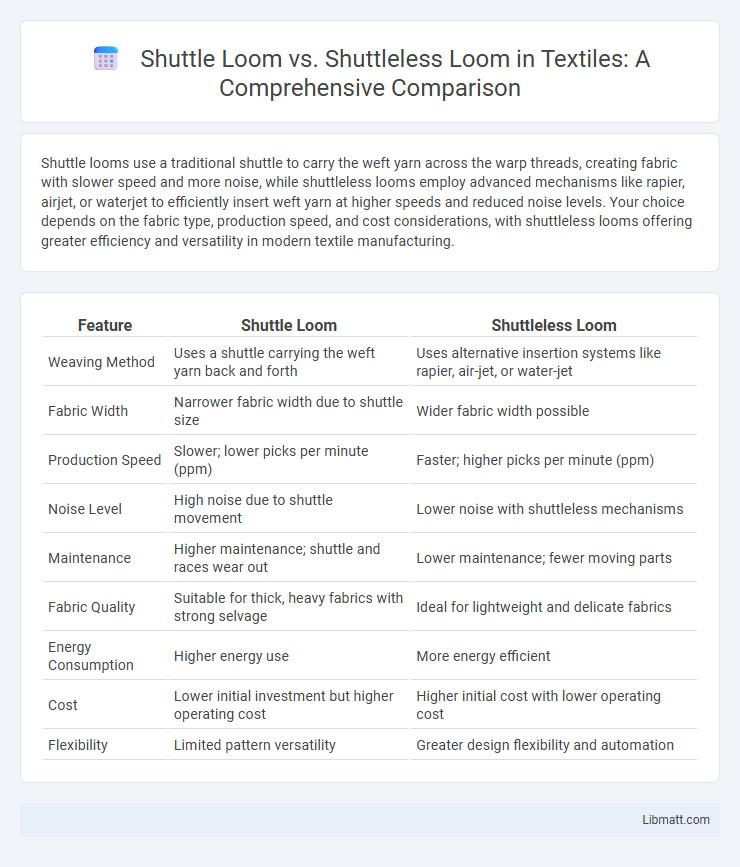
Shuttle looms use a traditional shuttle to carry the weft yarn across the warp threads, creating fabric with slower speed and more noise, while shuttleless looms employ advanced mechanisms like rapier, airjet, or waterjet to efficiently insert weft yarn at higher speeds and reduced noise levels. Your choice depends on the fabric type, production speed, and cost considerations, with shuttleless looms offering greater efficiency and versatility in modern textile manufacturing.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Shuttle Loom | Shuttleless Loom |
|---|---|---|
| Weaving Method | Uses a shuttle carrying the weft yarn back and forth | Uses alternative insertion systems like rapier, air-jet, or water-jet |
| Fabric Width | Narrower fabric width due to shuttle size | Wider fabric width possible |
| Production Speed | Slower; lower picks per minute (ppm) | Faster; higher picks per minute (ppm) |
| Noise Level | High noise due to shuttle movement | Lower noise with shuttleless mechanisms |
| Maintenance | Higher maintenance; shuttle and races wear out | Lower maintenance; fewer moving parts |
| Fabric Quality | Suitable for thick, heavy fabrics with strong selvage | Ideal for lightweight and delicate fabrics |
| Energy Consumption | Higher energy use | More energy efficient |
| Cost | Lower initial investment but higher operating cost | Higher initial cost with lower operating cost |
| Flexibility | Limited pattern versatility | Greater design flexibility and automation |
Introduction to Shuttle Looms and Shuttleless Looms
Shuttle looms use a traditional shuttle to carry the weft yarn back and forth across the warp threads, producing woven fabric with high stability and intricate patterns. Shuttleless looms, including air-jet, rapier, and projectile types, eliminate the shuttle mechanism, enabling faster weaving speeds and increased efficiency for mass production. Your choice between shuttle and shuttleless looms depends on the fabric type, production scale, and desired weaving precision.
