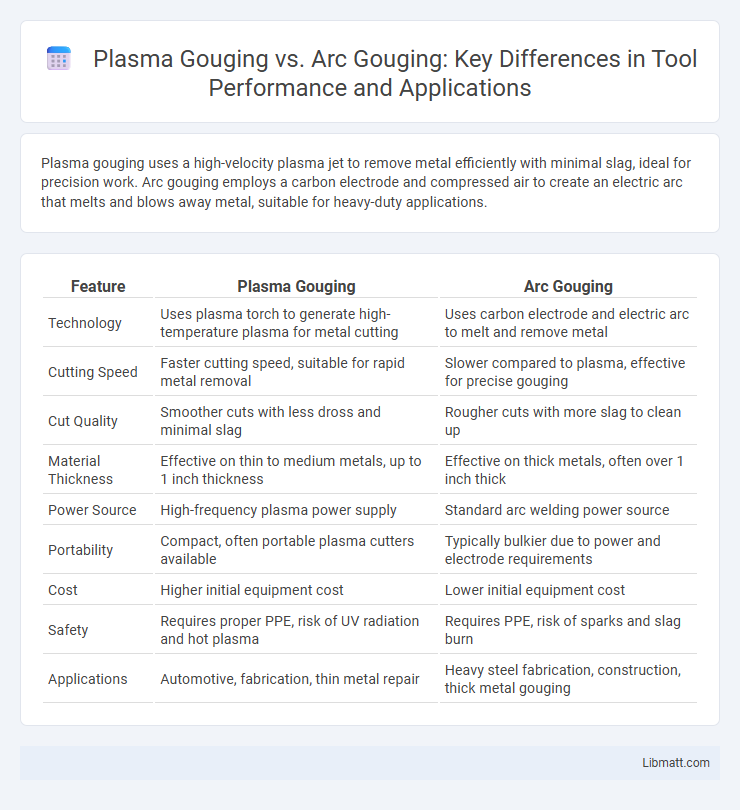
Plasma gouging uses a high-velocity plasma jet to remove metal efficiently with minimal slag, ideal for precision work. Arc gouging employs a carbon electrode and compressed air to create an electric arc that melts and blows away metal, suitable for heavy-duty applications.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Plasma Gouging | Arc Gouging |
|---|---|---|
| Technology | Uses plasma torch to generate high-temperature plasma for metal cutting | Uses carbon electrode and electric arc to melt and remove metal |
| Cutting Speed | Faster cutting speed, suitable for rapid metal removal | Slower compared to plasma, effective for precise gouging |
| Cut Quality | Smoother cuts with less dross and minimal slag | Rougher cuts with more slag to clean up |
| Material Thickness | Effective on thin to medium metals, up to 1 inch thickness | Effective on thick metals, often over 1 inch thick |
| Power Source | High-frequency plasma power supply | Standard arc welding power source |
| Portability | Compact, often portable plasma cutters available | Typically bulkier due to power and electrode requirements |
| Cost | Higher initial equipment cost | Lower initial equipment cost |
| Safety | Requires proper PPE, risk of UV radiation and hot plasma | Requires PPE, risk of sparks and slag burn |
| Applications | Automotive, fabrication, thin metal repair | Heavy steel fabrication, construction, thick metal gouging |
Introduction to Plasma Gouging and Arc Gouging
Plasma gouging utilizes a high-velocity jet of ionized gas to remove metal efficiently with precise control and minimal heat-affected zones, making it ideal for cleaning, shaping, and groove preparation. Arc gouging employs a carbon electrode to generate an electric arc that melts and ejects metal with slag, offering robust performance in heavy-duty metal removal and weld repair. Both methods serve critical roles in metal fabrication, with plasma gouging favored for speed and accuracy, while arc gouging is preferred for thicker, tougher materials.
