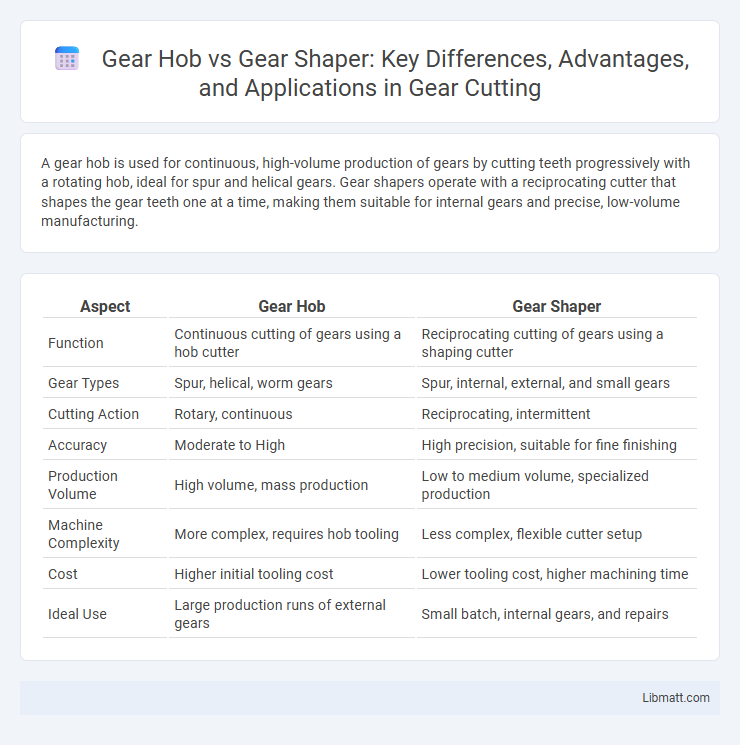
A gear hob is used for continuous, high-volume production of gears by cutting teeth progressively with a rotating hob, ideal for spur and helical gears. Gear shapers operate with a reciprocating cutter that shapes the gear teeth one at a time, making them suitable for internal gears and precise, low-volume manufacturing.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Gear Hob | Gear Shaper |
|---|---|---|
| Function | Continuous cutting of gears using a hob cutter | Reciprocating cutting of gears using a shaping cutter |
| Gear Types | Spur, helical, worm gears | Spur, internal, external, and small gears |
| Cutting Action | Rotary, continuous | Reciprocating, intermittent |
| Accuracy | Moderate to High | High precision, suitable for fine finishing |
| Production Volume | High volume, mass production | Low to medium volume, specialized production |
| Machine Complexity | More complex, requires hob tooling | Less complex, flexible cutter setup |
| Cost | Higher initial tooling cost | Lower tooling cost, higher machining time |
| Ideal Use | Large production runs of external gears | Small batch, internal gears, and repairs |
Introduction to Gear Hob and Gear Shaper
Gear hobs and gear shapers are essential machine tools used for manufacturing gears with precision and efficiency. Gear hobbing involves a rotating hob that cuts teeth continuously, ideal for producing large quantities of gears with consistent accuracy. Gear shaping, on the other hand, uses a reciprocating cutter that gradually forms gear teeth, making it suitable for internal gears and complex profiles where high precision is required.
Overview of Gear Manufacturing Processes
Gear hobbing and gear shaping are essential gear manufacturing processes with distinct applications and mechanisms. Gear hobbing uses a hob cutter to progressively generate gear teeth, offering high efficiency for producing spur, helical, and worm gears. Gear shaping employs a reciprocating pinion cutter that meshes with the gear blank, providing better precision for internal gears and small batch production, which can be crucial for your specific gear requirements.
What is Gear Hobbing?
Gear hobbing is a precision machining process used to cut gear teeth by rotating a cylindrical cutting tool called a hob against a gear blank. This efficient method allows the production of high-quality gears with accurate tooth profiles and is widely employed for spur, helical, and worm gears. Your manufacturing operations benefit from gear hobbing's ability to produce consistent, complex gear shapes quickly and with minimal tooling changes.
What is Gear Shaping?
Gear shaping is a manufacturing process that uses a rotating cutter similar in shape to the gear being produced, cutting teeth gradually by reciprocating and rotating motions. This technique enables the creation of internal and external gears with high precision and efficiency compared to gear hobbing, which employs a hob cutter for continuous cutting. Understanding gear shaping helps you choose the right method for complex gear profiles and intricate designs requiring superior accuracy.
Key Differences Between Gear Hobbing and Gear Shaping
Gear hobbing uses a rotating cutting tool called a hob to generate teeth through a continuous, synchronized process, ideal for high-volume production of spur and helical gears. Gear shaping employs a reciprocating cutter shaped like a gear, removing material with each stroke, making it suitable for internal and external gears with complex profiles. You should choose gear hobbing for faster, cost-effective manufacturing and gear shaping for precision in smaller batches or unusual gear types.
Advantages of Gear Hobbing
Gear hobbing offers faster production rates and higher precision compared to gear shaping, making it ideal for mass manufacturing of gears. The continuous cutting process with a hob tool reduces cycle time and improves surface finish, resulting in more efficient and cost-effective gear production. You benefit from greater versatility in producing various gear types and sizes with excellent accuracy using gear hobbing.
Advantages of Gear Shaping
Gear shaping offers precise internal and external gear cutting with the ability to produce complex gear profiles, including non-standard and internal gears, which gear hobbing cannot efficiently handle. It allows for the use of a single tool for various gear types, reducing tooling costs and setup time while enhancing flexibility in manufacturing. The process also provides superior surface finish and accuracy, making it ideal for high-precision applications like aerospace and automotive components.
Applications of Gear Hobbing vs Gear Shaping
Gear hobbing excels in high-volume production of spur, helical, and worm gears due to its continuous cutting process and ability to generate precise involute profiles efficiently. Gear shaping suits low to medium volume manufacturing and internal gear cutting, especially for gears with complex shapes or limited accessibility where the workpiece remains stationary and the cutter reciprocates. Industries such as automotive and aerospace prefer hobbing for mass production, while gear shaping is favored for custom, intricate, or internal gear applications in heavy machinery and repair work.
Factors to Consider When Choosing a Gear Machining Method
Selecting between gear hobbing and gear shaping depends on factors like gear size, tooth profile complexity, and production volume. Gear hobbing excels in high-volume manufacturing and producing external gears with precision and speed, while gear shaping is favored for internal gears and intricate tooth geometries. Your choice should also consider machine availability, setup time, and cost efficiency to optimize the gear manufacturing process.
Conclusion: Which Gear Cutting Process is Best?
Gear hobbing offers faster production speeds and is ideal for high-volume manufacturing of spur and helical gears with excellent accuracy. Gear shaping provides superior precision for internal and external gears with complex profiles, making it better suited for low to medium volume runs and specialized applications. Your choice depends on production volume, gear type, and required tolerances, with hobbing favored for efficiency and shaping for precision.
Gear hob vs gear shaper Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com