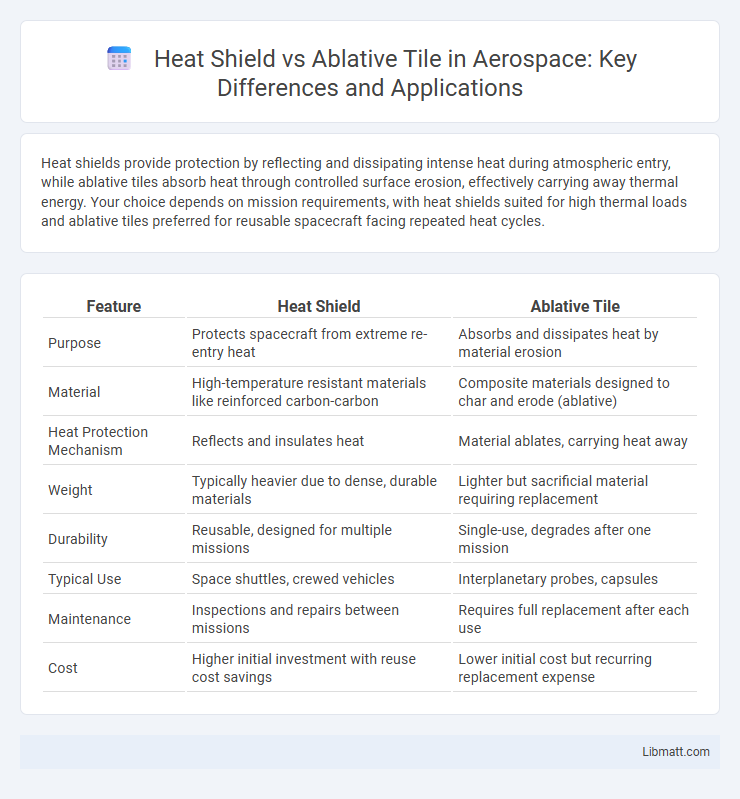
Heat shields provide protection by reflecting and dissipating intense heat during atmospheric entry, while ablative tiles absorb heat through controlled surface erosion, effectively carrying away thermal energy. Your choice depends on mission requirements, with heat shields suited for high thermal loads and ablative tiles preferred for reusable spacecraft facing repeated heat cycles.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Heat Shield | Ablative Tile |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Protects spacecraft from extreme re-entry heat | Absorbs and dissipates heat by material erosion |
| Material | High-temperature resistant materials like reinforced carbon-carbon | Composite materials designed to char and erode (ablative) |
| Heat Protection Mechanism | Reflects and insulates heat | Material ablates, carrying heat away |
| Weight | Typically heavier due to dense, durable materials | Lighter but sacrificial material requiring replacement |
| Durability | Reusable, designed for multiple missions | Single-use, degrades after one mission |
| Typical Use | Space shuttles, crewed vehicles | Interplanetary probes, capsules |
| Maintenance | Inspections and repairs between missions | Requires full replacement after each use |
| Cost | Higher initial investment with reuse cost savings | Lower initial cost but recurring replacement expense |
Introduction to Thermal Protection Systems
Thermal protection systems are essential components in spacecraft, designed to shield vehicles from extreme heat during atmospheric re-entry. Heat shields typically use ablative tiles that absorb and dissipate heat by gradually burning away, protecting your spacecraft's structural integrity. This technology ensures safe transit through high-temperature environments by managing thermal loads effectively.
What is a Heat Shield?
A heat shield is a protective barrier designed to absorb, reflect, or dissipate intense heat generated during atmospheric reentry or high-speed flight, safeguarding spacecraft and vehicles from thermal damage. Unlike ablative tiles that gradually burn away to manage heat, heat shields can be made from various materials, including reinforced carbon-carbon composites or ceramic coatings, providing reusable thermal protection. These shields are critical for maintaining the structural integrity and safety of space vehicles during extreme thermal conditions.
What are Ablative Tiles?
Ablative tiles are thermal protection materials designed to absorb and dissipate heat through a controlled erosion process during spacecraft reentry. These tiles protect spacecraft by gradually burning away, carrying heat away from the vehicle, unlike conventional heat shields that mainly reflect or insulate heat. Their lightweight and highly effective heat absorption capabilities make ablative tiles essential for missions involving extreme atmospheric reentry conditions.
Key Functions: Heat Shield vs Ablative Tile
Heat shields primarily protect spacecraft from extreme heat during atmospheric re-entry by reflecting and dissipating thermal energy, while ablative tiles safeguard by gradually eroding and absorbing heat through a controlled sacrificial process. Both systems are critical for thermal protection, but heat shields are typically reusable, whereas ablative tiles are designed for single-use missions due to their material degradation. Selecting the right option depends on mission duration, reusability requirements, and thermal environment conditions.
Material Composition Differences
Heat shields typically consist of reusable materials such as reinforced carbon-carbon or ceramic composites designed to withstand high temperatures and thermal cycling. Ablative tiles use sacrificial materials like phenolic resin or carbon-based composites that erode or char upon re-entry to dissipate heat effectively. The primary material composition difference lies in heat shields prioritizing durability and reusability, while ablative tiles focus on controlled material ablation for thermal protection.
Durability and Reusability Comparison
Heat shields made from ablative tiles offer high durability by gradually eroding during reentry, effectively dissipating heat but sacrificing reusability as the tiles require replacement after each mission. In contrast, reusable heat shields utilize advanced ceramic materials designed to withstand multiple reentries without significant damage, enhancing mission cost-efficiency and turnaround time. The choice between ablative tiles and reusable ceramic heat shields depends on mission requirements, balancing durability with the potential for repeated use.
Installation and Maintenance Factors
Heat shields typically require easier installation due to their rigid structure and fewer individual components compared to ablative tiles, which involve meticulous placement and bonding of numerous lightweight tiles. Maintenance for heat shields is generally lower, as their durable material withstands multiple reentries without significant degradation, whereas ablative tiles demand frequent inspection and replacement after each mission due to their sacrificial nature. The complexity and time-intensive upkeep of ablative tiles significantly increase operational costs and downtime compared to the more robust, reusable heat shields.
Performance in Spacecraft Re-entry
Ablative tiles excel in dissipating intense heat during spacecraft re-entry by gradually eroding and carrying away thermal energy, providing robust protection against extreme temperatures. Heat shields, often made from reinforced carbon-carbon or metallic materials, offer structural integrity and reusable thermal protection by absorbing and radiating heat without significant material loss. The choice between ablative tiles and heat shields depends on mission requirements, such as reusability, weight constraints, and peak thermal loads experienced during atmospheric descent.
Cost-Effectiveness Analysis
Heat shields generally offer greater cost-effectiveness than ablative tiles due to their ability to be reused multiple times, reducing long-term expenses in spacecraft missions. Ablative tiles require replacement after each mission, increasing maintenance costs and turnaround time. Your choice depends on mission frequency and budget constraints, with heat shields favored for repeated reentry scenarios.
Which Option is Better for Modern Spacecraft?
Heat shields and ablative tiles serve critical roles in spacecraft thermal protection, with ablative tiles offering superior performance due to their ability to absorb and dissipate intense reentry heat through controlled material erosion. Modern spacecraft often prefer ablative tiles for their lightweight properties, enhanced durability, and adaptability to diverse mission profiles, especially in high-velocity atmospheric entries. Advanced heat shield technologies, while still relevant, typically face limitations in weight and reusability compared to ablative materials optimized for contemporary aerospace demands.
heat shield vs ablative tile Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com