Heat setting stabilizes synthetic fibers by exposing them to controlled heat, preventing shrinkage and distortion during future use. Calendaring enhances fabric smoothness and sheen by passing the material through heated rollers, improving your textile's aesthetic and tactile qualities.
Table of Comparison
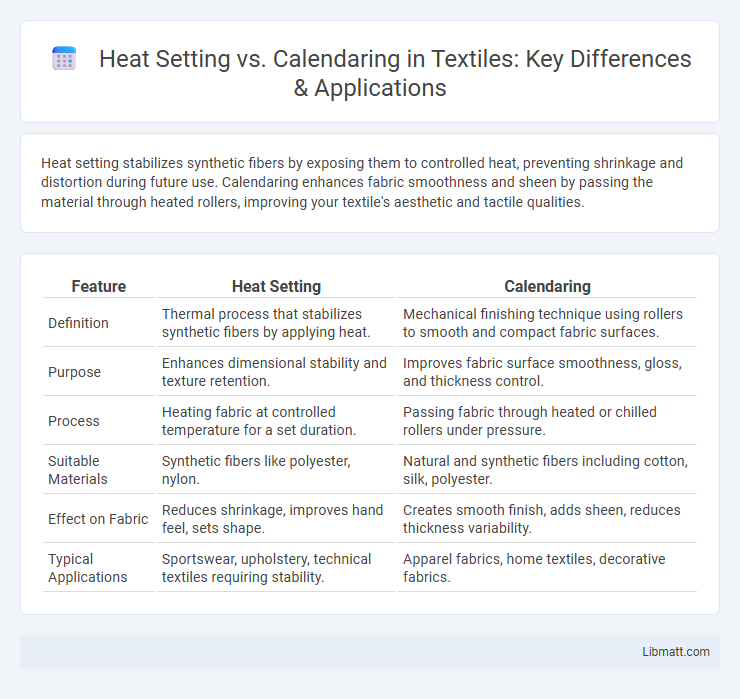
| Feature | Heat Setting | Calendaring |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Thermal process that stabilizes synthetic fibers by applying heat. | Mechanical finishing technique using rollers to smooth and compact fabric surfaces. |
| Purpose | Enhances dimensional stability and texture retention. | Improves fabric surface smoothness, gloss, and thickness control. |
| Process | Heating fabric at controlled temperature for a set duration. | Passing fabric through heated or chilled rollers under pressure. |
| Suitable Materials | Synthetic fibers like polyester, nylon. | Natural and synthetic fibers including cotton, silk, polyester. |
| Effect on Fabric | Reduces shrinkage, improves hand feel, sets shape. | Creates smooth finish, adds sheen, reduces thickness variability. |
| Typical Applications | Sportswear, upholstery, technical textiles requiring stability. | Apparel fabrics, home textiles, decorative fabrics. |
Understanding Heat Setting: Definition and Process
Heat setting is a thermal process used primarily in textile manufacturing to stabilize synthetic fibers by exposing them to controlled heat, which locks in shape and dimensions. This technique enhances fabric properties such as wrinkle resistance, dimensional stability, and texture retention by altering the molecular structure through heat exposure. Your choice to apply heat setting can significantly improve the durability and performance of polyester, nylon, and other synthetic materials in various applications.
What is Calendaring? An Overview
Calendaring is a textile finishing process where fabric passes through a series of heated rollers to improve surface smoothness, gloss, and thickness uniformity. This technique enhances fabric texture and appearance, making it suitable for materials like cotton, polyester, and blends. Your textile products benefit from improved tactile quality and visual appeal through calendaring, distinguishing it from heat setting, which stabilizes dimensional properties.
Key Differences Between Heat Setting and Calendaring
Heat setting involves stabilizing synthetic fibers through controlled heating to lock in shape and dimensional stability, whereas calendaring is a finishing process that smooths and enhances fabric surface using heated rollers to improve luster and texture. Heat setting primarily targets fiber structure to prevent shrinkage and distortion during laundering, while calendaring adjusts the fabric's appearance and hand feel without altering fiber integrity. Both processes operate at high temperatures but serve distinct purposes in textile manufacturing, affecting fabric durability and aesthetics differently.
Materials Suitable for Heat Setting
Heat setting is ideal for synthetic fibers such as polyester, nylon, and acrylic because it stabilizes their molecular structure through controlled heat, improving dimensional stability and wrinkle resistance. These materials benefit from heat setting as it locks in the desired fabric shape and texture by applying heat above their glass transition temperature. Natural fibers like cotton or wool are generally unsuitable for heat setting due to their lower melting points and different thermal properties.
Materials Best for Calendaring
Calendaring is most effective for synthetic fibers like polyester, nylon, and acetate, which respond well to heat and pressure, resulting in smooth, glossy, and wrinkle-resistant fabrics. Natural fibers such as cotton and wool can also be calendared but typically require blending with synthetics to achieve optimal results. This finishing process enhances fabric hand, luster, and dimensional stability, making calendaring ideal for textiles used in apparel, upholstery, and industrial applications.
Impact on Fabric Properties: Heat Setting vs Calendaring
Heat setting enhances fabric dimensional stability and reduces shrinkage by applying controlled heat to synthetic fibers, locking molecular structures in place. Calendaring improves fabric surface smoothness and luster through mechanical pressing between heated rollers, which compresses and flattens the fabric. While heat setting primarily stabilizes fabric shape and thermal properties, calendaring significantly influences fabric texture and appearance without altering its structural stability.
Applications and Industries Using Heat Setting
Heat setting is widely used in the textile industry to stabilize synthetic fibers like polyester and nylon, improving dimensional stability and wrinkle resistance in fabrics. It finds applications in carpet manufacturing, upholstery, and technical textiles where permanent shape retention and enhanced fabric appearance are critical. This process is essential in industries producing sportswear, automotive textiles, and home furnishings to ensure product durability and performance.
Applications and Industries Relying on Calendaring
Calendaring is crucial in industries like textiles, paper manufacturing, and plastics, where smoothness, gloss, and thickness uniformity are essential for product quality. Applications such as producing high-grade fabrics, glossy paper, and plastic films rely on calendaring to enhance surface finish and mechanical properties. Your products benefit from calendaring by achieving consistent texture and improved aesthetic appeal, which are vital for consumer satisfaction and industrial standards.
Advantages and Limitations of Each Technique
Heat setting enhances dimensional stability and reduces shrinkage in synthetic fibers, providing improved fabric durability and resistance to deformation, but it requires precise temperature control and can be energy-intensive. Calendaring offers a smooth, glossy finish and improved fabric hand, enhancing aesthetic appeal and surface uniformity, yet it may reduce fabric thickness and breathability, limiting its use in certain applications. Both techniques serve specific textile finishing goals, with heat setting optimizing structural attributes and calendaring focusing on surface properties.
Choosing the Right Method: Factors to Consider
Choosing the right method between heat setting and calendaring depends on your fabric type, desired finish, and production speed requirements. Heat setting is ideal for synthetic fibers to stabilize dimensions and improve wrinkle resistance, while calendaring enhances surface smoothness and sheen for natural fibers. Assessing your fabric's end-use and performance expectations ensures you select the most effective technique for your specific textile application.
Heat Setting vs Calendaring Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com