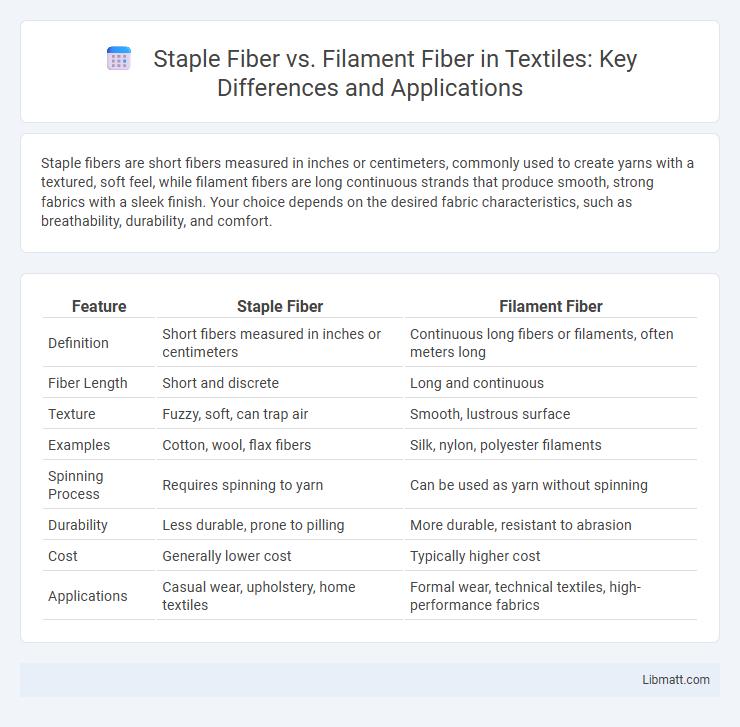
Staple fibers are short fibers measured in inches or centimeters, commonly used to create yarns with a textured, soft feel, while filament fibers are long continuous strands that produce smooth, strong fabrics with a sleek finish. Your choice depends on the desired fabric characteristics, such as breathability, durability, and comfort.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Staple Fiber | Filament Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Short fibers measured in inches or centimeters | Continuous long fibers or filaments, often meters long |
| Fiber Length | Short and discrete | Long and continuous |
| Texture | Fuzzy, soft, can trap air | Smooth, lustrous surface |
| Examples | Cotton, wool, flax fibers | Silk, nylon, polyester filaments |
| Spinning Process | Requires spinning to yarn | Can be used as yarn without spinning |
| Durability | Less durable, prone to pilling | More durable, resistant to abrasion |
| Cost | Generally lower cost | Typically higher cost |
| Applications | Casual wear, upholstery, home textiles | Formal wear, technical textiles, high-performance fabrics |
Introduction to Staple Fiber and Filament Fiber
Staple fibers are short fibers typically measuring less than 50 mm in length and are spun together to create yarn, commonly derived from natural sources like cotton or wool or manufactured fibers like polyester. Filament fibers are continuous, long fibers that can be miles in length, often produced artificially from synthetic materials such as nylon or rayon, providing smooth and strong yarns. The key difference lies in fiber length, where staple fibers produce textured and bulkier fabrics, while filament fibers result in smoother, finer textiles with higher tensile strength.
Definition and Characteristics of Staple Fiber
Staple fibers are short fibers typically measuring a few centimeters in length, known for their fuzzy texture and ease of spinning into yarns. These fibers, derived from natural sources like cotton or wool or manufactured synthetically, offer breathability and softness, making them ideal for comfortable textiles. Your choice of staple fibers influences fabric durability and warmth due to their inherent irregularity and moisture-absorbing properties.
Definition and Characteristics of Filament Fiber
Filament fibers are continuous strands of fiber that can be thousands of meters long, commonly made from synthetic materials like polyester, nylon, or natural sources such as silk. These fibers exhibit smooth, uniform surfaces and high tensile strength, making them ideal for producing strong, lustrous textiles with minimal fiber ends and pilling. Your choice of filament fiber impacts fabric durability, sheen, and overall quality, distinguishing it from staple fibers, which are shorter and more irregular in length.
Key Differences Between Staple and Filament Fibers
Staple fibers are short fibers, typically measured in inches or centimeters, commonly used in spun yarn production, whereas filament fibers are long continuous fibers, often used in filament yarns and rugs. Staple fibers create yarns with a fuzzier texture and more air pockets, enhancing warmth and insulation, while filament fibers produce smoother, stronger, and more lustrous fabrics. The manufacturing processes differ; staple fibers require spinning to bind fibers together, whereas filament fibers can be used directly without spinning, leading to distinct fabric properties and applications.
Manufacturing Processes: Staple vs Filament Fiber
Staple fibers are produced by chopping longer fibers into short lengths, typically from natural sources like cotton or wool, or synthetic fibers cut after extrusion, allowing for versatile spinning techniques to create yarns. Filament fibers are manufactured through continuous extrusion processes, such as melt spinning or solution spinning, resulting in long, unbroken fiber strands ideal for smooth, strong fabrics. Your choice between staple and filament fibers depends on the desired texture, strength, and manufacturing requirements of the end textile product.
Applications of Staple Fiber
Staple fibers are widely used in the textile industry for producing cotton, wool, and synthetic yarns due to their short length and ease of spinning. These fibers are ideal for making versatile fabrics such as denim, flannel, and tweed, commonly found in apparel and home textiles. Staple fibers also play a crucial role in nonwoven materials used in medical textiles, upholstery, and filtration products.
Applications of Filament Fiber
Filament fibers are extensively used in high-performance textiles such as lingerie, swimwear, and industrial fabrics due to their smooth, continuous length and strength. Their durability and ability to be produced in fine deniers make them ideal for applications requiring lightweight, breathable, and moisture-wicking properties. Your choice of filament fiber can enhance fabric aesthetics and functional performance in sectors ranging from fashion to technical textiles.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Staple Fiber
Staple fibers offer advantages such as greater versatility in textile applications, easier blending with other fibers, and improved airflow and insulation due to their shorter length and natural crimp. However, they tend to produce fabrics that are less smooth and strong compared to filament fibers, and they may result in higher fuzziness and pilling issues. Your choice depends on the desired fabric texture, durability, and end-use requirements, with staple fibers being ideal for soft, breathable textiles.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Filament Fiber
Filament fibers offer advantages such as smooth texture, high tensile strength, and resistance to abrasion, making them ideal for producing lustrous and durable fabrics like silk and polyester. However, their continuous length limits breathability and elasticity compared to staple fibers, and they can be more difficult to spin and handle in textile manufacturing. Despite higher cost and processing complexity, filament fibers provide superior fabric uniformity and reduced pilling issues often associated with shorter staple fibers.
Choosing the Right Fiber: Staple vs Filament
Choosing the right fiber depends on your project's requirements for texture, strength, and appearance. Staple fibers, made of short lengths, provide softness and warmth, ideal for knitwear and cozy fabrics, while filament fibers consist of continuous strands that offer smoothness and durability, perfect for high-strength textiles and fine fabrics. Understanding these differences helps you select fibers that optimize performance and comfort in your garments.
Staple fiber vs Filament fiber Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com