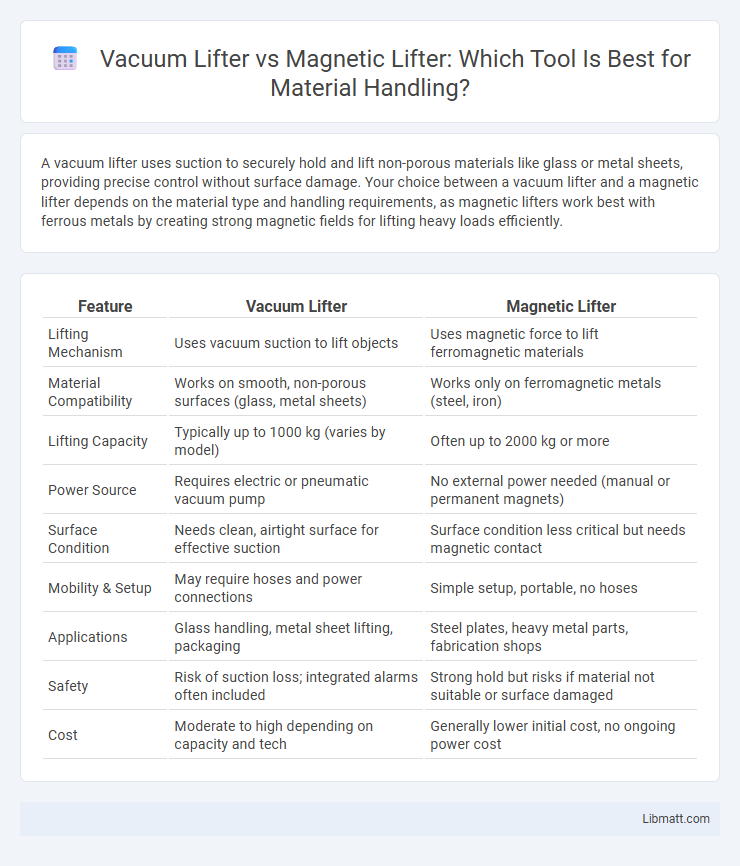
A vacuum lifter uses suction to securely hold and lift non-porous materials like glass or metal sheets, providing precise control without surface damage. Your choice between a vacuum lifter and a magnetic lifter depends on the material type and handling requirements, as magnetic lifters work best with ferrous metals by creating strong magnetic fields for lifting heavy loads efficiently.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Vacuum Lifter | Magnetic Lifter |
|---|---|---|
| Lifting Mechanism | Uses vacuum suction to lift objects | Uses magnetic force to lift ferromagnetic materials |
| Material Compatibility | Works on smooth, non-porous surfaces (glass, metal sheets) | Works only on ferromagnetic metals (steel, iron) |
| Lifting Capacity | Typically up to 1000 kg (varies by model) | Often up to 2000 kg or more |
| Power Source | Requires electric or pneumatic vacuum pump | No external power needed (manual or permanent magnets) |
| Surface Condition | Needs clean, airtight surface for effective suction | Surface condition less critical but needs magnetic contact |
| Mobility & Setup | May require hoses and power connections | Simple setup, portable, no hoses |
| Applications | Glass handling, metal sheet lifting, packaging | Steel plates, heavy metal parts, fabrication shops |
| Safety | Risk of suction loss; integrated alarms often included | Strong hold but risks if material not suitable or surface damaged |
| Cost | Moderate to high depending on capacity and tech | Generally lower initial cost, no ongoing power cost |
Introduction: Understanding Material Lifting Solutions
Vacuum lifters and magnetic lifters offer distinct advantages for material handling based on the type of materials and lifting environments. Vacuum lifters use suction to lift non-porous or smooth surfaces, while magnetic lifters target ferrous metals with strong magnetic fields for secure grip. Your choice depends on material composition, weight, and operational efficiency requirements in industrial settings.
