Batch control manages production processes by handling discrete quantities of materials in defined groups, ensuring precise coordination and quality in manufacturing cycles. Sequential control focuses on performing operations in a specific order, optimizing workflow by triggering actions one after another to maintain system efficiency.
Table of Comparison
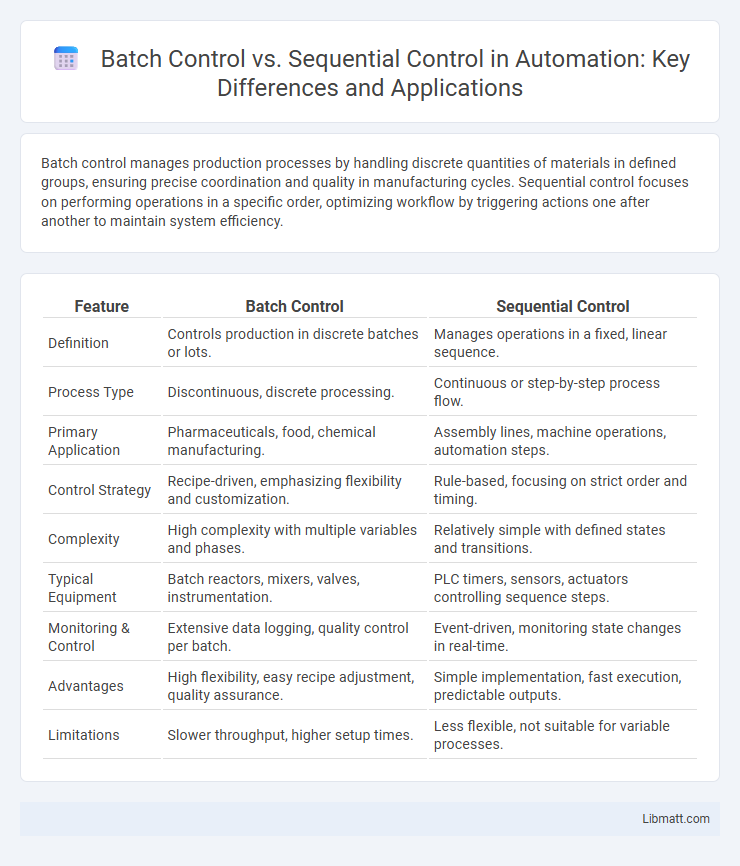
| Feature | Batch Control | Sequential Control |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Controls production in discrete batches or lots. | Manages operations in a fixed, linear sequence. |
| Process Type | Discontinuous, discrete processing. | Continuous or step-by-step process flow. |
| Primary Application | Pharmaceuticals, food, chemical manufacturing. | Assembly lines, machine operations, automation steps. |
| Control Strategy | Recipe-driven, emphasizing flexibility and customization. | Rule-based, focusing on strict order and timing. |
| Complexity | High complexity with multiple variables and phases. | Relatively simple with defined states and transitions. |
| Typical Equipment | Batch reactors, mixers, valves, instrumentation. | PLC timers, sensors, actuators controlling sequence steps. |
| Monitoring & Control | Extensive data logging, quality control per batch. | Event-driven, monitoring state changes in real-time. |
| Advantages | High flexibility, easy recipe adjustment, quality assurance. | Simple implementation, fast execution, predictable outputs. |
| Limitations | Slower throughput, higher setup times. | Less flexible, not suitable for variable processes. |
Introduction to Batch Control and Sequential Control
Batch Control manages production processes by handling groups of materials processed together, ensuring precise recipe execution and quality consistency in manufacturing industries such as pharmaceuticals and food production. Sequential Control governs operations that follow a specific order of steps or states, essential in automation systems like assembly lines or robotic applications where timing and event-driven actions are critical. Both control methods optimize industrial processes by enhancing productivity, safety, and operational accuracy based on the nature of tasks and equipment involved.
Defining Batch Control in Industrial Automation
Batch Control in industrial automation manages the processing of discrete quantities of materials through predefined sequences, ensuring precise control over production steps for consistency and quality. It involves controlling the start, stop, and transition of each batch operation, integrating recipe management and equipment coordination to optimize throughput. Your manufacturing process benefits from enhanced traceability and flexibility by implementing batch control systems compared to sequential control methods.
Understanding Sequential Control Systems
Sequential control systems manage operations by executing predefined steps in a specific order, ensuring processes follow a logical progression without overlap. These systems are essential in applications requiring precise timing and coordination, such as assembly lines or automated manufacturing processes. Unlike batch control, which processes entire lots simultaneously, sequential control emphasizes step-by-step execution to optimize workflow and reduce errors.
Core Differences Between Batch and Sequential Control
Batch control manages production processes by handling groups of items simultaneously through predefined recipes, optimizing consistency and repeatability in industries like pharmaceuticals and food manufacturing. Sequential control follows a strict, step-by-step procedure to execute operations in a specific order, commonly used in automation tasks such as assembly lines or robotic systems. The core difference lies in batch control's focus on processing quantities as units, while sequential control emphasizes the precise execution of individual process stages.
Advantages of Batch Control Systems
Batch control systems offer precise management of complex production processes by dividing operations into discrete steps, ensuring consistent quality and reducing waste. Your manufacturing efficiency improves through flexible recipe adjustments and real-time monitoring, enabling swift adaptations to varying production demands. Enhanced traceability and compliance with industry standards make batch control ideal for pharmaceuticals, food processing, and cosmetics industries.
Benefits of Sequential Control Approaches
Sequential control approaches offer precise management of process steps, ensuring tasks occur in a defined order that minimizes errors and increases operational efficiency. This method enhances flexibility in complex systems by allowing customization of sequences based on real-time data, improving responsiveness and overall system performance. Your production processes benefit from reduced downtime and improved quality control through the streamlined execution of sequentially controlled operations.
Key Applications: When to Use Batch vs Sequential Control
Batch control is ideal for processes requiring precise control over recipe formulation and flexible production runs, such as in pharmaceuticals, food processing, and chemical manufacturing. Sequential control excels in automated systems where tasks must occur in a specific order, like assembly lines, packaging, or conveyor systems. You should choose batch control for complex production involving discrete lots and sequential control when operations demand strict task sequencing.
Challenges in Implementing Batch and Sequential Controls
Challenges in implementing batch control include managing complex recipe configurations and ensuring precise timing for ingredient addition to maintain product consistency. Sequential control faces difficulties in handling dynamic process variations and real-time decision-making for transitions between steps, which can lead to delays or errors. Both control types require robust integration with sensors and actuators to avoid production downtime and ensure quality control compliance.
Industry Standards and Best Practices
Batch Control adheres to industry standards such as ISA-88, promoting modularity and flexibility in managing discrete production batches, ideal for complex manufacturing processes. Sequential Control follows strict procedural workflows defined by standards like IEC 61131-3, ensuring precise execution of step-by-step operations in automation systems. Your choice between these controls should align with best practices that emphasize standardized protocols for scalability, traceability, and regulatory compliance in industrial automation.
Future Trends in Control Systems Technology
Future trends in control systems technology emphasize the integration of advanced automation, artificial intelligence, and real-time data analytics to optimize both batch control and sequential control processes. Increased adoption of Industry 4.0 and IoT-enabled devices enhances precision, flexibility, and scalability in manufacturing operations. Your operations will benefit from predictive maintenance and adaptive control algorithms that improve efficiency and reduce downtime in complex production environments.
Batch Control vs Sequential Control Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com