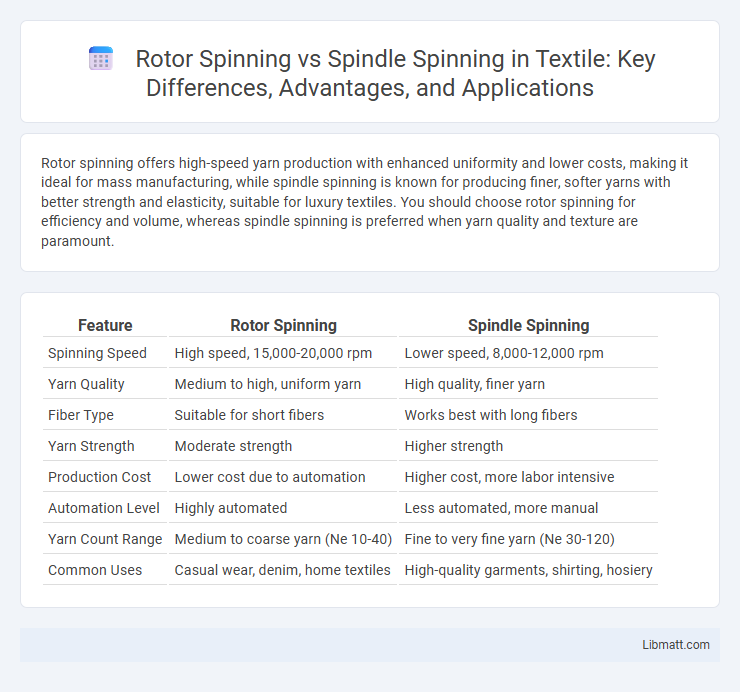
Rotor spinning offers high-speed yarn production with enhanced uniformity and lower costs, making it ideal for mass manufacturing, while spindle spinning is known for producing finer, softer yarns with better strength and elasticity, suitable for luxury textiles. You should choose rotor spinning for efficiency and volume, whereas spindle spinning is preferred when yarn quality and texture are paramount.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Rotor Spinning | Spindle Spinning |
|---|---|---|
| Spinning Speed | High speed, 15,000-20,000 rpm | Lower speed, 8,000-12,000 rpm |
| Yarn Quality | Medium to high, uniform yarn | High quality, finer yarn |
| Fiber Type | Suitable for short fibers | Works best with long fibers |
| Yarn Strength | Moderate strength | Higher strength |
| Production Cost | Lower cost due to automation | Higher cost, more labor intensive |
| Automation Level | Highly automated | Less automated, more manual |
| Yarn Count Range | Medium to coarse yarn (Ne 10-40) | Fine to very fine yarn (Ne 30-120) |
| Common Uses | Casual wear, denim, home textiles | High-quality garments, shirting, hosiery |
Introduction to Rotor and Spindle Spinning
Rotor spinning uses a high-speed rotating rotor to twist fibers into yarn, enabling rapid production of coarse yarns with lower hairiness. Spindle spinning employs a rotating spindle to spin fibers, producing finer, stronger yarns with better uniformity and elasticity. Both methods play crucial roles in textile manufacturing, with rotor spinning favored for mass production and spindle spinning preferred for quality and precision.
Historical Evolution of Spinning Technologies
Rotor spinning emerged in the mid-20th century as a faster, more efficient alternative to traditional spindle spinning, revolutionizing textile manufacturing. Spindle spinning, dating back thousands of years, laid the foundation for yarn production but was limited by slower speeds and higher labor intensity. You can appreciate how the evolution from spindle to rotor spinning reflects significant advancements in mechanization and productivity within the textile industry.
Principles of Rotor Spinning
Rotor spinning operates by feeding fibers into a rapidly rotating rotor, where centrifugal force aligns and twists the fibers to form yarn. This process enables high-speed production and creates yarn with a compact structure, offering improved strength and uniformity compared to spindle spinning. Unlike spindle spinning, which uses a spindle to twist fibers, rotor spinning relies on the mechanical action within the rotor to generate yarn twist efficiently.
Fundamentals of Spindle Spinning
Spindle spinning, a traditional fiber twisting technique, relies on manually spinning fibers around a spindle to form yarn by twisting fibers into a continuous thread. This method enables precise control over yarn thickness, tension, and twist, making it ideal for artisanal and small-scale textile production. Unlike rotor spinning, which uses high-speed rotors for automated yarn formation, spindle spinning emphasizes craftsmanship through manual operation of the spindle to align and twist fibers.
Key Differences Between Rotor and Spindle Spinning
Rotor spinning uses a rotating rotor to twist fibers into yarn, offering higher production speeds compared to spindle spinning, which relies on a spindle to rotate the yarn. Rotor spinning produces slightly coarser yarns with more uniformity, while spindle spinning yields finer, softer yarns with more irregularities. Your choice between these methods depends on the desired yarn quality, production scale, and application requirements.
Efficiency and Production Speed Comparison
Rotor spinning offers higher production speeds, reaching up to 400 meters per minute, significantly outperforming spindle spinning, which typically operates around 20-30 meters per minute. In terms of efficiency, rotor spinning reduces labor costs and energy consumption due to its automated process, whereas spindle spinning requires more manual intervention and consumes more power. The combination of increased output and lower operational costs makes rotor spinning more suitable for large-scale textile manufacturing focused on efficiency.
Yarn Quality and Applications
Rotor spinning produces yarn with lower hairiness and higher uniformity, making it suitable for coarse textiles and denim fabrics due to its strength and abrasion resistance. Spindle spinning yields finer, softer yarn with higher tensile strength and better elongation, ideal for high-quality apparel and knitwear requiring smooth texture. The choice between rotor and spindle spinning impacts yarn quality significantly, influencing its end-use in industries like hosiery, woven fabrics, and upholstery.
Cost Implications and Maintenance
Rotor spinning offers lower initial setup costs and faster production rates but often incurs higher maintenance expenses due to rotor wear and the need for specialized replacement parts. Spindle spinning requires higher capital investment for machinery but benefits from simpler, more cost-effective maintenance with widely available components and longer spindle lifespan. Evaluating total cost implications involves balancing rotor spinning's efficient output against spindle spinning's reduced upkeep expenses.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Rotor spinning demonstrates a lower environmental impact compared to spindle spinning due to its higher production efficiency and reduced energy consumption per unit of yarn produced. The compact design of rotor spinning machines minimizes waste and allows for easier integration of sustainable raw materials, enhancing overall sustainability. In contrast, spindle spinning often requires more raw material and energy input, increasing its carbon footprint and environmental burden.
Future Trends in Textile Spinning Methods
Rotor spinning offers higher production speeds and lower costs, making it a favorable choice for mass-market textile manufacturing, while spindle spinning provides superior yarn strength and quality suited for premium fabrics. The future trends indicate a shift towards automation and smart technologies integrated with both methods, enhancing precision and energy efficiency in textile spinning. You can expect increased adoption of sustainable materials and advanced monitoring systems to optimize yarn properties and reduce environmental impact in spinning processes.
Rotor spinning vs Spindle spinning Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com