Microdenier fibers are thicker and provide greater durability and softness, making them ideal for everyday textiles, while nanofibers, being much finer, offer superior filtration and enhanced surface area for advanced applications. Choosing between microdenier and nanofiber depends on your need for either strength and comfort or precision and high performance in materials.
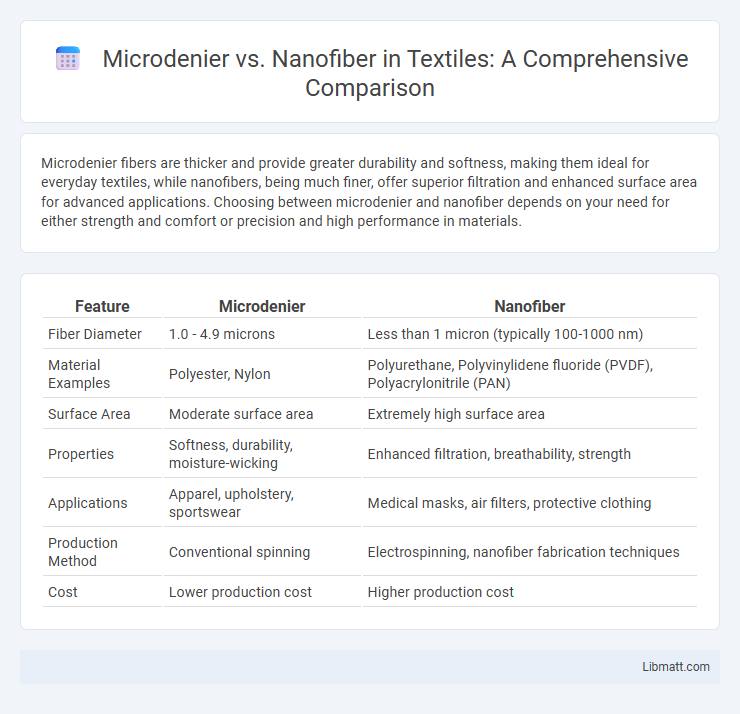
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Microdenier | Nanofiber |
|---|---|---|
| Fiber Diameter | 1.0 - 4.9 microns | Less than 1 micron (typically 100-1000 nm) |
| Material Examples | Polyester, Nylon | Polyurethane, Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF), Polyacrylonitrile (PAN) |
| Surface Area | Moderate surface area | Extremely high surface area |
| Properties | Softness, durability, moisture-wicking | Enhanced filtration, breathability, strength |
| Applications | Apparel, upholstery, sportswear | Medical masks, air filters, protective clothing |
| Production Method | Conventional spinning | Electrospinning, nanofiber fabrication techniques |
| Cost | Lower production cost | Higher production cost |
Introduction to Microdenier and Nanofiber
Microdenier fibers typically measure less than 1 denier in diameter, offering superior softness and lightweight properties ideal for textiles like activewear and upholstery. Nanofibers, with diameters in the nanometer range, provide exceptional surface area and enhanced filtration efficiency, making them essential in medical masks and advanced filtration systems. Understanding the differences helps you choose materials that optimize performance and comfort in various applications.
Defining Microdenier: Key Characteristics
Microdenier fibers measure between 0.3 and 1.0 denier, offering a balance of softness and durability ideal for textiles and filtration applications. These fibers exhibit fine diameters that increase surface area, enhancing breathability and moisture-wicking properties in performance fabrics. Their unique structure supports lightweight, high-strength materials used in advanced medical and industrial uses.
Understanding Nanofiber: Core Properties
Nanofibers boast ultra-fine diameters typically below 100 nanometers, resulting in an exceptionally high surface area-to-volume ratio that enhances filtration, absorption, and mechanical strength. Their unique core properties include superior porosity and fine pore structure, enabling efficient capture of airborne particles, liquids, and contaminants at the nanoscale. You can leverage nanofiber technology for advanced applications in healthcare, environmental protection, and high-performance textiles where microdenier fibers fall short.
Differences in Fiber Diameter and Structure
Microdenier fibers typically range from 0.7 to 2 denier per filament, offering a balance of softness and durability, while nanofibers have diameters less than 100 nanometers, often creating ultra-fine, high surface area structures. The larger diameter of microdenier fibers results in greater tensile strength and air permeability, whereas nanofibers provide enhanced filtration efficiency and water repellency due to their dense, intricate network. These structural differences make microdenier ideal for apparel and upholstery, while nanofibers excel in filtration, medical, and protective fabrics.
Manufacturing Processes: Microdenier vs Nanofiber
Microdenier fibers are manufactured through traditional spinning methods such as melt spinning, where polymer filaments are extruded and drawn to achieve fine diameters typically around 0.3 to 1 denier. Nanofiber production relies on advanced techniques like electrospinning, which uses electrical forces to create ultrafine fibers with diameters in the nanometer range, often below 100 nanometers. Your choice between microdenier and nanofiber textiles depends on the required fiber diameter, production complexity, and application-specific performance characteristics.
Performance in Textiles and Applications
Microdenier fibers offer enhanced softness and durability in textiles, making them ideal for activewear and upholstery, while nanofibers provide superior filtration efficiency and breathability, critical in medical masks and air purification fabrics. Nanofiber technology allows for ultra-fine fiber diameters under 100 nanometers, resulting in increased surface area and excellent moisture-wicking properties compared to microdenier fibers typically in the micrometer range. Your choice between microdenier and nanofiber textiles impacts the performance characteristics tailored to specific applications, balancing comfort, filtration, and durability needs.
Durability and Strength Comparison
Nanofiber materials typically exhibit superior strength and durability compared to microdenier fibers due to their smaller diameter and higher surface area, which contribute to enhanced tensile properties and resistance to wear. Microdenier fibers offer good durability but are more prone to fraying and degradation under intense mechanical stress. Your choice between microdenier and nanofiber should consider the specific application requirements for longevity and structural integrity.
Breathability and Comfort Factors
Microdenier fibers offer enhanced breathability due to their fine yet larger diameter compared to nanofibers, allowing better air circulation and moisture wicking for improved comfort. Nanofibers, with their ultra-fine structure, provide superior filtration but can sometimes reduce airflow, potentially impacting breathability. Your choice depends on balancing the need for comfort, where microdenier excels, against filtration efficiency often offered by nanofiber materials.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Microdenier fibers, being larger than nanofibers, typically require less energy-intensive production processes, resulting in a relatively lower carbon footprint compared to nanofiber manufacturing. Nanofibers, due to their ultra-fine structures, offer enhanced filtration and durability, potentially extending product lifespan and reducing waste, which supports sustainability despite higher initial environmental costs. The choice between microdenier and nanofiber materials involves balancing production energy demands with long-term environmental benefits from product efficiency and durability.
Choosing Between Microdenier and Nanofiber
Choosing between microdenier and nanofiber materials depends on the specific application requirements such as filtration efficiency, breathability, and durability. Nanofibers, with diameters typically below 100 nanometers, offer superior filtration and enhanced surface area, ideal for high-performance air and water filtration. Microdenier fibers, slightly larger but still fine, provide better tensile strength and are preferred in textiles and personal protective equipment requiring durability and comfort.
Microdenier vs Nanofiber Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com