What is a Vacuum Lifter?
A vacuum lifter uses suction cups powered by vacuum pressure to securely grip and lift heavy objects, making it ideal for handling smooth, non-porous surfaces like glass, metal, or plastic. Its versatile design allows precise control and reduces the risk of surface damage during material handling in industries such as manufacturing, construction, and warehousing. Understanding how a vacuum lifter operates can help you choose the right lifting equipment for your specific application needs.
What is a Magnetic Lifter?
A magnetic lifter is a device that uses powerful permanent magnets to lift and transport heavy ferrous metal objects without requiring electricity. It provides a secure grip on steel plates, pipes, and other metal components, enhancing safety and efficiency in material handling applications. Magnetic lifters are favored for their durability, ease of use, and ability to operate in various industrial environments where vacuum lifters may be less effective.
Key Differences Between Vacuum and Magnetic Lifters
Vacuum lifters use suction to securely hold smooth, non-porous materials like glass and metal, making them ideal for delicate surfaces without causing damage. Magnetic lifters rely on strong magnets to lift ferrous metals, offering a robust grip but limited to magnetic materials only. Your choice depends on the material type and surface condition, with vacuum lifters suited for gentle handling and magnetic lifters preferred for heavy-duty ferrous metal lifting.
Applications of Vacuum Lifters
Vacuum lifters are widely used in industries such as glass handling, sheet metal fabrication, and woodworking for safely lifting and transporting smooth, non-porous materials without causing damage. Their ability to create a secure suction grip makes them ideal for handling fragile items like glass panes, plastic sheets, and coated metals. Your choice of vacuum lifter ensures enhanced productivity and reduced manual labor risks in environments requiring careful material manipulation.
Applications of Magnetic Lifters
Magnetic lifters are widely used in industries for handling ferrous metal materials such as steel plates, pipes, and heavy machinery components, making them ideal for manufacturing, construction, and scrap yards. They provide safe and efficient lifting without the need for clamps, slings, or adhesives, enhancing productivity in metal fabrication and assembly lines. Their ability to quickly attach and release metal loads supports seamless material handling in shipbuilding and warehouse operations.
Advantages of Vacuum Lifters
Vacuum lifters offer significant advantages including the ability to handle non-metallic, porous, and irregularly shaped materials that magnetic lifters cannot securely grip. Their versatility extends to lifting a wide range of surface types without causing damage, making them ideal for glass, wood, and plastic. Your operations benefit from improved safety and reduced risk of material deformation with vacuum lifters' reliable suction technology.
Advantages of Magnetic Lifters
Magnetic lifters provide powerful and reliable lifting capabilities for ferromagnetic materials, enabling faster and safer handling without the need for clamps or straps. These lifters require minimal maintenance, eliminating the risk of vacuum leaks and offering a continuous gripping force independent of power supply once activated. Their compact design and ease of operation enhance efficiency in heavy-duty industrial environments, making them ideal for handling steel plates, bars, and cylindrical objects.
Factors to Consider When Choosing Between Vacuum and Magnetic Lifters
When choosing between vacuum lifters and magnetic lifters, consider the material type, surface condition, and weight of the load to ensure optimal safety and efficiency. Vacuum lifters excel with non-ferrous, smooth surfaces and lighter loads, while magnetic lifters are ideal for ferrous materials and heavier weights without surface contamination. Your specific lifting application, including environmental factors and required holding power, will determine the best choice for your operational needs.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Lifter for Your Needs
Vacuum lifters excel in handling smooth, non-porous surfaces with a gentle grip, making them ideal for glass and sheet metal, while magnetic lifters provide strong adhesion for ferrous materials like steel with no power source required. Your choice depends on the material type, weight capacity, and surface condition of the load you need to move. Selecting the right lifter ensures safety, efficiency, and optimal performance tailored to your specific lifting requirements.
Vacuum lifter vs magnetic lifter Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com