Historical Evolution of Weaving Looms
Shuttle looms have historically dominated textile production since the early Industrial Revolution, utilizing a wooden shuttle to carry the weft yarn through the warp threads, which allowed for slower but sturdy fabric weaving. Shuttleless looms, emerging in the mid-20th century, use advanced technologies such as air jets, water jets, and projectile mechanisms to increase weaving speed and fabric versatility while reducing noise and maintenance. Your understanding of the historical evolution highlights the transition from mechanical complexity to high-efficiency automation in modern textile manufacturing.
Working Principles of Shuttle Looms
Shuttle looms operate by using a shuttle that carries the weft yarn back and forth across the warp threads to create fabric, relying on a traditional weaving technique. The shuttle moves through the shed formed by lifting warp threads, enabling interlacing of the weft with high precision and durability. Your choice of a shuttle loom ensures slower production speeds but superior fabric strength and consistency compared to shuttleless looms.
Working Principles of Shuttleless Looms
Shuttleless looms operate by utilizing various weft insertion techniques such as rapier, air-jet, projectile, or water-jet systems, which replace the traditional shuttle used in shuttle looms. These modern looms increase weaving speed and efficiency by propelling the weft yarn across the warp shed without the mechanical limitations of a shuttle, enabling higher production rates and reduced thread breakage. The absence of a shuttle reduces machine vibration and noise, resulting in smoother operation and improved fabric quality.
Key Differences: Shuttle vs Shuttleless Looms
Shuttle looms use a traditional shuttle to carry the weft yarn back and forth through the warp threads, resulting in slower weaving speeds but producing tightly woven, durable fabrics. Shuttleless looms, including rapier, projectile, and air-jet types, eliminate the shuttle, enhancing weaving speed and efficiency while allowing for wider fabric widths and reduced noise levels. Your choice between shuttle and shuttleless looms depends on fabric type, production speed requirements, and operational costs.
Fabric Quality Comparison
Shuttle looms produce fabrics with superior selvedge quality and tighter weaves due to the continuous weft insertion, resulting in stronger and more durable textiles. Shuttleless looms, using rapier, projectile, or air-jet mechanisms, offer higher production speeds but may produce fabrics with less consistent selvedge strength and occasional yarn tension variations. The choice between shuttle and shuttleless looms impacts fabric uniformity, tensile strength, and edge finish, influencing suitability for high-end apparel versus mass-market textiles.
Speed and Efficiency Analysis
Shuttleless looms significantly outperform shuttle looms in speed, producing up to 1,200 picks per minute compared to the shuttle loom's average of 60-70 picks per minute. The reduced weight and friction in shuttleless looms enhance energy efficiency and minimize downtime due to lower thread breakage and maintenance requirements. Industrial textile production trends favor shuttleless technology for its superior efficiency, enabling higher fabric output and reduced operational costs.
Cost Implications and Maintenance
Shuttle looms generally incur higher operational costs due to increased energy consumption and slower production rates, requiring more frequent maintenance to address shuttle-related wear and tear. Shuttleless looms offer lower maintenance expenses and faster production speeds by utilizing alternative weft insertion methods like projectile, rapier, or air-jet systems, reducing downtime and labor costs. Investment in shuttleless loom technology may involve higher upfront costs but results in greater long-term cost efficiency through improved machine longevity and reduced repair needs.
Environmental Impact and Energy Consumption
Shuttleless looms offer significant environmental advantages by reducing energy consumption by up to 30% compared to traditional shuttle looms, due to their streamlined operation and fewer moving parts. The lower energy demand results in decreased carbon emissions, making shuttleless technology more eco-friendly for modern textile manufacturing. Choosing shuttleless looms can optimize your production process while minimizing your environmental footprint.
Choosing the Right Loom for Your Textile Needs
Choosing the right loom for your textile needs depends on factors like fabric type, production speed, and budget. Shuttle looms excel in producing traditional, high-quality woven fabrics with intricate patterns, ideal for artisanal or low-volume projects. Shuttleless looms, offering faster weaving and lower maintenance, are better suited for mass production and modern textile manufacturing.
Shuttle loom vs Shuttleless loom Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com