Supercritical CO2 dyeing uses carbon dioxide in its supercritical state to efficiently penetrate fabrics, resulting in lower water consumption, reduced chemical waste, and enhanced color vibrancy compared to conventional dyeing methods. Your choice of supercritical CO2 dyeing promotes sustainability by minimizing environmental impact and improving energy efficiency while maintaining high-quality textile coloration.
Table of Comparison
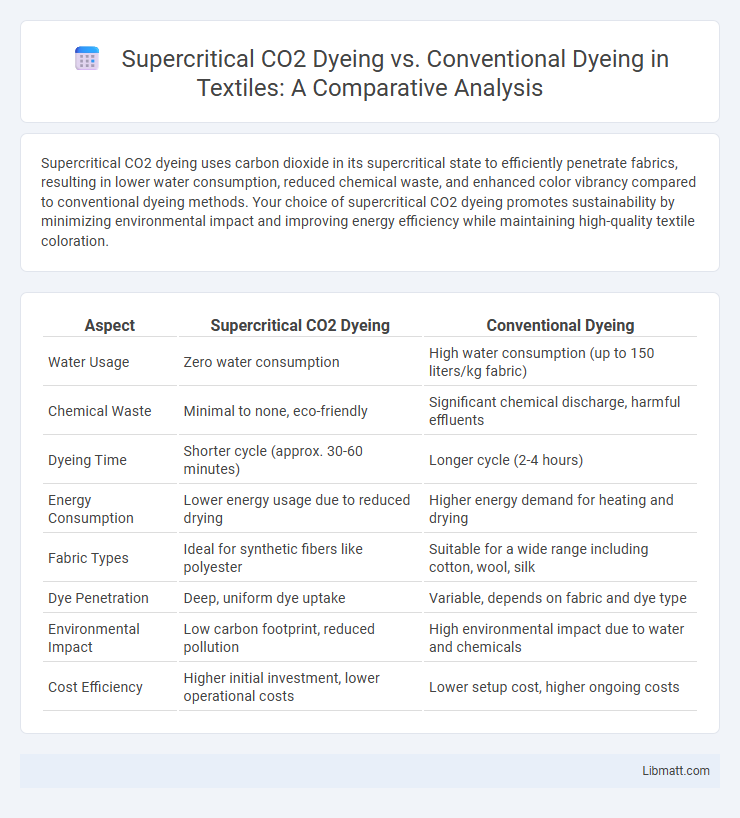
| Aspect | Supercritical CO2 Dyeing | Conventional Dyeing |
|---|---|---|
| Water Usage | Zero water consumption | High water consumption (up to 150 liters/kg fabric) |
| Chemical Waste | Minimal to none, eco-friendly | Significant chemical discharge, harmful effluents |
| Dyeing Time | Shorter cycle (approx. 30-60 minutes) | Longer cycle (2-4 hours) |
| Energy Consumption | Lower energy usage due to reduced drying | Higher energy demand for heating and drying |
| Fabric Types | Ideal for synthetic fibers like polyester | Suitable for a wide range including cotton, wool, silk |
| Dye Penetration | Deep, uniform dye uptake | Variable, depends on fabric and dye type |
| Environmental Impact | Low carbon footprint, reduced pollution | High environmental impact due to water and chemicals |
| Cost Efficiency | Higher initial investment, lower operational costs | Lower setup cost, higher ongoing costs |
Introduction to Textile Dyeing Methods
Supercritical CO2 dyeing uses carbon dioxide in a supercritical state as a solvent to transfer dyes into textile fibers, offering a sustainable alternative to water-intensive conventional dyeing that relies on aqueous dye baths. This advanced method reduces water consumption by up to 90% and eliminates the need for harmful chemical auxiliaries, significantly lowering environmental impact. Conventional dyeing remains prevalent due to its established infrastructure and compatibility with a wide range of fibers but faces challenges related to high water usage, wastewater treatment, and energy consumption.
