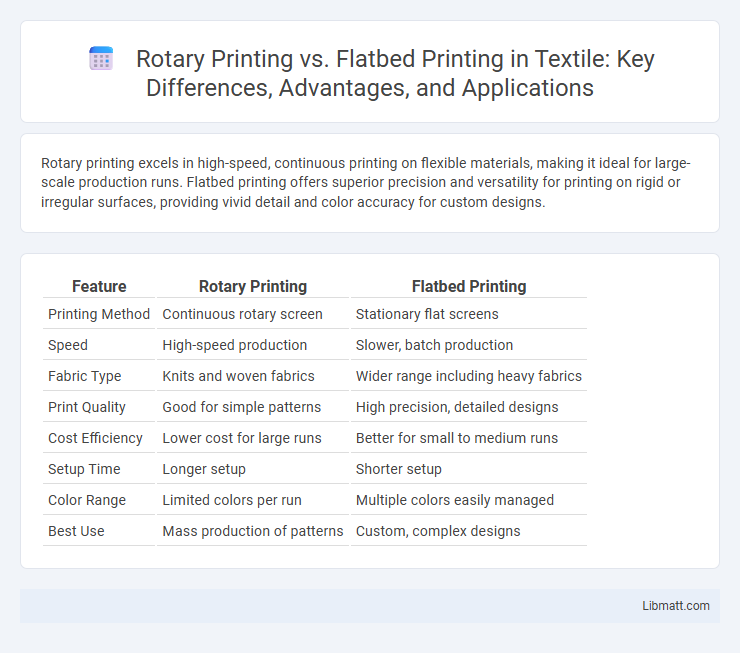
Rotary printing excels in high-speed, continuous printing on flexible materials, making it ideal for large-scale production runs. Flatbed printing offers superior precision and versatility for printing on rigid or irregular surfaces, providing vivid detail and color accuracy for custom designs.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Rotary Printing | Flatbed Printing |
|---|---|---|
| Printing Method | Continuous rotary screen | Stationary flat screens |
| Speed | High-speed production | Slower, batch production |
| Fabric Type | Knits and woven fabrics | Wider range including heavy fabrics |
| Print Quality | Good for simple patterns | High precision, detailed designs |
| Cost Efficiency | Lower cost for large runs | Better for small to medium runs |
| Setup Time | Longer setup | Shorter setup |
| Color Range | Limited colors per run | Multiple colors easily managed |
| Best Use | Mass production of patterns | Custom, complex designs |
Introduction to Rotary and Flatbed Printing
Rotary printing utilizes cylindrical rollers to transfer ink continuously onto flexible materials, making it ideal for high-speed production of textiles, packaging, and labels. Flatbed printing employs a flat surface where the substrate remains stationary while the print heads move, providing precise image quality for rigid or flat materials like signage and circuit boards. Both methods serve distinct industrial needs, with rotary excelling in volume and flatbed offering versatility in substrate types.
How Rotary Printing Works
Rotary printing works by continuously feeding the substrate through rotating cylinders, where one cylinder contains the patterned printing plate transferring ink onto the material at high speed. This method is ideal for long runs and flexible substrates such as textiles, wallpaper, and packaging films due to its efficiency and consistent output. The seamless rotation allows for rapid production with minimal setup time, making it cost-effective for large volume printing projects.
Flatbed Printing: Process and Technology
Flatbed printing uses a stationary flat surface to hold the material while print heads move across it, enabling precise ink placement and detailed image reproduction. This technology supports a wide range of substrates, including rigid materials like wood, glass, and metal, by applying UV-cured or solvent-based inks that bond quickly and produce durable prints. Your choice of flatbed printing benefits from its versatility and high resolution, ideal for short runs and customized designs on diverse materials.
Key Differences Between Rotary and Flatbed Printing
Rotary printing uses continuous cylindrical drums for high-speed production, ideal for long runs and flexible materials, whereas flatbed printing operates with a stationary flat surface, accommodating rigid substrates and detailed images. Rotary presses excel in speed and efficiency, making them suitable for newspapers and packaging, while flatbed printers offer superior precision and versatility for thick or uneven materials. Key differences include print speed, substrate compatibility, and the complexity of print detail achievable.
Advantages of Rotary Printing
Rotary printing offers high-speed production ideal for large-volume textile printing, significantly reducing turnaround times compared to flatbed printing. Its continuous roll-to-roll process enables consistent color application and fine detail reproduction, enhancing print quality on fabrics. The rotary method also lowers operational costs through efficient ink usage and less manual handling, making it a cost-effective solution for industrial-scale garment and home textile manufacturing.
Benefits of Flatbed Printing
Flatbed printing offers superior precision and quality for printing on rigid and uneven surfaces, making it ideal for materials like wood, glass, and metal. You benefit from the ability to produce vibrant, detailed images with less waste and faster setup times compared to rotary printing. Its versatility and durability make flatbed printing a preferred choice for customized, high-resolution designs on various substrates.
Common Applications of Rotary Printing
Rotary printing is commonly used for high-volume production of continuous materials such as textiles, wallpaper, and packaging films due to its ability to print rapidly on flexible substrates. It excels in applications requiring consistent, repetitive patterns like fabric designs, gift wrap, and labels. This method is favored for its efficiency in large-scale manufacturing environments where speed and cost-effectiveness are critical.
Typical Uses for Flatbed Printing
Flatbed printing is primarily used for printing on rigid, thick, or non-flexible substrates such as wood, glass, metal, and acrylic, making it ideal for creating signage, promotional items, and customized industrial components. Its ability to print directly onto uneven surfaces with high precision suits short to medium production runs requiring intricate designs or vibrant color quality. Flatbed printers excel in producing durable outdoor displays, personalized gifts, and architectural models where texture and material variety are crucial.
Cost Comparison: Rotary vs Flatbed Printing
Rotary printing generally offers lower operational costs due to its continuous printing process, which enhances efficiency and reduces labor expenses compared to flatbed printing. Flatbed printing incurs higher costs because of its slower, batch-based approach and increased material handling time, making it less economical for large-volume runs. Your choice between rotary and flatbed printing ultimately depends on balancing initial investment with long-term production costs, where rotary printing proves more cost-effective for high-volume projects.
Choosing the Right Printing Method for Your Needs
Rotary printing offers high-speed, continuous output ideal for large-scale production and flexible materials, while flatbed printing excels in precision and versatility for rigid substrates and intricate designs. Evaluating print volume, material type, and desired detail ensures optimal method selection, balancing efficiency with quality demands. Understanding these factors helps businesses align their printing approach with specific project requirements for cost-effective results.
Rotary Printing vs Flatbed Printing Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com