Sizing agent primarily improves the adhesion between fibers and matrix in composite materials, enhancing mechanical properties and durability. Sizing compound, a formulation containing sizing agents along with other additives, offers tailored processing benefits such as improved fiber handling and protection during manufacturing.
Table of Comparison
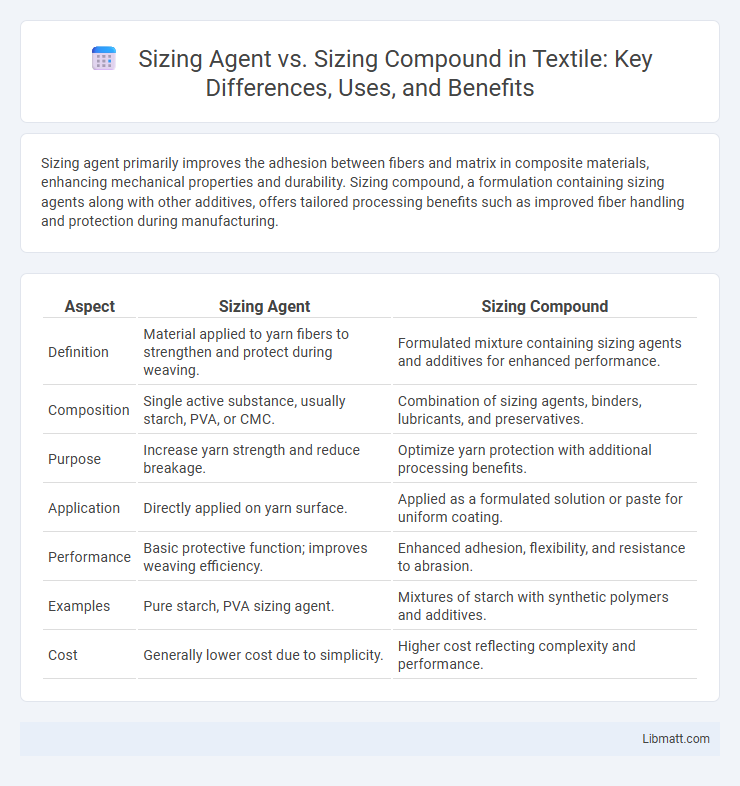
| Aspect | Sizing Agent | Sizing Compound |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Material applied to yarn fibers to strengthen and protect during weaving. | Formulated mixture containing sizing agents and additives for enhanced performance. |
| Composition | Single active substance, usually starch, PVA, or CMC. | Combination of sizing agents, binders, lubricants, and preservatives. |
| Purpose | Increase yarn strength and reduce breakage. | Optimize yarn protection with additional processing benefits. |
| Application | Directly applied on yarn surface. | Applied as a formulated solution or paste for uniform coating. |
| Performance | Basic protective function; improves weaving efficiency. | Enhanced adhesion, flexibility, and resistance to abrasion. |
| Examples | Pure starch, PVA sizing agent. | Mixtures of starch with synthetic polymers and additives. |
| Cost | Generally lower cost due to simplicity. | Higher cost reflecting complexity and performance. |
Introduction to Sizing Agents and Sizing Compounds
Sizing agents are chemical substances applied to fibers or fabrics to improve their strength, abrasion resistance, and weaving performance, often consisting of natural or synthetic polymers. Sizing compounds refer to formulated mixtures containing one or more sizing agents combined with additives like lubricants or preservatives to enhance application properties and durability. Both sizing agents and compounds play crucial roles in textile manufacturing, optimizing fabric quality and processing efficiency.
Definition: What is a Sizing Agent?
A sizing agent is a chemical applied to fibers or fabrics to enhance their strength, reduce fraying, and improve surface smoothness during weaving or processing. Unlike a sizing compound, which may refer to a mixture of chemicals including sizing agents, the sizing agent specifically acts as a protective coating to maintain fabric quality. You can optimize fabric performance by selecting the appropriate sizing agent based on the material and application requirements.
Definition: What is a Sizing Compound?
A sizing compound is a chemical substance applied to fibers or fabrics to improve their strength, durability, and surface finish during textile manufacturing. It functions by forming a protective layer that reduces abrasion and enhances adhesion between fibers and other materials. Unlike a sizing agent, which refers broadly to any substance used for sizing, a sizing compound specifically denotes the formulated chemicals designed for precise performance in textile production processes.
Key Differences Between Sizing Agents and Sizing Compounds
Sizing agents refer to chemicals applied to fibers or yarns to enhance strength, reduce friction, and improve weaving efficiency, typically involving single-component formulations. Sizing compounds are more complex mixtures often containing multiple ingredients like binders, lubricants, and anti-static agents to provide comprehensive performance benefits during textile processing. The key difference lies in the composition and functional complexity where sizing agents focus on specific fiber protection, while sizing compounds address broader processing challenges with multifunctional properties.
Common Types of Sizing Agents
Common types of sizing agents include starch, polyvinyl alcohol (PVA), and acrylic polymers, each designed to enhance fabric strength and surface smoothness. Sizing agents are typically water-soluble substances applied to yarns prior to weaving, improving tensile strength and reducing breakage during processing. Unlike sizing compounds, which may contain additional chemical additives for specific performance attributes, sizing agents primarily focus on adhesion and film formation on fibers.
Common Types of Sizing Compounds
Common types of sizing compounds include starch, polyvinyl alcohol (PVA), and epoxy resins, each designed to enhance fabric strength and water resistance. Starch is widely used for its affordability and ease of application, while PVA provides superior adhesion and flexibility. Epoxy resins offer excellent durability and chemical resistance, making them suitable for industrial textiles.
Applications in Textile Industry
Sizing agents in the textile industry are primarily used to apply a protective film on yarns, enhancing strength and reducing breakage during weaving, with common compounds including starch, polyvinyl alcohol, and carboxymethyl cellulose. Sizing compounds, often a formulated blend of synthetic or natural polymers and additives, are tailored for specific textile applications such as cotton, wool, or synthetic fibers, optimizing adhesion, elasticity, and desizing efficiency. The choice between sizing agents and compounds depends on fabric type, production speed, and end-use requirements, influencing fabric quality and process sustainability.
Applications in Paper Manufacturing
Sizing agents are chemical additives used in paper manufacturing to improve water resistance and printability by altering the surface properties of the paper fibers during the papermaking process. Sizing compounds, typically blends of sizing agents with other additives, enhance the durability and functionality of paper products by providing tailored surface characteristics suited for specific applications such as packaging or high-quality printing. These compounds optimize internal and surface sizing processes, ensuring better ink adhesion and reduced absorption of liquids.
Performance Comparison: Effectiveness and Efficiency
Sizing agents typically offer superior performance in improving fabric strength and water repellency due to their ability to form a uniform, flexible film on fibers, enhancing durability and fabric hand. Sizing compounds often work as multicomponent mixtures, delivering broader protection but sometimes compromising efficiency due to longer application and drying times. Your choice between them should consider the balance between desired fabric enhancement and production speed for optimal operational efficiency.
Market Trends and Future Developments
The sizing agent market is rapidly evolving with increased demand for eco-friendly, water-based formulations driven by stringent environmental regulations and rising awareness of sustainable manufacturing practices. Future developments in sizing compounds focus on enhancing performance properties such as durability, stiffness, and chemical resistance, integrating nanotechnology and bio-based materials to meet specific industry needs. Your choice between sizing agents and compounds will increasingly depend on advancements that balance cost-efficiency with environmental impact and end-use functionality.
Sizing agent vs Sizing compound Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com