniformity, and purity |
| Common Problems | Inadequate cleaning, uneven blending | Fiber breakage, nep formation |
Introduction to Blow Room and Carding
Blow room and carding are crucial processes in textile manufacturing that prepare raw cotton fibers for spinning. The blow room is designed to open, clean, and blend fibers by removing impurities and creating a uniform fiber mass, while carding further aligns fibers by disentangling and forming a continuous web or sliver. Both stages enhance fiber quality and consistency, directly influencing subsequent spinning efficiency and yarn quality.
Key Functions of Blow Room
The blow room is essential in textile processing for opening, cleaning, and blending raw fibers to prepare them for carding. It uses machinery like beaters and airflow systems to remove impurities such as dust and dirt, ensuring fiber quality before further processing. Your fabric production benefits from the blow room's role in enhancing fiber uniformity and cleanliness, which directly impacts the efficiency and effectiveness of the carding stage.
Essential Functions of Carding
Carding is a critical step in textile manufacturing that aligns fibers, removing impurities and creating a uniform web or sliver essential for quality yarn production. Unlike blow room processes that primarily open and clean cotton, carding transforms loose fibers into a continuous fiber sheet, enhancing fiber cohesion and preparing them for subsequent drawing and spinning stages. By ensuring fiber parallelization and removal of neps, carding directly impacts the strength, evenness, and appearance of the final fabric you produce.
Differences in Machinery Involved
Blow room machinery primarily consists of equipment like beaters, cleaners, and pneumatic systems designed to open and clean raw cotton by removing impurities and blending fibers. Carding machines, on the other hand, use a series of rotating cylinders covered with fine wire hooks to disentangle, align, and form a continuous sliver from the cleaned cotton fibers. The key difference lies in blow room machines focusing on fiber preparation and impurity removal, while carding machines specialize in fiber alignment and sliver formation.
Process Flow: Blow Room vs Carding
The blow room process initiates fiber cleaning by opening and blending raw cotton to remove impurities and prepare fibers for further processing. Carding follows by converting the cleaned fibers into a uniform web or sliver, aligning and disentangling them to enhance fiber separation and quality. Your textile production efficiency depends on seamless coordination between the blow room's fiber conditioning and carding's precise fiber alignment.
Impact on Fiber Quality
Blow room processing efficiently removes large contaminants and opens up fiber tufts, enhancing fiber uniformity but can cause slight fiber damage if overused. Carding further refines the fiber by aligning individual fibers and removing finer impurities, significantly improving fiber smoothness and consistency. The combined effect of blow room and carding optimizes fiber quality, balancing cleanliness and fiber integrity for superior yarn strength and appearance.
Role in Contaminant Removal
Blow room and carding processes play distinct roles in contaminant removal during textile manufacturing. The blow room primarily removes large impurities such as dust, dirt, and vegetable matter from raw fibers through opening, cleaning, and blending. Carding follows by further refining the fiber mass, eliminating finer contaminants and neps, ensuring a smoother and cleaner sliver for subsequent processing stages.
Energy Consumption Comparison
Blow room operations consume significantly more energy than carding due to their intensive process of cleaning and opening raw fibers using multiple machines such as beaters and suction systems, which require high power input. Carding typically uses less energy since it focuses on aligning and partially straightening fibers with fewer mechanical components and lower-speed rollers. Energy efficiency in carding improves with modern high-performance equipment, whereas blow room energy consumption largely depends on the capacity and condition of the opening and cleaning machinery.
Maintenance and Operational Challenges
Blow room machinery requires frequent cleaning and filter replacements to prevent fiber contamination and ensure smooth airflow, demanding consistent maintenance schedules. Carding machines face challenges such as regular card wire replacement and careful monitoring of roller settings to avoid fiber damage and maintain uniform sliver quality. Your operational efficiency depends on addressing these specific maintenance needs to minimize downtime and optimize fiber processing.
Conclusion: Selecting the Right Process
Choosing between blow room and carding depends on the specific stage of fiber processing and the desired fiber quality. Blow room optimizes initial cleaning and blending, removing impurities and preparing fibers for further processing, while carding enhances fiber alignment and uniformity, crucial for producing fine yarns. Selecting the right process improves overall textile efficiency, fiber consistency, and final product quality in cotton and synthetic fiber manufacturing.
Blow room vs Carding Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com