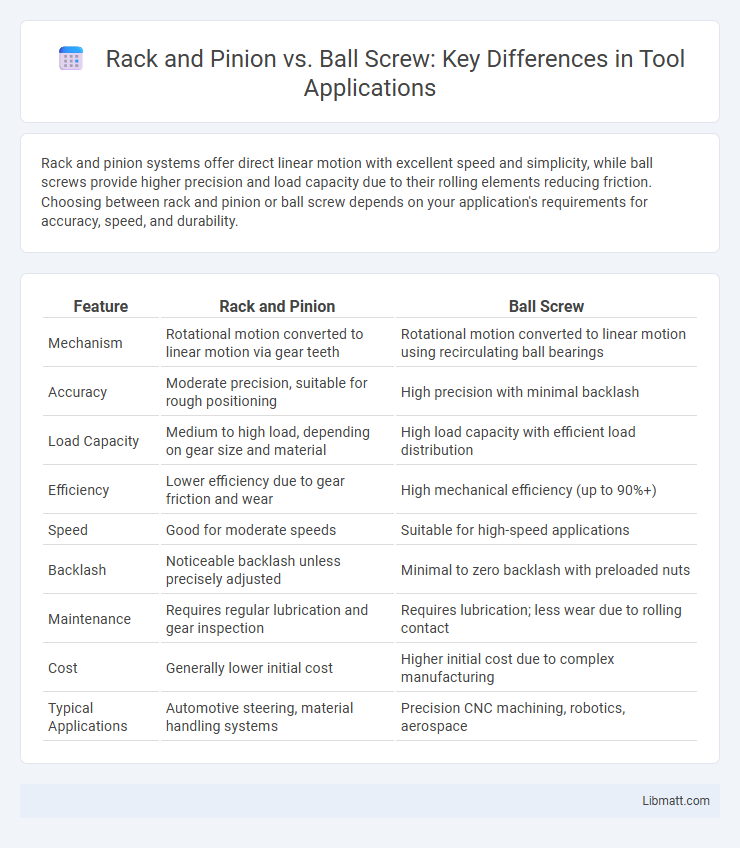
Rack and pinion systems offer direct linear motion with excellent speed and simplicity, while ball screws provide higher precision and load capacity due to their rolling elements reducing friction. Choosing between rack and pinion or ball screw depends on your application's requirements for accuracy, speed, and durability.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Rack and Pinion | Ball Screw |
|---|---|---|
| Mechanism | Rotational motion converted to linear motion via gear teeth | Rotational motion converted to linear motion using recirculating ball bearings |
| Accuracy | Moderate precision, suitable for rough positioning | High precision with minimal backlash |
| Load Capacity | Medium to high load, depending on gear size and material | High load capacity with efficient load distribution |
| Efficiency | Lower efficiency due to gear friction and wear | High mechanical efficiency (up to 90%+) |
| Speed | Good for moderate speeds | Suitable for high-speed applications |
| Backlash | Noticeable backlash unless precisely adjusted | Minimal to zero backlash with preloaded nuts |
| Maintenance | Requires regular lubrication and gear inspection | Requires lubrication; less wear due to rolling contact |
| Cost | Generally lower initial cost | Higher initial cost due to complex manufacturing |
| Typical Applications | Automotive steering, material handling systems | Precision CNC machining, robotics, aerospace |
Introduction to Rack and Pinion and Ball Screw Systems
Rack and pinion systems convert rotational motion into linear motion using a gear (pinion) engaging a toothed rail (rack), offering simplicity and durability in applications like steering and lifting. Ball screw systems use recirculating ball bearings to reduce friction and provide high precision and efficiency for positioning tasks in CNC machines and robotics. Selecting between these depends on your need for accuracy, load capacity, and maintenance preferences.
Basic Operating Principles
Rack and pinion systems convert rotational motion into linear motion through a gear (pinion) engaging with a toothed rack, providing direct and straightforward movement control. Ball screws utilize a threaded shaft and ball bearings to convert rotary motion to linear motion with high efficiency and minimal friction, offering precise positioning in applications requiring smooth operation. Both mechanisms serve linear motion tasks but differ significantly in mechanical design and efficiency characteristics.
Key Design Differences
Rack and pinion systems consist of a linear gear (rack) and a rotating gear (pinion) that convert rotational motion into linear motion, offering simplicity and high-speed capability. Ball screws use a threaded shaft and a nut with recirculating ball bearings, providing high precision, smooth motion, and superior load capacity. The key design difference lies in the contact mechanism: rack and pinion engage through direct gear teeth interaction, while ball screws rely on rolling elements to minimize friction and improve accuracy.
Precision and Accuracy Comparison
Rack and pinion systems offer moderate precision suitable for applications requiring quick linear movement with less stringent accuracy demands, while ball screws provide superior precision and repeatability due to their low backlash and high lead accuracy. The mechanical design of ball screws minimizes friction and ensures consistent positioning, making them ideal for CNC machines and precision machining tasks. You should choose ball screws when your application demands high accuracy and smooth motion control.
Load Capacity and Force Transmission
Rack and pinion systems excel in handling heavy loads and high-impact forces due to their robust tooth engagement, making them ideal for applications requiring high load capacity. Ball screws offer superior force transmission efficiency with minimal friction and smooth motion, resulting in precise positioning under moderate loads. For optimal load capacity combined with efficient force transmission, rack and pinion systems are preferred in heavy-duty applications, while ball screws suit precision-driven, lower load scenarios.
Speed and Efficiency Performance
Rack and pinion systems offer high-speed linear motion with rapid acceleration due to their direct mechanical connection, making them ideal for applications requiring quick repositioning. Ball screws provide superior efficiency by minimizing friction through rolling elements, resulting in precise movement and higher load capacity at moderate speeds. Your choice depends on whether speed or energy-efficient precision is the priority for your mechanical system.
Durability and Maintenance Requirements
Rack and pinion systems offer robust durability with simple maintenance, making them ideal for heavy-duty applications where frequent lubrication and inspection keep performance steady. Ball screws provide higher precision and efficiency but require more careful maintenance, including regular lubrication and protection against contamination to ensure longevity. Choosing between them depends on your need for durability with minimal upkeep or higher accuracy paired with meticulous care.
Cost Analysis and Budget Considerations
Rack and pinion systems generally offer lower initial costs due to simpler manufacturing and widespread availability, making them suitable for budget-conscious projects. Ball screws, while having higher upfront expenses, provide superior precision and efficiency, potentially reducing long-term maintenance costs and downtime. When analyzing cost-effectiveness, factors such as required accuracy, load capacity, and operational environment must be balanced against initial investment and lifecycle expenses.
Typical Applications in Industry
Rack and pinion mechanisms are commonly used in automotive steering systems, material handling equipment, and large-scale linear motion applications requiring high speed and moderate precision. Ball screws are preferred in CNC machinery, robotic arms, and precision manufacturing tools due to their superior accuracy, efficiency, and load capacity. Industries such as aerospace, semiconductor fabrication, and medical device production rely heavily on ball screws for precise control and repeatability.
Choosing the Right System for Your Needs
Selecting between rack and pinion and ball screw systems depends on precision, load capacity, and application speed. Rack and pinion excels in high-speed, long-travel applications with moderate accuracy, while ball screws offer superior positioning accuracy and efficiency for high-precision, lower-speed tasks. Assessing factors such as desired repeatability, stiffness, and environmental conditions ensures the optimal linear motion system choice for your specific engineering requirements.
Rack and pinion vs ball screw Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com