Fundamental Principles of Plasma Gouging
Plasma gouging utilizes a high-velocity jet of ionized gas to melt and remove metal with precision, relying on the plasma arc's intense heat and stability. Unlike arc gouging, which employs a carbon electrode to generate a gouging arc for metal removal, plasma gouging offers cleaner cuts and greater control over depth and width. Your choice between plasma and arc gouging should consider factors such as material type, desired finish quality, and productivity requirements.
How Arc Gouging Works
Arc gouging works by utilizing a high-velocity stream of molten metal and slag propelled by compressed air through a carbon or graphite electrode, which creates a localized heat source that melts the base metal. The process effectively removes large volumes of metal quickly, making it ideal for heavy-duty applications like weld preparation and defect removal. Your choice between plasma gouging and arc gouging depends on factors such as cutting speed, precision, and material thickness.
Equipment Required for Plasma and Arc Gouging
Plasma gouging requires specialized plasma cutting machines equipped with high-frequency start systems, torch assemblies, and gas supply for plasma arc generation, ensuring precise metal removal. Arc gouging utilizes more straightforward equipment, including carbon electrodes, air compressors for slag removal, and standard welding power sources capable of sustaining a stable arc. Your choice between plasma and arc gouging equipment depends on project precision, metal type, and required cut quality.
Material Suitability: Metals and Alloys
Plasma gouging offers superior versatility for a wide range of metals and alloys, including stainless steel, aluminum, and high-strength steels, due to its high-energy plasma jet that efficiently cuts through both thick and thin materials. Arc gouging, typically using carbon electrodes, is highly effective on carbon steels and low alloy steels but less suitable for non-ferrous metals and materials with low electrical conductivity. The choice between plasma and arc gouging depends on material composition, thickness, and desired precision in metal removal.
Speed and Efficiency Comparison
Plasma gouging operates at higher speeds than arc gouging, often removing metal two to three times faster due to its concentrated plasma jet and higher energy density. The efficiency of plasma gouging is enhanced by reduced electrode wear and less slag formation, leading to quicker cleanup and longer operational periods. In contrast, arc gouging, while effective for thicker materials, tends to be slower and requires more frequent electrode replacement, resulting in lower overall productivity.
Surface Quality and Precision
Plasma gouging offers superior surface quality with minimal dross and a cleaner cut compared to arc gouging, resulting in smoother edges and less post-process cleanup. Precision is enhanced in plasma gouging due to its controlled, focused plasma arc, allowing for accurate material removal and detailed work on thinner metals. Your choice between plasma and arc gouging should consider the need for high-quality finishes and exactness, especially in applications demanding precise joint preparation or intricate cuts.
Safety Considerations in Plasma vs Arc Gouging
Plasma gouging offers enhanced safety by producing less smoke and fewer harmful gases compared to arc gouging, reducing respiratory hazards for operators. The controlled, localized heat in plasma gouging minimizes the risk of burns and fire, while arc gouging's high-temperature sparks and flying molten metal increase exposure to eye injuries and burns. Proper ventilation, personal protective equipment (PPE), and adherence to safety protocols remain critical in both methods to mitigate occupational risks.
Cost Analysis: Plasma Gouging vs Arc Gouging
Plasma gouging generally incurs higher initial equipment costs compared to arc gouging due to advanced technology and precision components. However, plasma gouging can reduce operational costs by offering faster cutting speeds, lower metal wastage, and less secondary finishing. Arc gouging features lower upfront expenses but may lead to increased labor and material costs over time because of slower processing and greater slag removal requirements.
Applications and Industry Use Cases
Plasma gouging is ideal for precise metal removal in aerospace and automotive manufacturing, where clean, controlled cuts are essential for component integrity. Arc gouging is widely used in heavy industries like shipbuilding and construction, effectively removing weld defects and preparing surfaces for repair on thick steel plates. Your choice between these methods depends on the required precision and metal thickness specific to your industrial application.
Plasma gouging vs arc gouging Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com