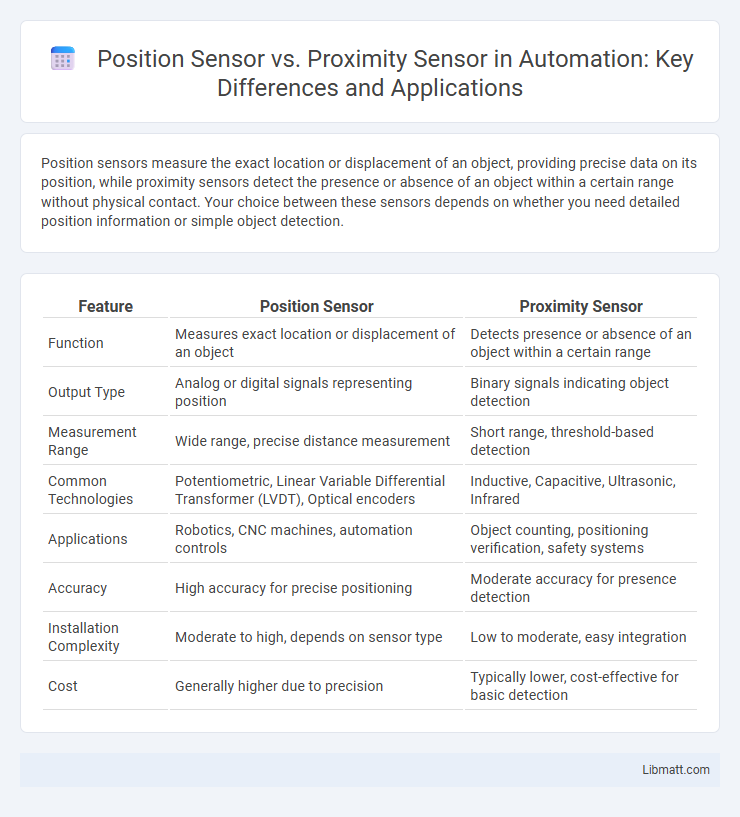
Position sensors measure the exact location or displacement of an object, providing precise data on its position, while proximity sensors detect the presence or absence of an object within a certain range without physical contact. Your choice between these sensors depends on whether you need detailed position information or simple object detection.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Position Sensor | Proximity Sensor |
|---|---|---|
| Function | Measures exact location or displacement of an object | Detects presence or absence of an object within a certain range |
| Output Type | Analog or digital signals representing position | Binary signals indicating object detection |
| Measurement Range | Wide range, precise distance measurement | Short range, threshold-based detection |
| Common Technologies | Potentiometric, Linear Variable Differential Transformer (LVDT), Optical encoders | Inductive, Capacitive, Ultrasonic, Infrared |
| Applications | Robotics, CNC machines, automation controls | Object counting, positioning verification, safety systems |
| Accuracy | High accuracy for precise positioning | Moderate accuracy for presence detection |
| Installation Complexity | Moderate to high, depends on sensor type | Low to moderate, easy integration |
| Cost | Generally higher due to precision | Typically lower, cost-effective for basic detection |
Introduction to Position and Proximity Sensors
Position sensors detect the precise location or movement of an object along a path, measuring parameters such as displacement, angle, or linear position. Proximity sensors, on the other hand, identify the presence or absence of an object within a predefined range without physical contact, using technologies like capacitive, inductive, or ultrasonic sensing. Both sensor types are essential in automation and robotics, enabling accurate control and safety by providing critical spatial information.
Definition of Position Sensor
A position sensor is a device designed to detect the physical location or displacement of an object or component and convert this information into an electrical signal. It measures variables such as linear or angular position, providing critical data for motion control, automation, and robotics. Common types of position sensors include potentiometers, LVDTs (Linear Variable Differential Transformers), and rotary encoders.
Definition of Proximity Sensor
A proximity sensor detects the presence or absence of an object within a specific range without physical contact, using electromagnetic fields, light, or ultrasound. In contrast, a position sensor measures the exact location or displacement of an object relative to a reference point. Proximity sensors are commonly used in industrial automation, robotics, and consumer electronics for object detection and safety applications.
Working Principle of Position Sensors
Position sensors operate by detecting the precise location or displacement of an object, often using mechanisms such as potentiometers, linear variable differential transformers (LVDTs), or optical encoders. These sensors convert physical movement into electrical signals, allowing accurate measurement of angular or linear positions. Your application's accuracy relies on selecting the appropriate position sensor technology that matches the required range, resolution, and environmental conditions.
Working Principle of Proximity Sensors
Proximity sensors detect the presence or absence of an object by emitting an electromagnetic field or a beam of electromagnetic radiation and monitoring changes in the field or return signal. Capacitive proximity sensors measure changes in capacitance caused by the target, while inductive sensors generate an electromagnetic field and detect disturbances caused by metal objects. Optical proximity sensors use infrared light to sense reflected signals, enabling non-contact object detection with high precision and reliability.
Key Differences Between Position and Proximity Sensors
Position sensors measure the exact location or displacement of an object, providing precise data on its movement or angle, while proximity sensors detect the presence or absence of an object within a certain range without physical contact. Position sensors often use technologies like potentiometers, encoders, or LVDTs, whereas proximity sensors rely on inductive, capacitive, ultrasonic, or optical methods. Your choice depends on whether you need detailed positional information or simple detection of an object's presence.
Common Applications of Position Sensors
Position sensors are widely used in robotics for precise arm movement control, automotive systems for throttle and crankshaft position monitoring, and industrial automation to track the exact location of machine parts. These sensors enable real-time feedback in CNC machines, ensuring accurate tool positioning and enhancing production quality. In aerospace, position sensors monitor control surfaces to maintain stability and performance during flight operations.
Typical Uses of Proximity Sensors
Proximity sensors are commonly used in industrial automation for object detection, counting, and positioning without physical contact, enhancing equipment safety and operational efficiency. These sensors find applications in automotive systems for parking assistance, manufacturing lines for detecting parts, and consumer electronics for screen activation. Your systems benefit from proximity sensors through precise, non-invasive sensing, reducing wear and maintenance costs.
Advantages and Limitations of Each Sensor
Position sensors offer high accuracy and precise measurement of an object's exact location, making them ideal for applications requiring detailed positional feedback, but they often involve higher costs and complex installation. Proximity sensors excel in detecting the presence or absence of objects without physical contact, providing durability and low maintenance, though they lack the fine positional detail that position sensors provide. Choosing your sensor depends on the required precision and environmental conditions, balancing the advantages and limitations of each technology.
How to Choose Between Position and Proximity Sensors
Choosing between position sensors and proximity sensors depends on the application's need for precise location measurement or simple object detection. Position sensors provide accurate data on the exact location, angle, or displacement of an object, ideal for automation systems requiring detailed motion control. Proximity sensors detect the presence or absence of an object within a certain range without physical contact, suitable for safety systems and obstacle detection.
Position Sensor vs Proximity Sensor Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com