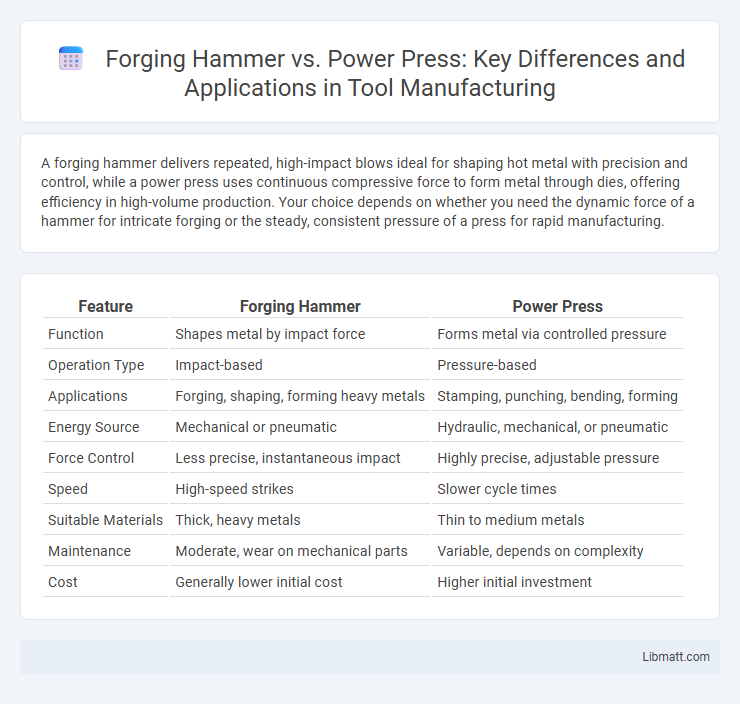
A forging hammer delivers repeated, high-impact blows ideal for shaping hot metal with precision and control, while a power press uses continuous compressive force to form metal through dies, offering efficiency in high-volume production. Your choice depends on whether you need the dynamic force of a hammer for intricate forging or the steady, consistent pressure of a press for rapid manufacturing.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Forging Hammer | Power Press |
|---|---|---|
| Function | Shapes metal by impact force | Forms metal via controlled pressure |
| Operation Type | Impact-based | Pressure-based |
| Applications | Forging, shaping, forming heavy metals | Stamping, punching, bending, forming |
| Energy Source | Mechanical or pneumatic | Hydraulic, mechanical, or pneumatic |
| Force Control | Less precise, instantaneous impact | Highly precise, adjustable pressure |
| Speed | High-speed strikes | Slower cycle times |
| Suitable Materials | Thick, heavy metals | Thin to medium metals |
| Maintenance | Moderate, wear on mechanical parts | Variable, depends on complexity |
| Cost | Generally lower initial cost | Higher initial investment |
Introduction to Forging Hammer and Power Press
Forging hammers deliver high-impact force through a heavy, free-falling weight, ideal for shaping metal with precision and texture. Power presses use hydraulic or mechanical energy to apply controlled pressure, enabling consistent and repetitive stamping or forming tasks in manufacturing. Your choice between these tools depends on the required force, material properties, and the desired level of automation in the production process.
Definition and Working Principle of Forging Hammer
A forging hammer is a mechanical tool that shapes metal by delivering high-impact blows, using a heavy ram lifted and dropped onto the workpiece. It operates on the principle of converting potential energy, stored by raising the hammer, into kinetic energy during the fall, thereby deforming the metal through repeated strikes. Unlike power presses that exert continuous pressure, forging hammers produce rapid, percussive force for shaping hot or cold metal.
Definition and Working Principle of Power Press
A power press is a mechanical device used for shaping or cutting metal by applying high force through a die, driven by an electric motor or flywheel. It works on the principle of converting rotary motion into linear motion, where the ram moves downwards to exert pressure on the workpiece positioned on the bed. This equipment offers precise control and consistent force, making it suitable for high-volume metal forming compared to the manual or hydraulic action of a forging hammer.
Key Differences Between Forging Hammer and Power Press
Forging hammers deliver rapid, high-impact blows ideal for shaping metal through repeated strikes, while power presses apply controlled, consistent force for precise metal forming tasks such as stamping and punching. The hammer's kinetic energy enables deformation at high speeds, making it suitable for heavy forging, whereas the power press utilizes hydraulic or mechanical pressure for accuracy and repeatability in mass production. Understanding these distinctions helps you choose the optimal equipment for your metalworking needs, balancing force type, precision, and application scale.
Applications of Forging Hammer in Industry
Forging hammers are widely used in the automotive, aerospace, and construction industries for shaping metal components with high precision and strength. Their ability to deliver rapid, high-impact force makes them ideal for producing large, complex parts such as crankshafts, gears, and heavy-duty tools. You can rely on forging hammers to create durable, high-quality metal products that withstand extreme conditions and heavy usage.
Common Uses of Power Press in Manufacturing
Power presses in manufacturing are commonly used for tasks such as stamping, punching, bending, and forming metal sheets with high precision and speed. These machines excel in repetitive, high-volume production environments where consistent force and accuracy are critical. Unlike forging hammers, power presses offer controlled, mechanical force ideal for intricate sheet metal fabrication and assembly line automation.
Advantages of Forging Hammer over Power Press
Forging hammers offer superior impact energy, which results in better material flow and improved grain structure, enhancing the mechanical properties of forged components compared to power presses. They enable greater versatility in shaping complex and large workpieces due to their high force and rapid strike capability. Forging hammers also provide faster production rates for certain applications, reducing cycle times and increasing overall manufacturing efficiency.
Advantages of Power Press over Forging Hammer
Power presses offer superior precision and repeatability compared to forging hammers, enabling consistent production of complex metal parts with tight tolerances. The automated nature of power presses reduces labor costs and enhances safety by minimizing manual intervention during metal forming processes. Furthermore, power presses provide higher energy efficiency and faster production rates, making them ideal for large-scale manufacturing environments.
Factors to Consider When Choosing Between Forging Hammer and Power Press
When choosing between a forging hammer and a power press, key factors include the required precision, production volume, and material type. Forging hammers excel at high-impact, rapid metal deformation suitable for heavy, irregular shapes, whereas power presses offer precise, consistent force ideal for complex, repeatable parts. Consider energy efficiency, maintenance costs, and customization capabilities to optimize manufacturing productivity and product quality.
Conclusion: Forging Hammer vs Power Press – Which is Better?
Forging hammers deliver superior impact force ideal for shaping heavy-duty metal components, while power presses offer precise control and consistency for high-volume production. Your choice depends on the specific manufacturing requirements: forging hammers excel in custom, robust forging, whereas power presses optimize efficiency and accuracy in repetitive tasks. Evaluating factors such as production speed, part complexity, and material type determines which technology better suits your industrial application.
Forging hammer vs power press Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com