Fiber cross section significantly impacts the strength and flexibility of a fiber, with larger cross sections providing greater durability and load-bearing capacity. Fiber length influences the weaving process and final fabric texture, where longer fibers typically result in smoother, stronger textiles perfect for high-quality garments or industrial applications.
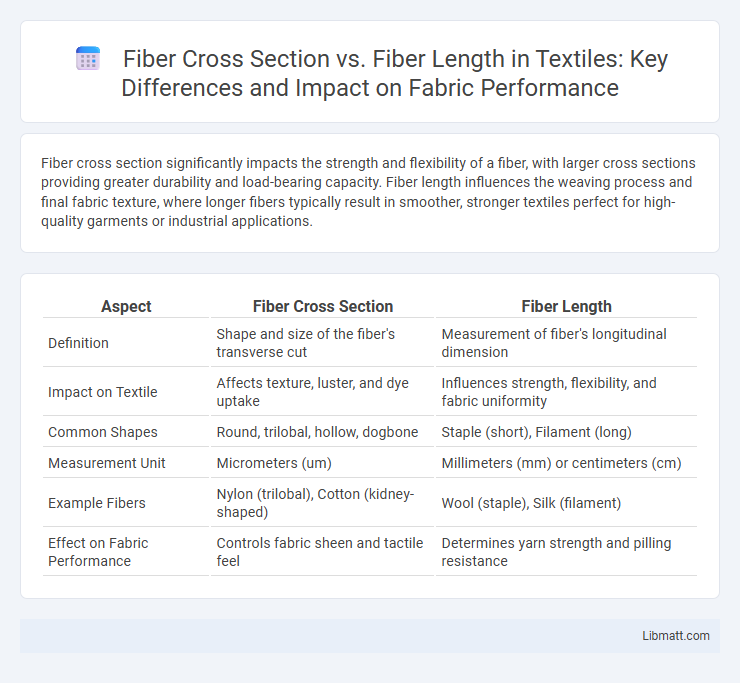
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Fiber Cross Section | Fiber Length |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Shape and size of the fiber's transverse cut | Measurement of fiber's longitudinal dimension |
| Impact on Textile | Affects texture, luster, and dye uptake | Influences strength, flexibility, and fabric uniformity |
| Common Shapes | Round, trilobal, hollow, dogbone | Staple (short), Filament (long) |
| Measurement Unit | Micrometers (um) | Millimeters (mm) or centimeters (cm) |
| Example Fibers | Nylon (trilobal), Cotton (kidney-shaped) | Wool (staple), Silk (filament) |
| Effect on Fabric Performance | Controls fabric sheen and tactile feel | Determines yarn strength and pilling resistance |
Introduction to Fiber Cross Section and Fiber Length
Fiber cross section defines the shape and diameter of an optical fiber's core, which directly impacts light propagation and signal quality. Fiber length determines the distance over which data signals must travel, influencing attenuation and potential signal loss in your network. Understanding both parameters is essential for optimizing fiber optic communication performance and ensuring efficient data transmission.
Defining Fiber Cross Section: Shape and Importance
Fiber cross section refers to the shape and area of a fiber's cut surface, typically circular, oval, or trilobal. This geometric characteristic directly influences the fiber's mechanical strength, flexibility, and light reflection, impacting performance in textiles and composites. Understanding your fiber's cross-sectional shape is crucial for optimizing durability and aesthetic appeal in material applications.
Understanding Fiber Length: Measurement and Types
Fiber length is a critical parameter measured in millimeters or inches, affecting textile strength and fabric quality. It is classified into staple fibers, which are short and measured in inches, and filament fibers, which are continuous and significantly longer. Your choice of fiber length influences spinning processes and the resulting yarn properties.
Influence of Cross Section on Fiber Properties
The cross section of a fiber significantly influences its mechanical properties, including tensile strength, flexibility, and durability. Different cross-sectional shapes, such as circular, trilobal, or hollow, affect the fiber's surface area, light reflection, and moisture absorption, which in turn impact performance characteristics in textiles and composites. Optimizing fiber cross section enables manufacturers to tailor physical attributes for specific applications, enhancing overall material functionality.
Role of Fiber Length in Performance and Processing
Fiber length directly influences the mechanical properties and processability of composite materials, with longer fibers enhancing tensile strength and impact resistance by providing better stress transfer. Shorter fibers facilitate easier processing, improved flow characteristics, and uniform dispersion, making them ideal for injection molding and complex shapes. Understanding your product's performance requirements helps determine the optimal balance between fiber length and cross section for efficient manufacturing and superior end-use properties.
Comparative Impact on Textile Strength and Durability
Fiber cross section significantly influences textile strength by determining the surface area available for bonding and load distribution, with larger or irregular cross sections providing enhanced mechanical interlocking. Fiber length contributes to durability by affecting the yarn's cohesiveness and resistance to wear, where longer fibers promote better fiber alignment and fewer weak points in the fabric. Comparative studies reveal that an optimal balance between fiber cross section and length maximizes tensile strength and prolongs fabric lifespan in various textile applications.
Cross Section vs Length: Effects on Comfort and Feel
A larger fiber cross section generally increases durability but can reduce softness, while finer fibers with smaller cross sections enhance comfort and a smoother feel against your skin. Longer fibers create fewer fiber ends on the fabric surface, reducing pilling and increasing strength, contributing to a more luxurious texture. Balancing fiber cross section and length optimizes both comfort and fabric longevity for superior wearability.
Manufacturing Considerations: Cross Section vs Length
Manufacturing considerations for fiber cross section versus fiber length critically impact performance and cost efficiency in optical fiber production. Larger cross sections often require precise control to maintain uniformity and reduce signal loss over long distances, while longer fibers demand consistent tensile strength and flexibility to prevent breakage during installation. Understanding these variables helps optimize your fiber design for durability and signal integrity in various applications.
Applications Based on Fiber Cross Section and Length
Fiber cross section and fiber length play critical roles in determining the suitability of fibers for various applications. Short fibers with circular cross sections are ideal for reinforcing composites, enhancing mechanical strength in automotive and aerospace industries, while long fibers with non-circular cross sections, such as flat or trilobal, improve textile fabric durability and moisture-wicking properties. The selection of fiber length and cross-sectional shape influences performance characteristics including tensile strength, flexibility, and surface texture, enabling tailored solutions in sectors ranging from construction to fashion.
Conclusion: Optimizing Fiber Selection for End Use
Selecting the appropriate fiber cross section and fiber length is crucial for enhancing material performance tailored to specific applications. Larger cross sections typically offer increased strength and durability, while longer fibers improve tensile properties and reduce processing defects. Balancing these parameters ensures optimal fiber reinforcement, maximizing product efficiency and longevity in end-use scenarios.
Fiber Cross Section vs Fiber Length Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com