Grit blast uses angular abrasive grit to achieve aggressive surface cleaning and roughening, making it ideal for heavy-duty rust and paint removal. Shot blast employs spherical steel or ceramic shots to provide a smoother finish and compress the surface, enhancing durability without excessive material removal.
Table of Comparison
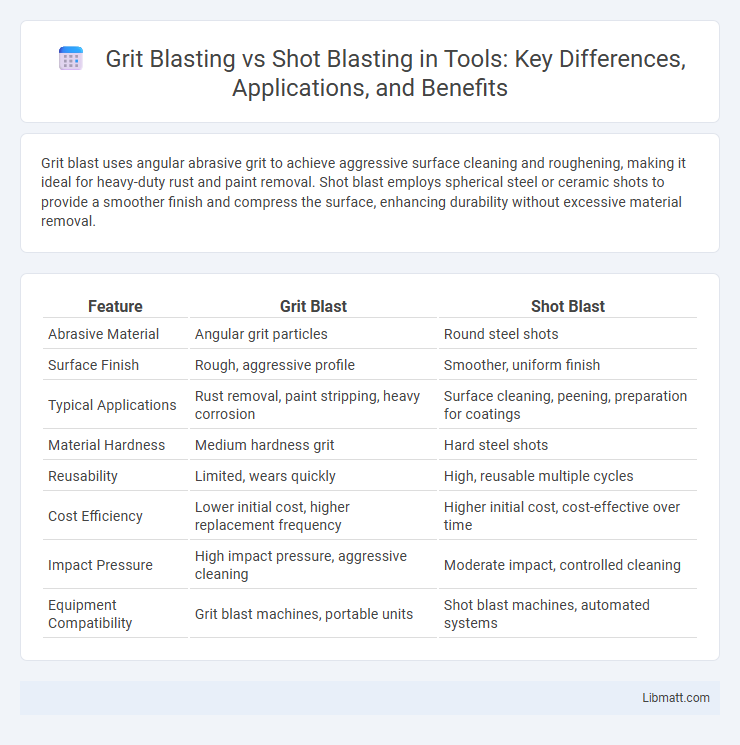
| Feature | Grit Blast | Shot Blast |
|---|---|---|
| Abrasive Material | Angular grit particles | Round steel shots |
| Surface Finish | Rough, aggressive profile | Smoother, uniform finish |
| Typical Applications | Rust removal, paint stripping, heavy corrosion | Surface cleaning, peening, preparation for coatings |
| Material Hardness | Medium hardness grit | Hard steel shots |
| Reusability | Limited, wears quickly | High, reusable multiple cycles |
| Cost Efficiency | Lower initial cost, higher replacement frequency | Higher initial cost, cost-effective over time |
| Impact Pressure | High impact pressure, aggressive cleaning | Moderate impact, controlled cleaning |
| Equipment Compatibility | Grit blast machines, portable units | Shot blast machines, automated systems |
Introduction to Surface Preparation Methods
Grit blast and shot blast are essential surface preparation methods used to clean, strengthen, or smooth metal surfaces before coating or painting. Grit blasting utilizes angular abrasive particles to create a rough profile for better coating adhesion, ideal for heavy rust or old paint removal. Shot blasting employs spherical steel shots to clean and strengthen surfaces while maintaining a smoother finish, making it suitable for delicate or precision applications on your metal parts.
Understanding Grit Blasting
Grit blasting uses abrasive particles like aluminum oxide or steel grit to clean or etch surfaces, providing a rough texture for better coating adhesion. Shot blasting employs spherical steel shots that impact surfaces with high velocity, ideal for heavy-duty cleaning and surface preparation on metal parts. Your choice between grit blast and shot blast depends on the desired surface finish and the specific material being treated.
Overview of Shot Blasting
Shot blasting uses high-velocity steel shots to clean, strengthen, or polish metal surfaces, providing a uniform finish and preparing surfaces for coating or painting. This method is effective in removing rust, scale, and contaminants, enhancing surface adhesion and durability. Shot blasting machines vary from portable units to large-scale industrial equipment, allowing for versatile applications in automotive, construction, and manufacturing industries.
Key Differences: Grit Blast vs Shot Blast
Grit blast uses abrasive particles like crushed glass or aluminum oxide to clean or prepare surfaces, creating a rough texture ideal for coating adhesion, while shot blast employs steel shots or balls to remove scale, rust, and old paint more aggressively, resulting in a smoother finish. The key difference lies in the media hardness and impact force, with grit blast being less aggressive and suitable for delicate surfaces, whereas shot blasting is preferred for heavy-duty cleaning and metal surface preparation. Your choice depends on the surface condition, desired finish, and specific industrial application.
Surface Finish and Texture Comparison
Grit blasting produces a rougher surface finish ideal for improving adhesion on coatings and paints, whereas shot blasting delivers a smoother and more uniform texture suited for preparing metal surfaces without deep abrasion. The angular particles in grit blasting create a more aggressive profile, enhancing mechanical bonding, while the spherical shape of shot blast media results in less surface deformation and a cleaner, glossy appearance. Choosing between grit blast and shot blast depends on the required surface roughness and the specific industrial application, such as metal fabrication or concrete surface preparation.
Applications: When to Use Grit Blasting
Grit blasting is ideal for heavy-duty surface preparation, such as removing thick coatings, rust, and scale from steel structures and machinery before painting or coating. It is preferred in industrial applications requiring aggressive cleaning to ensure strong adhesion and surface profile for protective coatings. Use grit blasting when dealing with robust materials or surfaces needing thorough abrasion to meet stringent surface preparation standards.
Applications: When to Use Shot Blasting
Shot blasting is ideal for preparing large metal surfaces such as steel plates, ship hulls, and heavy machinery parts requiring thorough cleaning and surface profiling to enhance coating adhesion. It is commonly used in industries like construction, automotive, and foundries where removal of rust, scale, and old paint is critical before applying new finishes. Shot blasting provides a consistent and efficient surface treatment, making it preferable over grit blasting for large-scale industrial applications demanding high productivity and uniform surface texture.
Equipment and Media Types
Grit blast equipment typically uses abrasive granules such as silica or aluminum oxide, effective for surface cleaning and preparation with a focused, high-impact stream. Shot blast systems employ steel or cast iron pellets that recycle continuously, ideal for heavy-duty applications like metal deburring and rust removal. The choice of media in shot blasting allows for higher durability and efficiency in industrial settings compared to the more abrasive and consumable grit media.
Environmental and Safety Considerations
Grit blast produces more dust and debris compared to shot blast, increasing the need for effective dust control measures to protect worker health and the environment. Shot blast uses steel shots that can be recycled multiple times, reducing waste and minimizing environmental impact. Both methods require appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) and ventilation systems to ensure safety during operation.
Cost Analysis and Efficiency
Grit blast systems typically have lower initial investment costs compared to shot blast machines, making them more budget-friendly for smaller projects or businesses. Shot blasting offers higher efficiency in material removal and surface preparation, resulting in faster project completion and lower long-term operational costs. Your choice should consider both upfront expenses and the desired throughput, as shot blasting delivers superior productivity for large-scale applications despite a higher initial cost.
Grit blast vs shot blast Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com