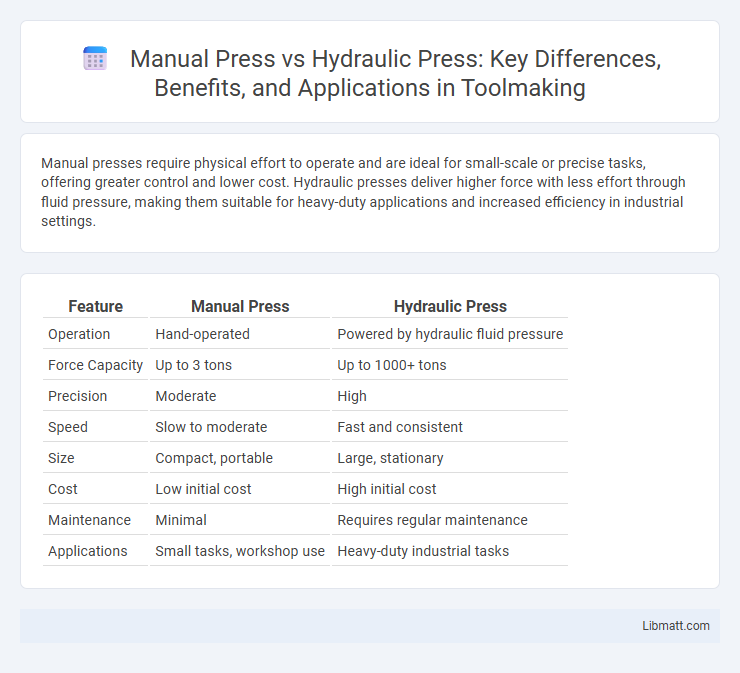
Manual presses require physical effort to operate and are ideal for small-scale or precise tasks, offering greater control and lower cost. Hydraulic presses deliver higher force with less effort through fluid pressure, making them suitable for heavy-duty applications and increased efficiency in industrial settings.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Manual Press | Hydraulic Press |
|---|---|---|
| Operation | Hand-operated | Powered by hydraulic fluid pressure |
| Force Capacity | Up to 3 tons | Up to 1000+ tons |
| Precision | Moderate | High |
| Speed | Slow to moderate | Fast and consistent |
| Size | Compact, portable | Large, stationary |
| Cost | Low initial cost | High initial cost |
| Maintenance | Minimal | Requires regular maintenance |
| Applications | Small tasks, workshop use | Heavy-duty industrial tasks |
Introduction to Manual and Hydraulic Presses
Manual presses operate through direct human force, making them ideal for small-scale tasks requiring precision and control, while hydraulic presses utilize fluid pressure to generate powerful, consistent force suitable for heavy-duty industrial applications. Manual presses offer portability and cost-effectiveness for light-duty operations, whereas hydraulic presses provide higher tonnage, versatility, and automation potential, enhancing productivity in manufacturing processes. Selecting between manual and hydraulic presses depends on factors like production volume, force requirements, and operational efficiency.
Key Differences Between Manual and Hydraulic Presses
Manual presses require human force to generate pressure, making them suitable for low-volume or precision tasks, while hydraulic presses use fluid power to produce high and consistent force for heavy-duty applications. Hydraulic presses offer greater control over pressure and speed, enabling repetitive and complex operations with enhanced safety features. Manual presses are typically more affordable and simpler to maintain, but hydraulic presses provide superior efficiency and versatility in industrial manufacturing.
Working Principles of Manual Presses
Manual presses operate through direct human force applied on a lever or handle, transferring mechanical energy to shape or cut materials via a simple linkage mechanism. These presses typically use a screw, cam, or toggle system to multiply the input force, enabling precision control during operations such as punching, embossing, or assembling. Unlike hydraulic presses, manual presses rely on operator strength and skill, making them ideal for low-volume, detailed tasks requiring minimal power.
How Hydraulic Presses Operate
Hydraulic presses operate by using Pascal's principle, where fluid pressure applied to a confined liquid transmits force evenly throughout the system, enabling powerful and precise pressing actions. The hydraulic cylinder exerts force on the ram, which compresses the material with consistent pressure, making it ideal for heavy-duty applications such as metal forming and molding. Your choice of a hydraulic press ensures efficient operation with adjustable force control, surpassing the manual press in strength and reliability.
Applications: Manual Press vs Hydraulic Press
Manual presses are ideal for small-scale applications such as jewelry making, assembly tasks, and light metalworking, offering precision and control in low-volume production. Hydraulic presses excel in heavy-duty applications including automotive part manufacturing, metal forming, and large-scale stamping, delivering high force and consistent pressure for repetitive tasks. The choice depends on production volume and force requirements, with manual presses suited for detailed, low-force operations and hydraulic presses designed for industrial-strength tasks.
Advantages of Manual Presses
Manual presses offer significant advantages such as greater control and precision for small-scale or detailed work, making them ideal for intricate tasks requiring careful handling. They are more affordable and require less maintenance compared to hydraulic presses, reducing operational costs for your workshop or production line. Their compact size and ease of transport also make manual presses a practical choice for limited space environments or mobile applications.
Benefits of Hydraulic Presses
Hydraulic presses offer superior force control and consistency, enabling precise metal forming and shaping with minimal operator fatigue. Their ability to generate high pressure with lower energy consumption enhances efficiency and reduces operational costs in industrial applications. Advanced safety features and automated controls in hydraulic presses contribute to improved workplace safety and productivity.
Limitations and Challenges of Each Press Type
Manual presses often face limitations in applying consistent force and handling high-volume production due to operator fatigue and limited pressure capacity. Hydraulic presses, while capable of delivering greater force and precision, experience challenges such as higher maintenance costs, slower cycle times, and complex hydraulic system failures. Understanding the specific operational demands of your workflow helps determine which press type best mitigates these limitations for efficiency and reliability.
Cost and Maintenance Comparison
Manual presses generally have lower upfront costs and simpler maintenance requirements due to their mechanical operation and fewer components. Hydraulic presses involve higher initial investment but offer greater durability and efficiency, resulting in longer service life with periodic hydraulic fluid checks and seal replacements. Maintenance expenses for hydraulic presses tend to be higher, though their performance benefits can justify the cost in heavy-duty or high-volume production settings.
Choosing the Right Press for Your Needs
Selecting the right press depends on the specific requirements of your project, including force capacity, precision, and frequency of use. Manual presses offer greater control and are ideal for light-duty tasks or occasional use, while hydraulic presses deliver higher power and consistency suited for heavy-duty or repetitive operations. Assessing your production volume and material specifications ensures you choose a press that maximizes efficiency and meets your manufacturing demands.
Manual press vs hydraulic press Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com