An IO Module primarily handles input and output operations, facilitating data exchange between sensors, actuators, and the control system. A Communication Module focuses on enabling reliable data transfer between different devices or networks, enhancing Your system's connectivity and integration capabilities.
Table of Comparison
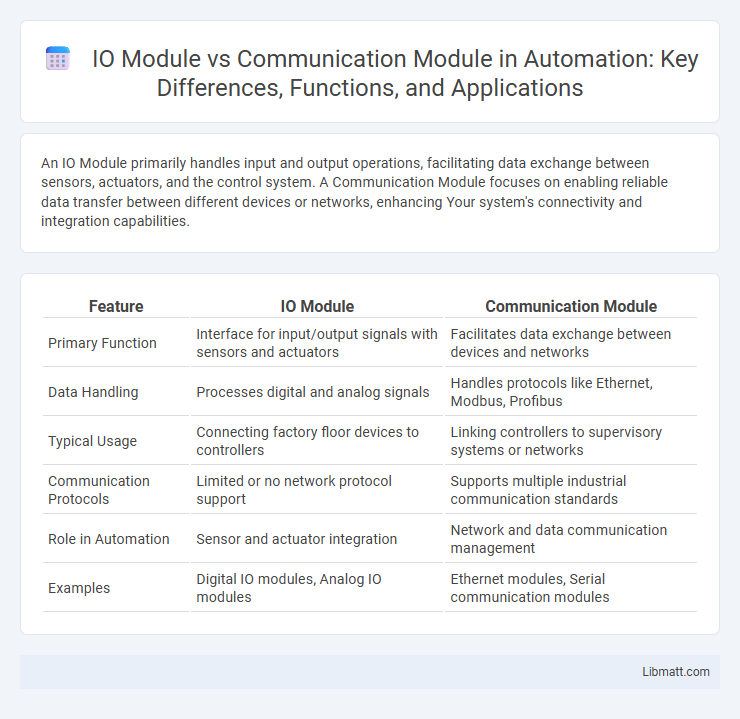
| Feature | IO Module | Communication Module |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Function | Interface for input/output signals with sensors and actuators | Facilitates data exchange between devices and networks |
| Data Handling | Processes digital and analog signals | Handles protocols like Ethernet, Modbus, Profibus |
| Typical Usage | Connecting factory floor devices to controllers | Linking controllers to supervisory systems or networks |
| Communication Protocols | Limited or no network protocol support | Supports multiple industrial communication standards |
| Role in Automation | Sensor and actuator integration | Network and data communication management |
| Examples | Digital IO modules, Analog IO modules | Ethernet modules, Serial communication modules |
Introduction to IO Modules and Communication Modules
IO Modules handle direct input and output signals between sensors, actuators, and the main control system, ensuring accurate data acquisition and device control. Communication Modules enable seamless data exchange across networks, supporting protocols like Ethernet/IP, Modbus, and Profibus for efficient system integration. Understanding the differences between your IO and Communication Modules improves industrial automation performance and connectivity.
Core Functions of IO Modules
IO modules primarily serve as interfaces between a controller and field devices, managing digital and analog input and output signals for process control and automation systems. They perform signal conversion, conditioning, and isolation to ensure accurate data exchange between sensors, actuators, and the control system. Communication modules, in contrast, handle network protocols and data transmission between devices and controllers but do not process direct input or output signals.
Main Roles of Communication Modules
Communication modules facilitate data exchange between devices and systems, enabling seamless integration and real-time information transfer in industrial automation. They manage protocols, signal conversion, and ensure synchronization across networks, enhancing operational efficiency and reducing downtime. Your systems rely on these modules to maintain connectivity and support complex communication tasks across various platforms.
Key Differences Between IO and Communication Modules
IO modules primarily handle input and output signals between field devices and control systems, enabling real-time data acquisition and control actions. Communication modules facilitate data exchange between different network protocols or systems, ensuring interoperability and seamless integration across various automation platforms. The key difference lies in IO modules focusing on physical signal interfacing, whereas communication modules manage protocol translation and network connectivity.
Hardware Design and Structure Comparison
IO modules are designed with multiple input and output ports tailored for direct sensor and actuator connections, featuring robust connectors and isolation components to handle electrical noise and signal integrity. Communication modules incorporate advanced interface chips and protocols such as Ethernet, CAN, or Modbus, emphasizing signal conversion, data encoding, and network compatibility within a compact PCB layout. Hardware structures of IO modules prioritize signal conditioning circuitry, whereas communication modules focus on processors and transceivers for protocol management and data transmission.
Application Areas for IO Modules
IO modules are primarily used in industrial automation systems for real-time data acquisition and control of sensors and actuators on the factory floor. They facilitate direct connection to field devices in applications such as manufacturing plants, process control, and robotics. Communication modules, by contrast, focus on enabling network connectivity and data exchange between controllers and higher-level systems across various industrial networks.
Use Cases for Communication Modules
Communication modules enable seamless data exchange between industrial devices and control systems, facilitating remote monitoring, real-time data acquisition, and integration with enterprise networks. Use cases include connecting Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs) to Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition (SCADA) systems, enabling Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) applications, and supporting protocols like Modbus, Ethernet/IP, and Profinet for interoperable machine communication. These modules are essential in automation environments requiring robust network connectivity, diagnostics, and interoperability across heterogeneous equipment.
Integration in Industrial Automation Systems
An IO Module directly interfaces with sensors and actuators, enabling real-time monitoring and control within industrial automation systems by providing essential data acquisition and signal conditioning. Communication Modules facilitate seamless data exchange between various devices and networks, supporting protocols such as Ethernet/IP, Modbus, and PROFINET to ensure interoperability and system scalability. Your choice between these modules impacts the efficiency and reliability of automation integration, depending on the specific requirements for device connectivity and network communication.
Selection Criteria: IO vs Communication Modules
Selection criteria for IO modules prioritize the type and number of input/output signals, signal voltage compatibility, response time, and environmental resilience, ensuring seamless integration with sensors and actuators. Communication modules are chosen based on supported communication protocols (e.g., Ethernet/IP, Modbus, Profibus), data transfer rates, network topology compatibility, and security features to maintain robust and efficient data exchange between devices. Evaluating system architecture requirements, scalability, and industry standards is essential for choosing the appropriate module to optimize performance and connectivity.
Future Trends in Industrial Module Technology
Future trends in industrial module technology emphasize increased integration of IO Modules and Communication Modules to enhance real-time data exchange and system scalability. Advances in IO Modules focus on higher channel density and precision, while Communication Modules prioritize protocols like OPC UA and TSN for seamless interoperability and cybersecurity. Emerging smart modules leverage AI-driven diagnostics and edge computing to optimize automation processes and predictive maintenance in Industry 4.0 environments.
IO Module vs Communication Module Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com