Physical keys provide a traditional, tangible method of securing property but can be lost, copied, or stolen easily. RFID key access offers enhanced security with contactless entry and the ability to track usage, making it a more convenient and manageable option for your security needs.
Table of Comparison
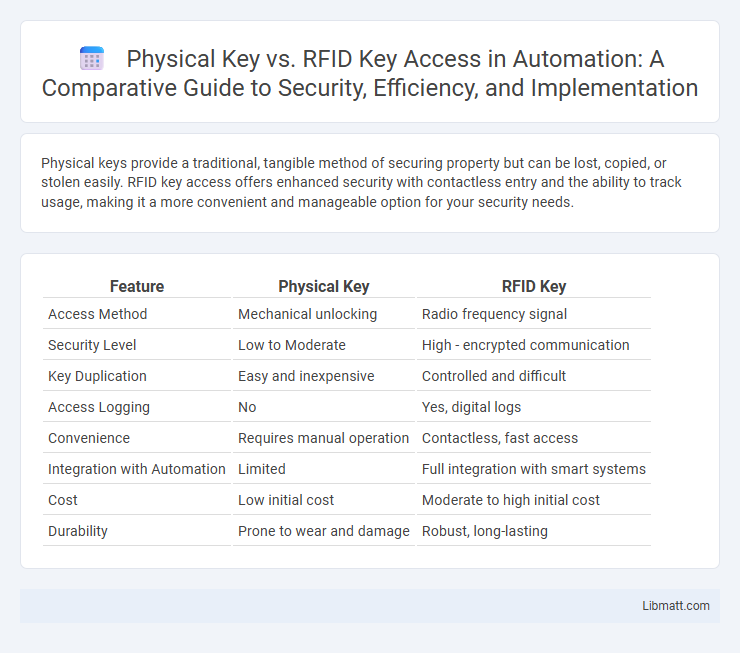
| Feature | Physical Key | RFID Key |
|---|---|---|
| Access Method | Mechanical unlocking | Radio frequency signal |
| Security Level | Low to Moderate | High - encrypted communication |
| Key Duplication | Easy and inexpensive | Controlled and difficult |
| Access Logging | No | Yes, digital logs |
| Convenience | Requires manual operation | Contactless, fast access |
| Integration with Automation | Limited | Full integration with smart systems |
| Cost | Low initial cost | Moderate to high initial cost |
| Durability | Prone to wear and damage | Robust, long-lasting |
Introduction: Understanding Physical and RFID Key Access
Physical keys rely on mechanical tumblers and locks to grant entry, offering a traditional, low-tech security method that is susceptible to duplication and wear over time. RFID key access uses radio frequency identification technology to wirelessly transmit data between a key fob and a reader, providing enhanced convenience and security with encrypted signals that are difficult to replicate. Your choice between physical and RFID keys impacts access control efficiency, security level, and ease of use in various environments.
How Physical Key Access Works
Physical key access operates by mechanically aligning the internal pins or tumblers within a lock cylinder when the correct key is inserted, allowing the lock to turn and grant entry. This traditional method relies on the unique physical pattern cut into the key, ensuring only a key with the precise configuration can unlock it. Your security depends on keeping the physical key safe, as unauthorized duplication can compromise access control.
How RFID Key Access Systems Operate
RFID key access systems operate by using radio frequency identification technology to communicate between a key fob or card and an electronic reader. When the RFID key is brought within proximity of the reader, it transmits a unique code stored on a microchip via radio waves, which the system then verifies to grant or deny access. This wireless communication allows for secure, contactless entry without the need to physically insert a key.
Security Comparison: Physical Key vs RFID Key
Physical keys are vulnerable to duplication, theft, and lock picking, making them less secure compared to RFID keys, which use encrypted wireless signals to restrict unauthorized access. RFID keys offer enhanced security features such as unique identification codes, access logs, and the ability to be deactivated remotely if lost or stolen. The risk of cloning RFID keys exists but is significantly reduced with advanced encryption standards, providing a more reliable security solution than traditional physical keys.
Convenience and User Experience
RFID key access offers superior convenience with swift, contactless entry, eliminating the need to fumble with traditional keys and reducing wear and tear. Physical keys, while reliable, require manual handling and are prone to loss or duplication, impacting security and user experience. Your access is streamlined with RFID systems, enhancing both efficiency and ease of use in daily interactions.
Costs and Maintenance Considerations
Physical key access systems typically incur lower initial costs but can lead to higher maintenance expenses due to key duplication, lock replacements, and security vulnerabilities. RFID key systems involve higher upfront investments for electronic readers and key fobs but offer lower long-term maintenance costs with easier reprogramming and enhanced access control management. Organizations often find RFID solutions more cost-effective over time by reducing physical security risks and administrative overhead.
Vulnerabilities and Potential Risks
Physical key access systems are vulnerable to risks such as lock picking, key duplication, and physical theft, which can lead to unauthorized entry and security breaches. RFID key access carries risks including signal interception, cloning, and relay attacks that exploit wireless communication vulnerabilities. Your choice between these access methods should consider their susceptibility to tampering and the specific security requirements of your environment.
Scalability and Integration with Other Systems
RFID key access systems offer greater scalability compared to physical key systems by allowing easy addition or removal of authorized users through software updates without the need to replace locks. Integration with other security and management systems is seamless for RFID, enabling real-time monitoring, access logs, and remote control, whereas physical keys lack such connectivity. This makes RFID access control highly adaptable for expanding facilities and integrated security environments.
Use Cases: When to Choose Each Access Method
Physical keys provide reliable access control for environments with limited user turnover or low-tech infrastructure, such as residential homes and small offices. RFID key access is ideal for high-traffic locations requiring scalable security solutions, including corporate buildings, hospitals, and universities. Selecting between physical keys and RFID cards depends on factors like user management complexity, desired convenience, and integration with existing security systems.
Future Trends in Access Control Technologies
RFID key access is rapidly advancing with biometric integration and IoT connectivity, enabling smarter, more secure entry systems that can be managed remotely via smartphones. Physical keys, while still reliable, face obsolescence due to their vulnerability to duplication and lack of real-time access monitoring. Your security infrastructure will benefit from adopting RFID technology, aligning with the future trend toward seamless, contactless, and data-driven access control solutions.
Physical Key vs RFID Key Access Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com