A lathe shapes materials by rotating the workpiece against a fixed cutting tool, ideal for cylindrical parts, while a milling machine uses rotary cutters to remove material from a stationary workpiece for complex shapes and flat surfaces. Your choice depends on the specific machining task, with lathes suited for turning operations and milling machines excelling at precise, multi-axis cuts.
Table of Comparison
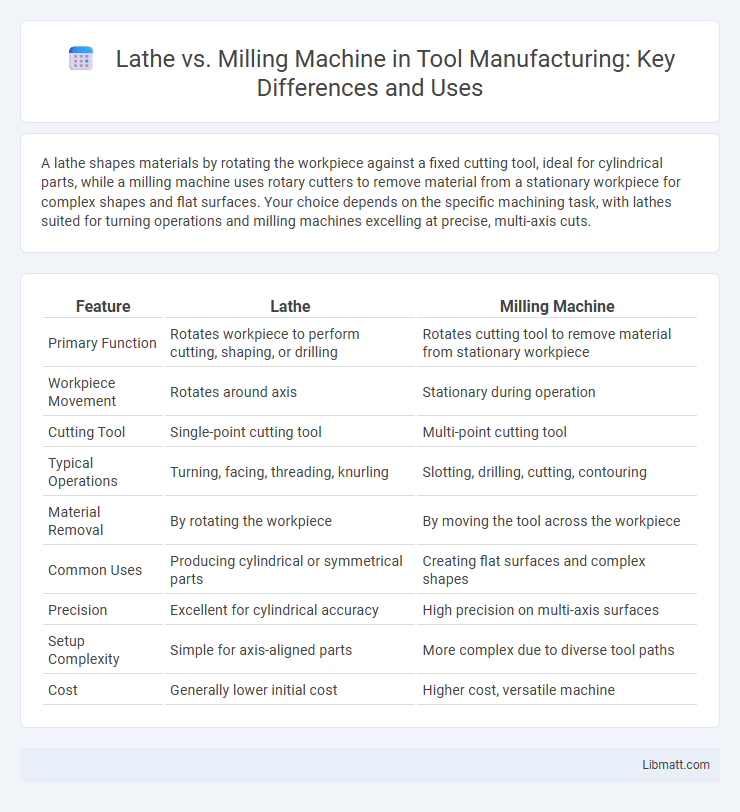
| Feature | Lathe | Milling Machine |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Function | Rotates workpiece to perform cutting, shaping, or drilling | Rotates cutting tool to remove material from stationary workpiece |
| Workpiece Movement | Rotates around axis | Stationary during operation |
| Cutting Tool | Single-point cutting tool | Multi-point cutting tool |
| Typical Operations | Turning, facing, threading, knurling | Slotting, drilling, cutting, contouring |
| Material Removal | By rotating the workpiece | By moving the tool across the workpiece |
| Common Uses | Producing cylindrical or symmetrical parts | Creating flat surfaces and complex shapes |
| Precision | Excellent for cylindrical accuracy | High precision on multi-axis surfaces |
| Setup Complexity | Simple for axis-aligned parts | More complex due to diverse tool paths |
| Cost | Generally lower initial cost | Higher cost, versatile machine |
Introduction to Lathe and Milling Machines
Lathe machines primarily focus on rotating workpieces to perform various operations such as cutting, sanding, or drilling, making them ideal for shaping cylindrical objects. Milling machines use rotary cutters to remove material by advancing workpieces against the cutting tool, offering precision in creating complex shapes and surfaces. Your choice between lathe and milling machines depends on the specific machining tasks and desired accuracy in manufacturing processes.
Key Differences Between Lathes and Milling Machines
Lathes primarily perform rotational cutting by spinning the workpiece against a stationary cutting tool, ideal for cylindrical shapes, while milling machines use rotary cutters to remove material from a stationary workpiece, allowing for complex flat or irregular surfaces. The key differences also include motion axes: lathes generally operate on two axes (X and Z), whereas milling machines often function on three or more axes (X, Y, Z), enhancing versatility in shaping parts. Understanding these distinctions helps you choose the appropriate machine for precise manufacturing or prototyping needs.
Core Functions and Applications
A lathe primarily performs rotational cutting operations, shaping cylindrical or conical parts by spinning the workpiece against a stationary cutting tool. Milling machines use rotary cutters to remove material from a stationary workpiece, enabling complex 3D shapes, slots, and surface profiles. Your choice between lathe and milling machine depends on whether precision spindle-focused turning or versatile multi-axis shaping is required for your project.
Design and Construction Comparison
Lathes feature a rotating spindle with a fixed cutting tool that shapes cylindrical workpieces, while milling machines utilize a rotating cutting tool to remove material from a stationary workpiece, allowing for complex surface contours. The construction of lathes includes a bed, headstock, tailstock, and carriage, designed to support and rotate the workpiece precisely, whereas milling machines consist of a worktable, spindle, and column that facilitate multi-axis movement and versatile cutting angles. Both machines rely on robust frameworks, but lathes emphasize rotational stability, and milling machines prioritize rigidity and precise tool positioning for diverse machining operations.
Typical Materials Processed
Lathe machines typically process materials such as metals like steel, aluminum, brass, and plastics, focusing on cylindrical or rotational parts. Milling machines handle a broader range of materials, including metals, wood, plastics, and composites, enabling complex shapes and flat surfaces to be machined. Both machines are essential in manufacturing for shaping parts but differ primarily in the type of material geometry they can efficiently produce.
Advantages of Using a Lathe
Lathes provide precise cylindrical shaping and turning capabilities, making them ideal for producing symmetrical parts like shafts and bolts. Their ability to handle high rotational speeds allows for efficient material removal and smooth surface finishes, enhancing overall productivity. You benefit from the lathe's versatility in performing various tasks such as cutting, drilling, and threading on different materials with consistent accuracy.
Benefits of Milling Machines
Milling machines offer high precision and versatility, enabling complex shapes and patterns to be created with ease, which is ideal for producing intricate parts in aerospace, automotive, and manufacturing industries. They provide superior surface finish quality and allow for multi-axis machining, improving efficiency and reducing production time. The capability to perform various cutting operations such as drilling, slotting, and contouring makes milling machines indispensable in modern machining processes.
Precision and Accuracy Considerations
Lathe machines excel in precision when shaping cylindrical objects, offering superior accuracy in rotational symmetry and concentricity, which is crucial for parts like shafts and bolts. Milling machines provide high precision in multi-axis operations, enabling intricate cuts and detailed surface finishes on flat or irregular surfaces. Your choice between lathe and milling machine should consider the specific geometric requirements and tolerance levels of your project to ensure optimal accuracy.
Cost and Maintenance Factors
Lathes generally have lower initial costs compared to milling machines, making them more accessible for small workshops and hobbyists. Maintenance for lathes tends to be simpler and less expensive due to fewer moving parts and less complex automation systems. Milling machines often require higher maintenance investment because of their intricate components, like multiple axes and advanced tooling systems, which also contribute to their higher overall cost.
Choosing the Right Machine for Your Project
Choosing between a lathe and a milling machine depends on the specific requirements of your project, such as the type of material, desired shape, and precision needed. Lathes excel in shaping cylindrical parts by rotating the workpiece, while milling machines are ideal for creating complex shapes and flat surfaces through rotating cutters. Evaluating the project's design complexity and production volume will help determine the machine that enhances efficiency and accuracy for your manufacturing process.
Lathe vs milling machine Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com