Batching systems handle materials in discrete, measured quantities, ensuring precise control over each batch's composition, while blending systems continuously mix components to achieve a uniform product. Your choice between these systems depends on production requirements, with batching offering flexibility for varied recipes and blending providing efficiency for consistent mixtures.
Table of Comparison
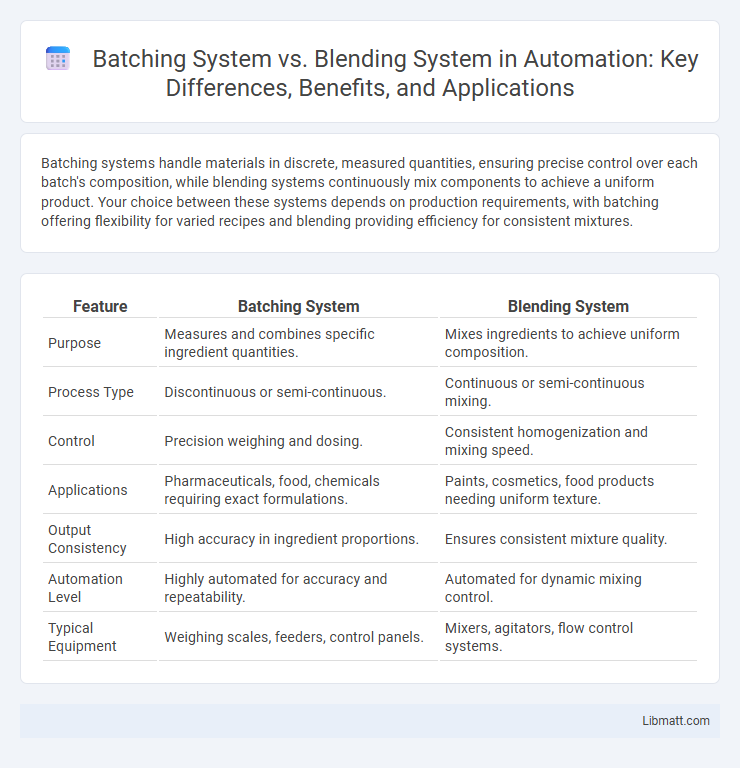
| Feature | Batching System | Blending System |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Measures and combines specific ingredient quantities. | Mixes ingredients to achieve uniform composition. |
| Process Type | Discontinuous or semi-continuous. | Continuous or semi-continuous mixing. |
| Control | Precision weighing and dosing. | Consistent homogenization and mixing speed. |
| Applications | Pharmaceuticals, food, chemicals requiring exact formulations. | Paints, cosmetics, food products needing uniform texture. |
| Output Consistency | High accuracy in ingredient proportions. | Ensures consistent mixture quality. |
| Automation Level | Highly automated for accuracy and repeatability. | Automated for dynamic mixing control. |
| Typical Equipment | Weighing scales, feeders, control panels. | Mixers, agitators, flow control systems. |
Introduction to Batching and Blending Systems
Batching systems measure and combine precise quantities of materials sequentially, ensuring accuracy in production processes like concrete mixing or food processing. Blending systems continuously mix ingredients in specific proportions to achieve uniformity and consistency in products such as paints or chemicals. Understanding your production needs helps determine whether a batching or blending system optimizes efficiency and quality.
Overview of Batching Systems
Batching systems are automated processes designed to measure and combine specific quantities of materials to create a mixture or product. These systems ensure precise control over ingredient proportions, improving consistency and quality in industries such as construction, food production, and pharmaceuticals. You can optimize production efficiency and reduce waste by implementing a batching system tailored to your operational requirements.
Overview of Blending Systems
Blending systems combine multiple raw materials or ingredients to create a homogeneous mixture, ensuring consistent product quality across batches in industries like food, pharmaceuticals, and chemicals. These systems utilize precise measurement and mixing technologies to optimize formulation accuracy and process efficiency. Advanced blending systems incorporate automated controls and sensors to maintain uniformity and reduce production variability.
Key Differences Between Batching and Blending
Batching systems precisely measure and dispense individual ingredients sequentially, ensuring accuracy and consistency in each batch, while blending systems combine ingredients continuously or intermittently to create a homogeneous mixture. The key differences lie in their operational methods: batching controls quantity for discrete production, whereas blending focuses on uniform mixing of materials during processing. Your choice depends on whether precise measurement or uniform mixture quality is the primary requirement in your production line.
Efficiency Comparison: Batching vs Blending
Batching systems offer high precision in measuring individual components, resulting in consistent product quality but often require more time for sequential ingredient addition. Blending systems enhance efficiency by simultaneously mixing multiple components, significantly reducing processing time and energy consumption while maintaining product uniformity. The choice depends on production scale and complexity, with batching favored for customized or small-batch production, and blending suited for large-scale, continuous processes.
Accuracy and Consistency in Material Processing
Batching systems provide high accuracy in material processing by measuring and delivering precise quantities of each component, ensuring consistent end-product quality through controlled batch sequences. Blending systems excel in maintaining uniform consistency by continuously mixing materials in real-time, reducing variability and enabling smoother transitions between production runs. Your choice depends on whether precise ingredient measurement (batching) or consistent mixture uniformity (blending) better meets your manufacturing accuracy and consistency requirements.
Cost Analysis: Investment and Operational Expenses
Batching systems typically involve higher initial investment costs due to their complex equipment and automation requirements, but they offer lower operational expenses through precise ingredient control and reduced waste. Blending systems tend to have lower upfront costs, leveraging simpler machinery, yet they may incur higher operational expenses because of increased manual labor and less efficient ingredient use. Evaluating cost efficiency depends on production scale, product consistency needs, and long-term operational savings.
Industry Applications: Which System Fits Where?
Batching systems excel in industries like concrete production and pharmaceuticals, where precise, repeatable quantities of materials must be combined in discrete batches to ensure quality control and consistency. Blending systems are ideal for industries such as food processing, paints, and chemicals that require continuous mixing of ingredients to achieve uniformity and smooth texture. Choosing between batching and blending depends on production volume, process control needs, and material characteristics specific to sectors like construction, manufacturing, or chemical production.
Scalability and Flexibility Considerations
Batching systems offer high scalability by processing large quantities of materials in segmented, repeatable cycles, making them ideal for industries requiring precise control over ingredient proportions. Blending systems provide superior flexibility through continuous mixing capabilities, accommodating variable input materials and adapting quickly to formulation changes without downtime. Organizations must weigh batching's strength in accuracy and scalability against blending's advantage in operational flexibility and dynamic recipe adjustments.
Choosing the Right System: Factors to Evaluate
When choosing between a batching system and a blending system, consider factors such as the precision of ingredient measurement, production volume, and flexibility in formulation changes. Batching systems excel in accurate, repeatable ingredient quantities for large-scale, consistent production runs, while blending systems offer versatility for mixing diverse raw materials in varying proportions. Your decision should align with your operational goals, weighing cost efficiency against the need for customization and scalability.
Batching System vs Blending System Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com