Overview of Supercritical CO2 Dyeing Technology
Supercritical CO2 dyeing technology uses carbon dioxide in a supercritical state to dissolve and transfer dyes directly onto fabrics, eliminating the need for water and reducing chemical waste. This eco-friendly method offers faster dyeing cycles and lower energy consumption compared to conventional water-based dyeing processes. Your textile production can achieve improved color vibrancy and sustainability by adopting supercritical CO2 dyeing technology.
Conventional Dyeing: Processes and Techniques
Conventional dyeing involves processes such as batch, continuous, and semi-continuous dyeing, where fabrics are immersed in water-based dye baths using methods like exhaust, padding, and jet dyeing. These techniques rely heavily on water, energy, and chemicals to achieve uniform coloration, often resulting in significant wastewater and environmental impact. Your choice of conventional dyeing processes can influence fabric quality, dye uptake, and ecological footprint, making efficiency and sustainability key considerations.
Environmental Impact: Supercritical CO2 vs Conventional Dyeing
Supercritical CO2 dyeing eliminates the use of water, reducing water pollution and consumption by over 90% compared to conventional dyeing, which relies heavily on large volumes of water and generates toxic wastewater. This method decreases chemical waste and energy usage, thereby minimizing carbon emissions and environmental contamination. Your choice of supercritical CO2 dyeing promotes sustainable textile production with significantly lower ecological footprints than traditional dyeing processes.
Water and Energy Consumption Comparison
Supercritical CO2 dyeing drastically reduces water consumption by eliminating the need for water as a solvent, using CO2 in its supercritical state to effectively carry dyes into fibers. Compared to conventional dyeing methods, which require vast quantities of water for rinsing and dye baths, supercritical CO2 technology cuts down energy use by minimizing heating and drying processes. Your textile production can benefit from significant savings in both water and energy, promoting sustainability and cost efficiency.
Dye Uptake and Color Quality Differences
Supercritical CO2 dyeing enhances dye uptake by enabling deeper fiber penetration without water, resulting in more vibrant and uniform color quality compared to conventional aqueous dyeing methods. The absence of water in the supercritical CO2 process eliminates dye dilution, ensuring higher color intensity and improved fastness properties. Your fabrics benefit from consistent hues and eco-friendly processing that reduce chemical waste and energy consumption.
Cost Analysis: Initial Investment and Operational Expenses
Supercritical CO2 dyeing requires a higher initial investment due to specialized high-pressure equipment and advanced technology, while conventional dyeing systems generally entail lower startup costs with widely available machinery. Operational expenses for supercritical CO2 dyeing tend to be lower in terms of water and energy consumption, as the process is waterless and reduces drying times, leading to significant long-term savings. Conventional dyeing involves higher costs associated with large water usage, wastewater treatment, and energy-intensive drying, increasing ongoing operational expenditures compared to supercritical CO2 technology.
Fiber Compatibility and Dye Range
Supercritical CO2 dyeing offers superior fiber compatibility, especially with synthetic fibers like polyester, enabling efficient dye penetration without water use. Conventional dyeing accommodates a broader dye range across natural and synthetic fibers but often requires significant water and energy for fixation. The selective solubility of dyes in supercritical CO2 limits its use to disperse dyes, whereas conventional methods support reactive, acid, and direct dyes, expanding application versatility.
Industrial Adoption and Scalability
Supercritical CO2 dyeing has seen increasing industrial adoption due to its environmentally friendly process, eliminating water usage and reducing energy consumption compared to conventional dyeing methods. Major textile manufacturers scale the technology for mass production, benefiting from faster dyeing cycles and easier solvent recovery systems integrated into existing lines. However, conventional dyeing remains dominant in global markets due to established infrastructure and lower upfront costs despite its higher environmental footprint.
Future Trends in Sustainable Textile Dyeing
Supercritical CO2 dyeing is emerging as a sustainable alternative to conventional water-intensive dyeing methods, significantly reducing water consumption and eliminating harmful chemical effluents. Innovations in this technology focus on enhancing dye solubility and fabric compatibility to expand its application across diverse textile fibers. Future trends indicate a shift towards integrating supercritical CO2 processes with renewable energy sources and advanced automation to further minimize environmental impact and improve production efficiency.
Supercritical CO2 dyeing vs Conventional dyeing Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com