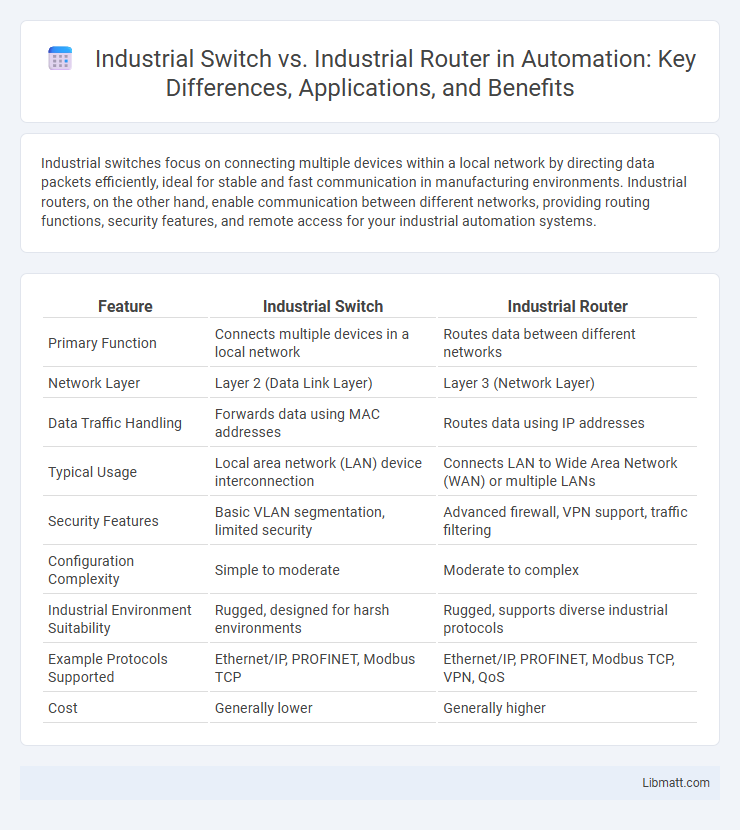
Industrial switches focus on connecting multiple devices within a local network by directing data packets efficiently, ideal for stable and fast communication in manufacturing environments. Industrial routers, on the other hand, enable communication between different networks, providing routing functions, security features, and remote access for your industrial automation systems.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Industrial Switch | Industrial Router |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Function | Connects multiple devices in a local network | Routes data between different networks |
| Network Layer | Layer 2 (Data Link Layer) | Layer 3 (Network Layer) |
| Data Traffic Handling | Forwards data using MAC addresses | Routes data using IP addresses |
| Typical Usage | Local area network (LAN) device interconnection | Connects LAN to Wide Area Network (WAN) or multiple LANs |
| Security Features | Basic VLAN segmentation, limited security | Advanced firewall, VPN support, traffic filtering |
| Configuration Complexity | Simple to moderate | Moderate to complex |
| Industrial Environment Suitability | Rugged, designed for harsh environments | Rugged, supports diverse industrial protocols |
| Example Protocols Supported | Ethernet/IP, PROFINET, Modbus TCP | Ethernet/IP, PROFINET, Modbus TCP, VPN, QoS |
| Cost | Generally lower | Generally higher |
Introduction to Industrial Switches and Routers
Industrial switches manage data traffic within a local network by directing Ethernet frames between connected devices, ensuring efficient communication in harsh environments. Industrial routers connect multiple networks, often linking your internal industrial network to external systems or the Internet, while providing advanced security and routing capabilities. Understanding the distinct roles of industrial switches and routers is essential for optimizing network performance and reliability in industrial settings.
Key Functions of Industrial Switches
Industrial switches primarily manage data traffic within a local network by connecting multiple devices and directing data packets efficiently to their destinations. They offer features such as VLAN support, Quality of Service (QoS), and redundancy protocols to ensure reliable and real-time communication in harsh industrial environments. Unlike industrial routers, which route data between different networks, industrial switches optimize internal network performance and device communication in automated manufacturing and control systems.
