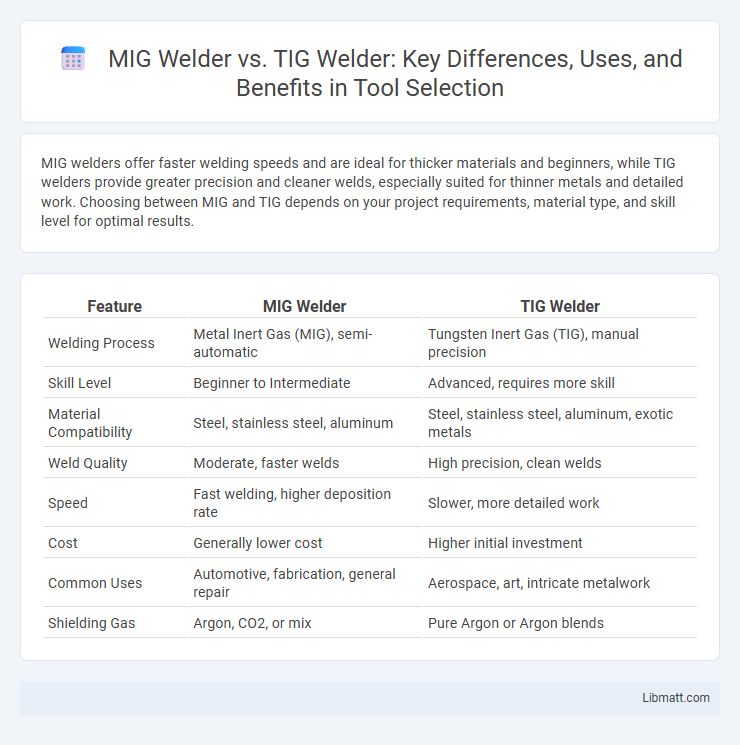
MIG welders offer faster welding speeds and are ideal for thicker materials and beginners, while TIG welders provide greater precision and cleaner welds, especially suited for thinner metals and detailed work. Choosing between MIG and TIG depends on your project requirements, material type, and skill level for optimal results.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | MIG Welder | TIG Welder |
|---|---|---|
| Welding Process | Metal Inert Gas (MIG), semi-automatic | Tungsten Inert Gas (TIG), manual precision |
| Skill Level | Beginner to Intermediate | Advanced, requires more skill |
| Material Compatibility | Steel, stainless steel, aluminum | Steel, stainless steel, aluminum, exotic metals |
| Weld Quality | Moderate, faster welds | High precision, clean welds |
| Speed | Fast welding, higher deposition rate | Slower, more detailed work |
| Cost | Generally lower cost | Higher initial investment |
| Common Uses | Automotive, fabrication, general repair | Aerospace, art, intricate metalwork |
| Shielding Gas | Argon, CO2, or mix | Pure Argon or Argon blends |
Introduction to MIG and TIG Welding
MIG welding utilizes a continuously fed wire electrode and inert gas to join metals quickly, making it ideal for thicker materials and high-production environments. TIG welding employs a non-consumable tungsten electrode and separate filler rod, providing precise control and high-quality welds on thinner metals and specialty alloys. Both methods serve distinct industrial applications, with MIG favored for speed and TIG preferred for detailed, clean welds.
Core Differences Between MIG and TIG Welders
MIG welders use a continuous wire electrode and inert gas to create faster, easier welds ideal for thicker materials and high-production environments. TIG welders employ a non-consumable tungsten electrode and inert gas to produce precise, high-quality welds suitable for thin metals and detailed work. Core differences include speed, weld quality, material compatibility, and operator skill level required for each welding method.
How MIG Welding Works
MIG welding works by feeding a continuous solid wire electrode through a welding gun, while an inert shielding gas, typically argon or a mix of argon and CO2, protects the weld pool from contamination. This process allows for faster welding speeds and easier learning curves compared to TIG welding, making it ideal for thicker materials and high-volume applications. Your choice between MIG and TIG should consider the precision needed, as MIG excels in efficient, robust welds but lacks the fine control TIG provides.
How TIG Welding Works
TIG welding, or Tungsten Inert Gas welding, uses a non-consumable tungsten electrode to produce a precise and high-quality weld. The process involves creating an electric arc between the tungsten electrode and the workpiece while an inert gas, typically argon, shields the weld area from contamination and oxidation. This technique provides greater control over the weld bead and is ideal for welding thin materials or metals like stainless steel and aluminum.
Material Compatibility: MIG vs TIG
MIG welders excel at welding a wide range of materials including mild steel, stainless steel, and aluminum due to their versatile wire feed system and faster welding speed. TIG welders provide superior control and precision, making them ideal for thin materials and alloys such as stainless steel, aluminum, copper, and magnesium where cleaner, high-quality welds are essential. Material compatibility depends on project requirements, with MIG favored for thicker metals and industrial applications, while TIG is preferred for delicate, high-strength, and aesthetically critical welds.
Welding Speed and Efficiency Comparison
MIG welders offer faster welding speeds and higher efficiency by using a continuous wire feed, making them ideal for large-scale or production work. TIG welders, while slower due to their precise manual process, provide superior control and weld quality for detailed or thin materials. Choosing your welder depends on whether speed or precision is the priority for your welding projects.
Weld Quality and Appearance
MIG welders produce strong, consistent welds with moderate spatter, making them suitable for thicker metals and quick fabrication tasks. TIG welders offer superior weld quality and appearance, delivering precise, clean weld beads with minimal spatter, ideal for thin materials and detailed projects. The choice affects the final weld integrity, with TIG providing finer control and a smoother finish compared to MIG welding.
Skill Level Required: MIG vs TIG
MIG welding requires less skill and is easier for beginners to learn due to its faster wire feed and simpler technique. TIG welding demands a higher skill level, precision, and steady hand control, making it ideal for detailed or thin metal work. Your choice depends on your experience and the complexity of the welding tasks you need to perform.
Cost Considerations: MIG and TIG Welders
MIG welders generally offer a lower initial cost and higher efficiency, making them more budget-friendly for beginners and high-volume welding tasks. TIG welders tend to have a higher upfront price due to precision control features but provide superior weld quality, ideal for detailed projects and thin materials. Maintenance costs for TIG machines can be higher due to consumables like tungsten electrodes, while MIG welders use more affordable wire spools, influencing long-term expenses.
Which Welder Is Best for Your Project?
MIG welders offer faster welding speeds and are ideal for thicker materials and large projects, providing ease of use for beginners and efficient welding on carbon steel, stainless steel, and aluminum. TIG welders deliver higher precision and cleaner welds, making them perfect for detailed work on thin metals or projects requiring high-quality finishes and strong corrosion resistance. Your choice depends on whether you prioritize speed and versatility with a MIG welder or precision and aesthetic quality with a TIG welder for your specific welding project.
MIG welder vs TIG welder Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com