2-wire sensors simplify wiring by combining power and signal lines, making them ideal for long-distance applications with minimal installation effort. 4-wire sensors provide separate power and signal connections, enhancing accuracy and reducing interference, which benefits your system when precision is critical.
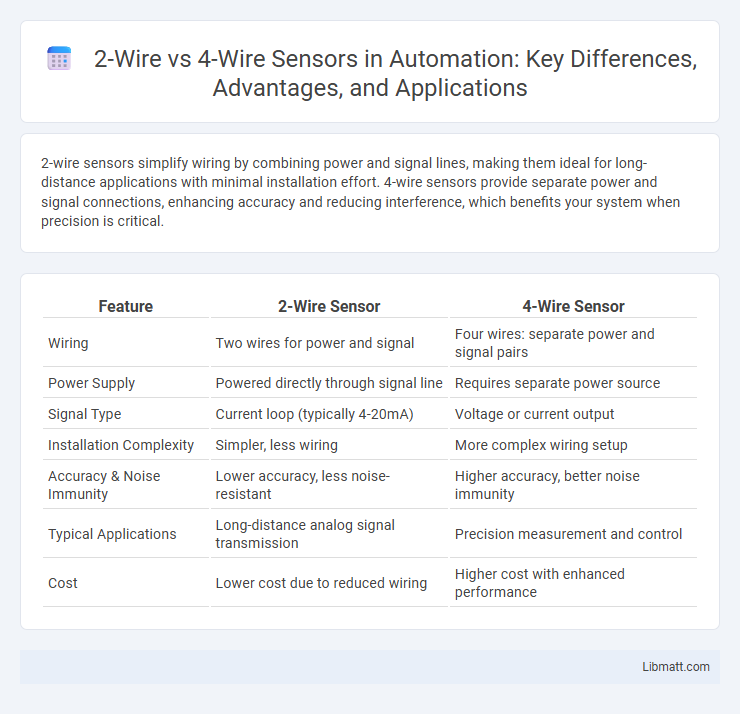
Table of Comparison
| Feature | 2-Wire Sensor | 4-Wire Sensor |
|---|---|---|
| Wiring | Two wires for power and signal | Four wires: separate power and signal pairs |
| Power Supply | Powered directly through signal line | Requires separate power source |
| Signal Type | Current loop (typically 4-20mA) | Voltage or current output |
| Installation Complexity | Simpler, less wiring | More complex wiring setup |
| Accuracy & Noise Immunity | Lower accuracy, less noise-resistant | Higher accuracy, better noise immunity |
| Typical Applications | Long-distance analog signal transmission | Precision measurement and control |
| Cost | Lower cost due to reduced wiring | Higher cost with enhanced performance |
Introduction to 2-Wire and 4-Wire Sensors
2-wire sensors integrate power and signal transmission within two wires, offering simplified installation and reduced wiring costs, commonly used in proximity and temperature sensing applications. In contrast, 4-wire sensors separate power supply and signal output through distinct pairs of wires, enabling improved signal accuracy and noise resistance, favored in precision measurement environments. Choosing between 2-wire and 4-wire configurations depends on factors such as system complexity, required signal fidelity, and environmental interference.
Basic Working Principles
A 2-wire sensor operates by using the same pair of wires for both power supply and signal transmission, typically relying on current loops like the 4-20mA standard to transmit sensor data efficiently over long distances with minimal interference. In contrast, a 4-wire sensor separates the power supply and signal lines, providing dedicated wires for power input and signal output, which allows for more stable and accurate voltage-based signal transmission. The choice between 2-wire and 4-wire sensors depends on application requirements such as distance, accuracy, and power availability.
Key Differences Between 2-Wire and 4-Wire Sensors
2-wire sensors integrate power and signal transmission within the same two wires, simplifying installation and reducing wiring costs, but they may suffer from signal loss over long distances. In contrast, 4-wire sensors separate power and signal lines, providing more stable and accurate readings, especially in industrial environments requiring high precision. The 4-wire configuration typically supports higher power devices and allows for easier troubleshooting due to distinct power and signal paths.
Advantages of 2-Wire Sensors
2-wire sensors offer the advantage of simplified wiring and reduced installation costs by combining power and signal transmission into a single pair of wires. You benefit from easier maintenance and enhanced reliability in industrial environments due to fewer connection points prone to failure. Their compact design often allows for better integration into space-constrained applications while maintaining accurate sensor performance.
Advantages of 4-Wire Sensors
4-wire sensors offer improved accuracy and stability by separating the current supply and voltage measurement lines, which minimizes the effects of lead resistance and voltage drops. These sensors provide more reliable readings essential for precision applications, particularly over long cable runs. Your measurements benefit from reduced noise and enhanced signal integrity compared to 2-wire sensor configurations.
Common Applications for 2-Wire Sensors
2-wire sensors are commonly used in industrial automation, process control, and HVAC systems due to their simplicity and cost-effectiveness. These sensors typically operate with a 4-20 mA current loop, making them ideal for long-distance signal transmission in harsh environments. Their minimal wiring requirements reduce installation complexity and maintenance costs in applications such as level measurement, pressure monitoring, and flow control.
Common Applications for 4-Wire Sensors
4-wire sensors are commonly used in applications requiring precise and stable measurements, such as industrial automation, laboratory instrumentation, and process control systems. Their separate excitation and measurement wires minimize the effects of lead resistance and ensure high accuracy, making them ideal for strain gauges, thermocouples, and precision temperature sensors. Your systems will benefit from enhanced signal integrity when employing 4-wire sensors in scenarios demanding exact electrical characterization.
Wiring and Installation Considerations
2-wire sensors simplify wiring by combining the power supply and signal transmission into two wires, reducing installation complexity and material costs. 4-wire sensors separate power and signal lines, providing more accurate measurements and minimizing signal interference but requiring additional wiring effort. Selection depends on installation environment, required signal integrity, and budget constraints.
Selecting the Right Sensor for Your Application
Selecting the right sensor involves understanding the differences between 2-wire and 4-wire configurations, where 2-wire sensors simplify wiring and reduce installation costs but may offer limited accuracy and signal stability. In contrast, 4-wire sensors provide separate power and signal lines, enhancing measurement precision, minimizing electrical noise, and supporting longer cable runs, which is critical in industrial environments. Application requirements such as distance, accuracy, and environmental conditions must guide the choice to ensure optimal sensor performance and reliable data acquisition.
Conclusion: 2-Wire vs 4-Wire Sensor Comparison
2-wire sensors simplify installation and reduce wiring costs by combining power and signal transmission over the same pair of wires, making them ideal for basic monitoring tasks with limited distance. In contrast, 4-wire sensors provide separate paths for power and signal, enhancing measurement accuracy, reducing electrical noise, and supporting longer cable runs critical in industrial automation and precise control systems. Choosing between 2-wire and 4-wire sensors depends on factors like required signal fidelity, installation complexity, and environmental conditions.
2-wire vs 4-wire Sensor Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com