Core Capabilities of Industrial Routers
Industrial routers provide advanced network management, secure remote access, and support for multiple communication protocols, ensuring seamless data transmission in harsh industrial environments. Unlike industrial switches that primarily focus on connecting devices within a local network, industrial routers enable wide-area network (WAN) connectivity and dynamic routing between different subnets. Your industrial setup benefits from features like VPN support, firewall protection, and failover mechanisms, enhancing reliability and security across complex, distributed systems.
Main Differences Between Switches and Routers
Industrial switches primarily manage data traffic within a local area network (LAN) by directing data frames between connected devices based on MAC addresses, enhancing network efficiency and segmentation. Industrial routers operate at a higher network layer to route data packets between different networks, using IP addresses to determine the best path for forwarding information and enabling Internet connectivity or communication between distinct LANs. Switches facilitate device-to-device communication within a single network, while routers provide inter-network connectivity, often incorporating security features like firewalls and network address translation (NAT).
Industrial Network Topologies: Switch vs Router
Industrial switches enable efficient data flow within local network topologies by connecting multiple devices in a star or ring configuration, optimizing real-time communication and minimizing latency. Industrial routers manage network traffic between different subnetworks, facilitating complex topologies like meshed or hierarchical networks by directing data packets based on IP addresses. Understanding your industrial network topology helps determine whether a switch or router best supports your operational needs for reliability and scalability.
Performance and Data Handling Comparison
Industrial switches deliver high-speed data transfer and low latency by efficiently managing traffic within a local area network (LAN) using MAC address-based forwarding. Industrial routers provide advanced data handling by enabling routing between different networks, supporting diverse protocols, and offering enhanced security features like VPNs and firewalls. While switches excel in performance for internal network segmentation, routers optimize data flow across multiple networks, ensuring reliable connectivity and traffic management in complex industrial environments.
Security Features: Switches vs Routers
Industrial routers incorporate advanced security features like firewall integration, VPN support, and intrusion detection to protect data traffic across multiple networks, while industrial switches primarily focus on segmenting and managing local network traffic with basic Layer 2 security functions such as MAC address filtering and VLAN segmentation. Routers enable network-wide access control and encryption protocols, whereas switches offer limited protection mechanisms mostly confined to the local area network. The enhanced security capabilities in industrial routers are critical for safeguarding connectivity in complex, multi-site industrial environments.
Use Cases and Applications in Industrial Environments
Industrial switches are primarily utilized for reliable, high-speed data exchange within localized networks on factory floors, connecting devices such as sensors, control systems, and machinery to ensure seamless communication in automated processes. Industrial routers enable secure, wide-area network connectivity by linking multiple industrial sites, facilitating remote monitoring, centralized control, and integration with cloud-based platforms for real-time data analysis and operational efficiency. Your choice between an industrial switch and router depends on whether you need robust local device interconnectivity or expansive network routing capabilities across industrial environments.
Factors to Consider When Choosing
When choosing between an industrial switch and an industrial router, consider network topology, bandwidth requirements, and environmental conditions such as temperature and vibration resistance. Industrial switches excel in managing local traffic efficiently with low latency, while industrial routers provide robust WAN connectivity and advanced security features like VPN support. Evaluate your need for protocols compatibility, scalability, and redundancy to ensure seamless integration within your industrial network infrastructure.
Conclusion: Switch or Router for Industrial Networks
Industrial switches offer reliable, high-speed local data transmission within industrial networks, ideal for connecting multiple devices in a robust, low-latency environment. Industrial routers provide advanced traffic management, security features, and WAN connectivity, making them essential for integrating diverse network segments and remote monitoring. Choosing between a switch or router depends on network architecture needs--switches for efficient intra-network communication and routers for external network access and complex data routing.
Industrial Switch vs Industrial Router Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com